
Pipeline forwarding
Encyclopedia
Pipeline forwarding applies to packet forwarding in computer network
s the basic concept of pipelining, which has been widely and successfully used in computing — specifically, in the architecture of all major central processing unit
s (CPUs) — and manufacturing — specifically in assembly lines of various industries starting from automotive to many others. Pipelining is known to be optimal independent of the specific instantiation. In particular, PF is optimal from various points of view:
Various aspects of the technology are covered by several patents issued by both the United States Patent and Trademark Office
and the European Patent Office
.
) that is globally available via GPS (global positioning system
) or Galileo in the near future. For example the UTC second is divided into fixed duration time frames, which are grouped into time cycles so that in each UTC second there is a predefined integer number of time cycles. Alternatively, or complementary, the CTR can be obtained through the network by means of synchronization protocols such as IEEE 1588.
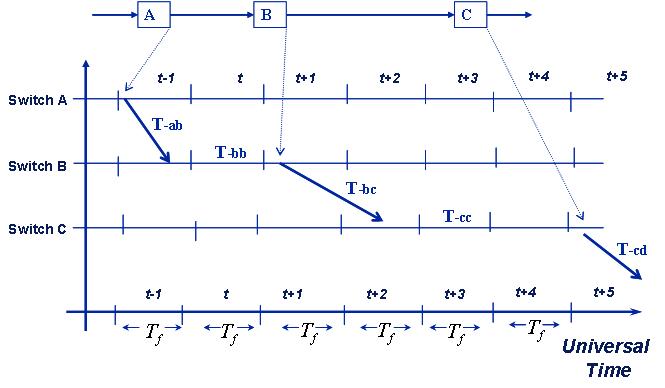
Packets are forwarded from node to node according to predefined schedules, as shown in the figure below, i.e., each node forwards packets of a certain flow during predefined time frames. The time cycles define the periodic re-occurrence of the various predefined schedules. The periodic scheduling within each node results in a periodic packet forwarding across the network, which is referred to as pipeline forwarding for the ordered, step-by-step fashion with which packets travel toward their destination.
Through a resource reservation procedure transmission capacity is booked for a flow on each link it traverses during the time frame (or time frames) predefined for its forwarding, thus setting up a synchronous virtual pipe
(SVP
). The capacity during each time frame can be is partially or totally reserved to one or more flows. Consequently, the time cycle provides the basis for a periodic repetition of the reservation that ensures enough transmission resources to be available on each link to forward the packets of each flow, which prevents delays due to resource contention and loss resulting to congestion.
Two implementations of the pipeline forwarding were proposed: Time-Driven Switching
(TDS
) - a.k.a. Fractional lambda switching
(FλS
) in the context of optical networks -
and time-driven priority
(TDP) and can be used to create pipeline forwarding parallel network in the future Internet
.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
s the basic concept of pipelining, which has been widely and successfully used in computing — specifically, in the architecture of all major central processing unit
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s (CPUs) — and manufacturing — specifically in assembly lines of various industries starting from automotive to many others. Pipelining is known to be optimal independent of the specific instantiation. In particular, PF is optimal from various points of view:
- High efficiency in utilization of network resources, which enables accommodating a larger amount of traffic on the network, thus lowering operation cost and being the foundation for accommodating the exponential growth of modern networks.
- Low implementation complexity, which enables the realization of larger and more powerful networking systems at low cost, thus offering further support to network growth.
- High scalability, which is an immediate consequence of the above two features.
- Deterministic and predictable operation with minimum delay and no packet loss even under full load condition, which is key in supporting the demanding requirements of the new and valuable services that are being deployed, or envisioned to be deployed, on modern networks, such as telephony, videoconferencing, virtual presence, video on demand, distributed gaming.
Various aspects of the technology are covered by several patents issued by both the United States Patent and Trademark Office
United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office is an agency in the United States Department of Commerce that issues patents to inventors and businesses for their inventions, and trademark registration for product and intellectual property identification.The USPTO is based in Alexandria, Virginia,...
and the European Patent Office
European Patent Office
The European Patent Office is one of the two organs of the European Patent Organisation , the other being the Administrative Council. The EPO acts as executive body for the Organisation while the Administrative Council acts as its supervisory body as well as, to a limited extent, its legislative...
.
Operating principles
As in other pipelining implementations, a common time reference (CTR) is needed to perform pipeline forwarding. In the context of global networks the CTR can be effectively realized by using UTC (coordinated universal timeCoordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
) that is globally available via GPS (global positioning system
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
) or Galileo in the near future. For example the UTC second is divided into fixed duration time frames, which are grouped into time cycles so that in each UTC second there is a predefined integer number of time cycles. Alternatively, or complementary, the CTR can be obtained through the network by means of synchronization protocols such as IEEE 1588.
Packets are forwarded from node to node according to predefined schedules, as shown in the figure below, i.e., each node forwards packets of a certain flow during predefined time frames. The time cycles define the periodic re-occurrence of the various predefined schedules. The periodic scheduling within each node results in a periodic packet forwarding across the network, which is referred to as pipeline forwarding for the ordered, step-by-step fashion with which packets travel toward their destination.

Through a resource reservation procedure transmission capacity is booked for a flow on each link it traverses during the time frame (or time frames) predefined for its forwarding, thus setting up a synchronous virtual pipe
Synchronous virtual pipe
When realizing pipeline forwarding a predefined schedule for forwarding a pre-allocated amount of bytes during one or more time frames along a path of subsequent switches establishes a synchronous virtual pipe . The SVP capacity is determined by the total number of bits allocated in every time...
(SVP
Synchronous virtual pipe
When realizing pipeline forwarding a predefined schedule for forwarding a pre-allocated amount of bytes during one or more time frames along a path of subsequent switches establishes a synchronous virtual pipe . The SVP capacity is determined by the total number of bits allocated in every time...
). The capacity during each time frame can be is partially or totally reserved to one or more flows. Consequently, the time cycle provides the basis for a periodic repetition of the reservation that ensures enough transmission resources to be available on each link to forward the packets of each flow, which prevents delays due to resource contention and loss resulting to congestion.
Forwarding options
As exemplified in the figure above, which depicts the journey of a packet from node A to node D along three pipeline forwarding switches, the forwarding delay may have different values for different nodes, due to different propagation delays on different links (e.g., Tab, Tbc, and Tcd), and different packet processing and switching times in heterogeneous nodes (e.g., Tbb and Tcc). Moreover, two variants of the basic pipeline forwarding operation are possible. When node n deploys immediate forwarding the forwarding delay has the same value for all the packets received by node n on input link i and it is the minimum necessary to accommodate the packet propagation, processing, and switching time. When implementing non-immediate forwarding, node n may use different forwarding delays for different packets.Two implementations of the pipeline forwarding were proposed: Time-Driven Switching
Time-driven switching
In Telecommunication and Computer networking, Time-Driven Switching is a node by node time variant implementation of Circuit switching, where the propagating datagram is shorter in space than the distance between source and destination...
(TDS
Time-driven switching
In Telecommunication and Computer networking, Time-Driven Switching is a node by node time variant implementation of Circuit switching, where the propagating datagram is shorter in space than the distance between source and destination...
) - a.k.a. Fractional lambda switching
Fractional lambda switching
Fractional lambda switching leverages on time-driven switching to realize sub-lambda switching in highly scalable dynamic optical networking, which requires minimum buffers. Fractional lambda switching implies switching fractions of optical channels as opposed to whole lambda switching where...
(FλS
Fractional lambda switching
Fractional lambda switching leverages on time-driven switching to realize sub-lambda switching in highly scalable dynamic optical networking, which requires minimum buffers. Fractional lambda switching implies switching fractions of optical channels as opposed to whole lambda switching where...
) in the context of optical networks -
and time-driven priority
Time-Driven Priority
Time-driven priority is a synchronous packet scheduling technique that implements UTC-based pipeline forwardingand can be combined with conventional IP routing to achieve the higher flexibility than another pipeline forwarding implementation known as time-driven switching or fractional lambda...
(TDP) and can be used to create pipeline forwarding parallel network in the future Internet
.

