
Probability of Precipitation
Encyclopedia
A probability of precipitation (POP) is a formal measure of the likelihood
of precipitation
that is often published from weather
forecasting models
. Its definition varies.
weather forecasting
, POP is the probability that more than 1/100th of an inch of precipitation will fall in a single spot, averaged over the forecast area. For instance, if there is a 100% probability
of rain covering one side of a city
, and a 0% probability of rain
on the other side of the city
, the POP would be 50%. A 50% chance of a rainstorm covering the entire city would also lead to a POP of 50%.
Note that the POP measure is meaningless unless it is associated with a period of time
. U.S.
forecasts commonly use POP defined over 12-hour periods (POP12), though 6-hour periods (POP6) and other measures are also published.
The mathematical definition of Probability of Precipitation is defined as:
For example; a forecaster may be 50% confident that under the current weather conditions that precipitation will occur, and that should rain happen to occur it will happen over 80% of the area. This results in a PoP of 40%: .
.
So, most of the time, the forecaster is expressing a combination of degree of confidence and areal coverage. The NWS explains this as follows: "Chance of rain 40 percent" means there is a 40 percent chance that rain will occur at any given point in the area. Another way to express "Chance of rain 40 percent" is that on average for all of the points in the area during the specified time period (usually 12-hour periods), chance that rain will occur (on average) is 40%.
Clearly, Mt. Haleakala pulls up the average for Maui, and clearly, the smaller the area, the more meaningful and accurate "chance of rain" is.
Terms typically in weather forecasts based on POP:
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
of precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
that is often published from weather
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
forecasting models
Ensemble forecasting
Ensemble forecasting is a numerical prediction method that is used to attempt to generate a representative sample of the possible future states of a dynamical system...
. Its definition varies.
U.S. usage
In U.S.United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
weather forecasting
Weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
, POP is the probability that more than 1/100th of an inch of precipitation will fall in a single spot, averaged over the forecast area. For instance, if there is a 100% probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
of rain covering one side of a city
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
, and a 0% probability of rain
Rain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
on the other side of the city
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
, the POP would be 50%. A 50% chance of a rainstorm covering the entire city would also lead to a POP of 50%.
Note that the POP measure is meaningless unless it is associated with a period of time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
. U.S.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
forecasts commonly use POP defined over 12-hour periods (POP12), though 6-hour periods (POP6) and other measures are also published.
The mathematical definition of Probability of Precipitation is defined as:
-
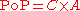
- C = the confidence that precipitation will occur somewhere in the forecast area.
- A = the percent of the area that will receive measurable precipitation, if it occurs at all.
For example; a forecaster may be 50% confident that under the current weather conditions that precipitation will occur, and that should rain happen to occur it will happen over 80% of the area. This results in a PoP of 40%:
 .
.So, most of the time, the forecaster is expressing a combination of degree of confidence and areal coverage. The NWS explains this as follows: "Chance of rain 40 percent" means there is a 40 percent chance that rain will occur at any given point in the area. Another way to express "Chance of rain 40 percent" is that on average for all of the points in the area during the specified time period (usually 12-hour periods), chance that rain will occur (on average) is 40%.
Explanation
Suppose the forecast were for Maui, HI. One "given" point is your house near the top of Mt. Haleakala, where it rains almost constantly. A forecast of 40% percent is obviously not accurate for that given point. So assume that Mt. Haleakala is 10% of the area of Maui and that the average chance of rain today there is 80%. And assume that the average chance of rain for the other 90% of the island is 35%. So for the entire island, the average chance of rain is (0.9 × 0.35) + (0.1 × 0.8) = 0.4 = 40%.Clearly, Mt. Haleakala pulls up the average for Maui, and clearly, the smaller the area, the more meaningful and accurate "chance of rain" is.
Terms typically in weather forecasts based on POP:
- 0% – No mention of precipitation
- 10% – No mention of precipitation, or isolated/slight chance
- 20% – Isolated/slight chance
- 30% – (Widely) scattered/chance
- 40% or 50% – Scattered/chance
- 60% or 70% – Numerous/likely
- 80%, 90% or 100% – No additional modifiers (i.e. "showers and thunderstorms")

