
Poly(A)-binding protein
Encyclopedia
Poly-binding protein (PAB or PABP) is a RNA-binding protein
which binds to the poly(A) tail of mRNA. The poly(A) tail is located on the 3' end of mRNA. The nuclear isoforms selectively binds to around 50 nucleotides and stimulates the activity of Polyadenylate polymerase.
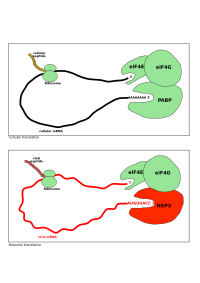
The cytosolic isoform of eukaryotes Poly(A) binding protein binds to the initiation factor eIF-4G via its C-terminal domain. EIF-4G is bound to eIF-4E, another initiation factor bound to the 5' cap
on the 5' end of mRNA. This binding forms the characteristic loop structure of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Poly(A)-binding protein interacting proteins in the cytosol compete for the eIF-4G binding sites. Poly(A)-binding protein has also been shown to interact with a termination factor (eRF3)
 Rotavirus
Rotavirus
RNA-binding protein
NSP3 interacts with eIF4GI
and evicts the poly(A) binding protein from eIF4F
. And NSP3A, by taking the place of PABP on eIF4GI
, is responsible for the shut-off of cellular protein synthesis.
RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding proteins are proteins that bind to RNA. They bind to either double-strand or single-strand RNAs through RNA recognition motif . RNA-binding proteins may regulate the translation of RNA, and post-transcriptional events, such as RNA splicing, editing.They are cytoplasmic and nuclear...
which binds to the poly(A) tail of mRNA. The poly(A) tail is located on the 3' end of mRNA. The nuclear isoforms selectively binds to around 50 nucleotides and stimulates the activity of Polyadenylate polymerase.
Expression and binding
The expression of mammalian Poly(A)-binding protein is regulated at the translational level by a feed-back mechanism: the mRNA encoding PABP contains in its 5' UTR an A-rich sequence which binds Poly(A)-binding protein. This leads to repression of translationThe cytosolic isoform of eukaryotes Poly(A) binding protein binds to the initiation factor eIF-4G via its C-terminal domain. EIF-4G is bound to eIF-4E, another initiation factor bound to the 5' cap
5' cap
The 5' cap is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5' end of precursor messenger RNA and some other primary RNA transcripts as found in eukaryotes. The process of 5' capping is vital to creating mature messenger RNA, which is then able to undergo translation...
on the 5' end of mRNA. This binding forms the characteristic loop structure of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Poly(A)-binding protein interacting proteins in the cytosol compete for the eIF-4G binding sites. Poly(A)-binding protein has also been shown to interact with a termination factor (eRF3)
Rotavirus NSP3

Rotavirus
Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea among infants and young children, and is one of several viruses that cause infections often called stomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza. It is a genus of double-stranded RNA virus in the family Reoviridae. By the age of five,...
RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding proteins are proteins that bind to RNA. They bind to either double-strand or single-strand RNAs through RNA recognition motif . RNA-binding proteins may regulate the translation of RNA, and post-transcriptional events, such as RNA splicing, editing.They are cytoplasmic and nuclear...
NSP3 interacts with eIF4GI
Eukaryotic initiation factor
Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. They function in forming a complex with the 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAi called the 43S preinitation complex , recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNA and recruiting the 43S PIC to mRNA,...
and evicts the poly(A) binding protein from eIF4F
Eukaryotic initiation factor
Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. They function in forming a complex with the 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAi called the 43S preinitation complex , recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNA and recruiting the 43S PIC to mRNA,...
. And NSP3A, by taking the place of PABP on eIF4GI
Eukaryotic initiation factor
Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. They function in forming a complex with the 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAi called the 43S preinitation complex , recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNA and recruiting the 43S PIC to mRNA,...
, is responsible for the shut-off of cellular protein synthesis.
Genes
There are several forms. These include:- PABPC1PABPC1Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PABPC1 gene.-Interactions:PABPC1 has been shown to interact with ANAPC5, GSPT2, CNOT7, PAIP1, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma, EIF4G3 and PAIP2....
, PABPC3PABPC3Polyadenylate-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PABPC3 gene.-Further reading:...
, PABPC4PABPC4Polyadenylate-binding protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PABPC4 gene.-Further reading:...
,

