
Polyamino carboxylic acid
Encyclopedia
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atoms connected through carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms to one or more carboxyl groups. Polyamino carboxylates, which have lost acidic protons, form strong complexes with metal ions by donation of electron pairs from the nitrogen and oxygen atoms to the metal ion to form multiple chelate rings. This property makes polyamino carboxylic acids useful in a wide variety of chemical, medical and environmental applications.
Structure
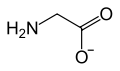
The simplest substance to which this class of compounds can be related is glycineGlycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
, H2NCH2CO2H, in which the amino group, NH2,is separated from the carboxyl group, COOH by a single methylene group, CH2. When the carboxyl group is deprotonated the glycinate ion can function as a bidentate ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
, donating through the nitrogen atom and a carboxylate oxygen atom, to form chelate complexes of metal ions.
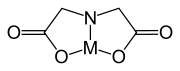
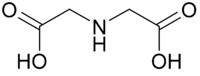
Replacement of a hydrogen atom on the nitrogen of glycine by another acetate residue, –CH2CO2H gives iminodiacetic acid
Iminodiacetic acid
Iminodiacetic acid, HN2, often abbreviated to IDA, is an dicarboxylic acid amine. The iminodiacetate anion can act as a tridentate ligand to form a metal complex with two, fused, five membered chelate rings...
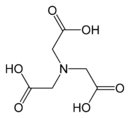
, IDA, which is a tridentate ligand. Further substitution gives nitrilotriacetic acid
Nitrilotriacetic acid
Nitrilotriacetic acid , C6H9NO6, is a polyamino carboxylic acid and is used as a chelating agent which forms coordination compounds with metal ions such as Ca2+, Cu2+ or Fe3+.The uses of NTA are similar to that of EDTA...
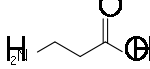
, NTA, which is a tetradentate ligand. These compounds can be described as polyamino acetates. Starting from β-alanine
Beta-alanine
β-Alanine is a naturally occurring beta amino acid, which are amino acids in which the amino group is at the β-position from the carboxylate group . The IUPAC name for β-alanine would be 3-aminopropanoic acid...
a series of polyamino propionates can be envisaged.
Denticity
Denticity refers to the number of atoms in a single ligand that bind to a central atom in a coordination complex. In many cases, only one atom in the ligand binds to the metal, so the denticity equals one, and the ligand is said to be monodentate...
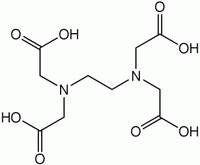
is achieved by linking two or more units together. EDTA
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, widely abbreviated as EDTA , is a polyamino carboxylic acid and a colourless, water-soluble solid. Its conjugate base is named ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is widely used to dissolve limescale. Its usefulness arises because of its role as a hexadentate ligand...
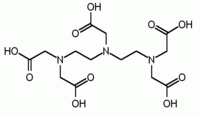
contains two IDA units with the nitrogen atoms linked by two methylene groups and is hexadentate. DTPA has two CH2CH2 bridges linking three nitrogen atoms and is octadentate. TTHA has ten potential donor atoms.
Applications
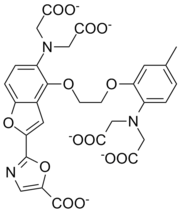
The chelating properties of polyamino carboxylates can be engineered by varying the groups linking the nitrogen atoms so as to increase selectivity for a particular metal ion. The number of carbon atoms between the nitrogen and carboxyl group can also be varied and substituents can be placed on these carbon atoms. Altogether this allows for a vast range of possibilities. Fura-2Fura-2
Fura-2, a polyamino carboxylic acid, is a ratiometric fluorescent dye which binds to free intracellular calcium. It was the first widely-used dye for calcium imaging, and remains very popular. Fura-2 is excited at 340 nm and 380 nm of light, and the ratio of the emissions at those...
is noteworthy as it combines two functionalities: it has high selectivity for calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
over magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
and it has a substituent which makes the complex fluorescent when it binds calcium. This provides a means of determining the calcium content in intra-cellular fluid. Details concerning applications of the following examples can be found in the individual articles and/or reference.
 |
 |
 |
| Fura-2 Fura-2 Fura-2, a polyamino carboxylic acid, is a ratiometric fluorescent dye which binds to free intracellular calcium. It was the first widely-used dye for calcium imaging, and remains very popular. Fura-2 is excited at 340 nm and 380 nm of light, and the ratio of the emissions at those... |
IDA Iminodiacetic acid Iminodiacetic acid, HN2, often abbreviated to IDA, is an dicarboxylic acid amine. The iminodiacetate anion can act as a tridentate ligand to form a metal complex with two, fused, five membered chelate rings... |
NTA Nitrilotriacetic acid Nitrilotriacetic acid , C6H9NO6, is a polyamino carboxylic acid and is used as a chelating agent which forms coordination compounds with metal ions such as Ca2+, Cu2+ or Fe3+.The uses of NTA are similar to that of EDTA... |
 |
 |
 |
| EDTA EDTA Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, widely abbreviated as EDTA , is a polyamino carboxylic acid and a colourless, water-soluble solid. Its conjugate base is named ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is widely used to dissolve limescale. Its usefulness arises because of its role as a hexadentate ligand... |
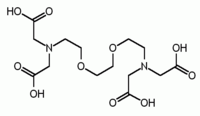
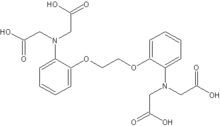
DTPA | EGTA EGTA (chemical) EGTA is a polyamino carboxylic acid, a chelating agent that is related to the better known EDTA, but with a much higher affinity for calcium than for magnesium ions... |
 |
 |
 |
| BAPTA BAPTA BAPTA is a calcium-specific polyamino carboxylic acid. The presence of four carboxylic acid functional groups makes possible the binding of two magnesium ions. The extensive flexibility of the carboxylate ligands is critical to the coordination of magnesium, or other metal ions... |
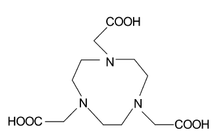
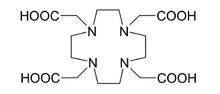
NOTA | DOTA |

