
Puccinia poarum
Encyclopedia
Puccinia poarum, Coltsfoot Rust gall or Meadow Grass Rust is a plant pathogen. This fungal parasite forms a bright yellow gall, 1–2 cm across, on the underside of leaves of the Coltsfoot
, Tussilago farfara and infects, but does not gall grasses of the poaceae
family.
is a rust fungus with which P. poarum is sometimes confused. C. tussilaginis usually appears somewhat later in the season and tends, not being a gall, to be spread all over the leaf rather than forming the discrete circular clusters typical of P. poarum; it is also less obvious on the upper leaf surface and lacks the purple margin with the central hole characteristic of the gall.
P. poarum is found on at least seventy plant hosts.
 Peter Nielsen
Peter Nielsen
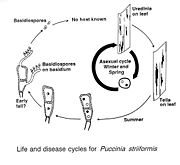
was the first to describe the heteroecious life-cycle of this fungus; it's aecial or sexual phase host is the Coltsfoot, a member of the Asteraceae
, spread by airborne spores; its telial or asexual host phase are members of the grass family, the Poaceae
.
Heteroecious
organisms are those that require two distinct and distantly related hosts (alternate hosts).
Coltsfoot
Tussilago farfara, commonly known as Coltsfoot, is a plant in the family Asteraceae.It has been used medicinally as a cough suppressant. The name "tussilago" itself means "cough suppressant." The plant has been used historically to treat lung ailments such as asthma as well as various coughs by way...
, Tussilago farfara and infects, but does not gall grasses of the poaceae
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
family.
Characteristics
This yellow gall consists of relatively large and circular raised yellow or orange-red spots on the underside of the leaf, often with a purple margin and sometimes a central hole. The cup structures on the lower surface are relatively few in number (20-30). The upper surface of the leaf shows a yellow ring and no swelling. The rust has distinctive reproductive structures (aecia and spermogonia), present. The rust is necrophytic, a term applied to a parasitic organism that obtains its nutrients from the dead cells and tissues of its host organism.Identification
Coleosporium tussilaginisColeosporium tussilaginis
Coleosporium tussilaginis is species of rust fungus in the Coleosporiaceae family. It is a plant pathogen....
is a rust fungus with which P. poarum is sometimes confused. C. tussilaginis usually appears somewhat later in the season and tends, not being a gall, to be spread all over the leaf rather than forming the discrete circular clusters typical of P. poarum; it is also less obvious on the upper leaf surface and lacks the purple margin with the central hole characteristic of the gall.
P. poarum is found on at least seventy plant hosts.
Life-cycle

Peter Nielsen (botanist)
Peter Nielsen was a Danish botanist and plant pathologist. He was born at a farm in Vonsbæk parish in the Duchy of Schleswig and started working in agriculture. He became a school teacher at Ørslev in Zealand and started studying the local flora. He remained interested in plants useful to...
was the first to describe the heteroecious life-cycle of this fungus; it's aecial or sexual phase host is the Coltsfoot, a member of the Asteraceae
Asteraceae
The Asteraceae or Compositae , is an exceedingly large and widespread family of vascular plants. The group has more than 22,750 currently accepted species, spread across 1620 genera and 12 subfamilies...
, spread by airborne spores; its telial or asexual host phase are members of the grass family, the Poaceae
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
.
Heteroecious
Heteroecious
A heteroecious parasite is one that requires at least two hosts. The primary host is the host in which the parasite spends its adult life; the other is the secondary host. Both the primary host and an unrelated alternate host are required for the parasite to complete its life cycle...
organisms are those that require two distinct and distantly related hosts (alternate hosts).

