Pigovian tax
Overview
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
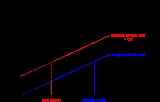
levied on a market activity that generates negative externalities
Externality
In economics, an externality is a cost or benefit, not transmitted through prices, incurred by a party who did not agree to the action causing the cost or benefit...
. The tax is intended to correct the market outcome
Economic equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a state of the world where economic forces are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. It is the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal...
. In the presence of negative externalities, the social cost
Social cost
Social cost, in economics, is generally defined in opposition to "private cost". In economics, theorists model individual decision-making as measurement of costs and benefits...
of a market activity is not covered by the private cost of the activity. In such a case, the market outcome is not efficient and may lead to over-consumption of the product. A Pigovian tax equal to the negative externality is thought to correct the market outcome back to efficiency.
In the presence of positive externalities, i.e., public benefits from a market activity, the market tends to under-supply the product.

