Pilot-induced oscillation
Encyclopedia

Aviator
An aviator is a person who flies an aircraft. The first recorded use of the term was in 1887, as a variation of 'aviation', from the Latin avis , coined in 1863 by G. de la Landelle in Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne...
of an aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
inadvertently commands an often increasing series of corrections in opposite directions, each an attempt to cover the aircraft's reaction to the previous input with an overcorrection in the opposite direction. An aircraft in such a condition can appear to be "porpoising" switching between upward and downward directions. As such it is a coupling of the frequency of the pilot's inputs and the aircraft's own frequency. During flight test
Flight test
Flight test is a branch of aeronautical engineering that develops and gathers data during flight of an aircraft and then analyzes the data to evaluate the flight characteristics of the aircraft and validate its design, including safety aspects...
, pilot-induced oscillation is one of the handling qualities
Handling qualities
Handling qualities is one of the two principal regimes in the science of flight test . Handling qualities involves the study and evaluation of the stability and control characteristics of an aircraft...
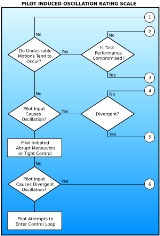
factors that is analyzed, with the aircraft being graded by an established scale (chart at right). In order to avoid any assumption that oscillation is necessarily the fault of the pilot, new terms have been suggested to replace pilot-induced oscillation. These include aircraft-pilot coupling, pilot–in-the-loop oscillations and pilot-assisted (or augmented) oscillations.
In a controls sense, the oscillation is the result of reduced phase margin induced by the lag of the pilot's response. The problem has been mitigated in some cases by adding lead to the instruments - for example, cause the climb rate indication to not only reflect the current climb rate, but also be sensitive to the rate of change of the climb rate.
The physics of flight
Flight
Flight is the process by which an object moves either through an atmosphere or beyond it by generating lift or propulsive thrust, or aerostatically using buoyancy, or by simple ballistic movement....
make such oscillations more probable for pilots than for automobile drivers. An attempt to cause the aircraft to climb, say, by applying up-elevator
Elevator (aircraft)
Elevators are flight control surfaces, usually at the rear of an aircraft, which control the aircraft's orientation by changing the pitch of the aircraft, and so also the angle of attack of the wing. In simplified terms, they make the aircraft nose-up or nose-down...
, will also result in a reduction in airspeed
Airspeed
Airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: indicated airspeed , calibrated airspeed , true airspeed , equivalent airspeed and density airspeed....
.
Another factor is the response rate of flight instruments
Flight instruments
Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with information about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as height, speed and altitude...
in comparison to the response rate of the aircraft itself. An increase in power will not result in an immediate increase in airspeed. An increase in climb rate will not show up immediately on the vertical speed indicator.
A pilot aiming for a 500 foot per minute descent, for example, may find himself descending too rapidly. He begins to apply up elevator until the vertical speed indicator shows 500 feet per minute. However, because the vertical speed indicator lags the actual vertical speed, the pilot is actually descending at much less than 500 feet per minute. The pilot then begins applying down elevator until the vertical speed indicator reads 500 feet per minute, starting the cycle over. It's harder than it might seem to stabilize the vertical speed because the airspeed also constantly changes.
Pilot-induced oscillations may be the fault of the aircraft, the pilot, or both. It is a common problem for inexperienced pilots, and especially student pilots. The problem is most acute when there is a relatively short distance between the wing and tail section
Empennage
The empennage , also known as the tail or tail assembly, of most aircraft gives stability to the aircraft, in a similar way to the feathers on an arrow...
, so called "short coupled" aircraft. It was also a problem for the top research test pilots on the NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
lifting body
Lifting body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing...
program.
The most dangerous pilot-induced oscillations can occur during landing
Landing
thumb|A [[Mute Swan]] alighting. Note the ruffled feathers on top of the wings indicate that the swan is flying at the [[Stall |stall]]ing speed...
. Too much up elevator during the flare can result in the plane getting dangerously slow and threatening to stall
Stall (flight)
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases. This occurs when the critical angle of attack of the foil is exceeded...
. A natural reaction to this is to push the nose down harder than one pulled it up, but then the pilot ends up staring at the ground. An even larger amount of up elevator starts the cycle over again.
While Pilot-Induced oscillations often start with fairly low amplitudes, which can adequately be treated with small perturbation linear theory, several PIO's will by definition become very large.
In February 1989 a JAS 39 Gripen
JAS 39 Gripen
The Saab JAS 39 Gripen is a lightweight single-engine multirole fighter manufactured by the Swedish aerospace company Saab. It was designed to replace the Saab 35 Draken and 37 Viggen in the Swedish Air Force...
prototype crashed
Accidents and incidents involving the JAS 39 Gripen
The JAS 39 Gripen is a fighter aircraft manufactured by the Swedish aerospace company Saab.As of May 2010, five Gripens were destroyed in crashes, two of them before the delivery to the Swedish Air Force. These aircraft included one prototype, one production aircraft and three in service with the...
when landing in Linköping, Sweden. Pilot-induced oscillation as a result of an over-sensitive, yet slow-response steering system was determined to be the cause. Subsequently, the steering system was redesigned.
Pilot-induced oscillation was blamed for the 1992 crash of the prototype F-22 Raptor
F-22 Raptor
The Lockheed Martin/Boeing F-22 Raptor is a single-seat, twin-engine fifth-generation supermaneuverable fighter aircraft that uses stealth technology. It was designed primarily as an air superiority fighter, but has additional capabilities that include ground attack, electronic warfare, and signals...
, landing at Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located on the border of Kern County, Los Angeles County, and San Bernardino County, California, in the Antelope Valley. It is southwest of the central business district of North Edwards, California and due east of Rosamond.It is named in...
in California. This crash was linked to actuator rate limiting, causing the pilot, Tom Morgenfeld, to over-compensate for pitch fluctuations.

