
Polar membrane
Encyclopedia
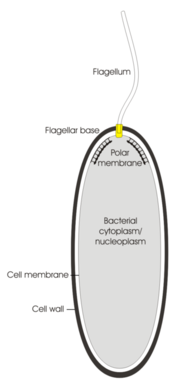
1) A lipid biomembrane expressing polarity in the electrical sense. Such membranes can be manipulated chemically and their electrical properties can be studied by application of biophysical techniques.
2) A specialized region of the lipid cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
in bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l cells, usually located at or near the so-called pole
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s (e.g. the ends of a cylindrical cell). This region can easily be distinguished from the "normal" membrane regions in ultrathin sections of embedded bacteria by electron microscopy when the cell membrane is orientated perpendicular to the viewing direction. There, the membrane appears slightly thickened with a finely-frilled layer facing the inside of the cell.
It is also possible to isolate these polar membranes from the bacterial cells and study them in face view in negatively-stained
Negative stain
Negative staining is an established method, often used in diagnostic microscopy, for contrasting a thin specimen with an optically opaque fluid....
preparations. The polar membrane bears a fine array of attached particles in hexagonal close packing and these have been shown to possess ATPase
ATPase
ATPases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of adenosine triphosphate into adenosine diphosphate and a free phosphate ion. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur...
activity. Interestingly, the polar membrane is invariably found in close juxtaposition to the points of insertion of the bacterial flagella into the plasma membrane, especially where multiple flagella bases are grouped in a region of the cell membrane. It may thus be inferred that the polar membrane could be of importance in the supply and transfer of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
to the bidirectional molecular rotational motor situated at the base of each individual bacterial flagellum (see also Electrochemical gradient
Electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a spatial variation of both electrical potential and chemical concentration across a membrane; that is, a combination of the membrane potential and the pH gradient...
).

