
Picard horn
Encyclopedia
A Picard horn, also called the Picard topology or Picard model, is a theoretical model for the
shape of the Universe
. It is a horn topology, meaning it has hyperbolic geometry
(the term "horn" is due to pseudosphere
models of hyperbolic space).
The term was coined by Ralf Aurich, Sven Lustig, Frank Steiner, and Holger Then in their paper Hyperbolic Universes with a Horned Topology and the CMB Anisotropy.
The space in question is the quotient of the upper half-plane model of hyperbolic 3-space
by the group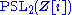 , which was first described by Émile Picard in 1884.
, which was first described by Émile Picard in 1884.
A modern description, in terms of fundamental domain and identifications, can be found in section 3.2, page 63 of Fritz Grunewald and Wolfgang Huntebrinker, A numerical study of eigenvalues of the hyperbolic Laplacian for polyhedra with one cusp, Experiment. Math. Volume 5, Issue 1 (1996), 57-80. The same source calculates the first 80 eigenvalues of the Laplacian, tabulated on p. 72, where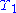 is a fundamental domain of the Picard space.
is a fundamental domain of the Picard space.
The model was created in an attempt to describe the microwave background radiation apparent in the universe, and has finite volume
and useful spectral characteristics (the first several eigenvalues of the Laplacian are computed and in good accord with observation). In this model one end of the figure curves finitely into the bell of the horn. The curve along any side of horn is considered to be a negative curve
. The other end extends to infinity.
shape of the Universe
Shape of the Universe
The shape of the universe is a matter of debate in physical cosmology over the local and global geometry of the universe which considers both curvature and topology, though, strictly speaking, it goes beyond both...
. It is a horn topology, meaning it has hyperbolic geometry
Hyperbolic geometry
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry is a non-Euclidean geometry, meaning that the parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced...
(the term "horn" is due to pseudosphere
Pseudosphere
In geometry, the term pseudosphere is used to describe various surfaces with constant negative gaussian curvature. Depending on context, it can refer to either a theoretical surface of constant negative curvature, to a tractricoid, or to a hyperboloid....
models of hyperbolic space).
The term was coined by Ralf Aurich, Sven Lustig, Frank Steiner, and Holger Then in their paper Hyperbolic Universes with a Horned Topology and the CMB Anisotropy.
The space in question is the quotient of the upper half-plane model of hyperbolic 3-space
Poincaré half-plane model
In non-Euclidean geometry, the Poincaré half-plane model is the upper half-plane , together with a metric, the Poincaré metric, that makes it a model of two-dimensional hyperbolic geometry....
by the group
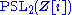 , which was first described by Émile Picard in 1884.
, which was first described by Émile Picard in 1884.A modern description, in terms of fundamental domain and identifications, can be found in section 3.2, page 63 of Fritz Grunewald and Wolfgang Huntebrinker, A numerical study of eigenvalues of the hyperbolic Laplacian for polyhedra with one cusp, Experiment. Math. Volume 5, Issue 1 (1996), 57-80. The same source calculates the first 80 eigenvalues of the Laplacian, tabulated on p. 72, where
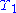 is a fundamental domain of the Picard space.
is a fundamental domain of the Picard space.The model was created in an attempt to describe the microwave background radiation apparent in the universe, and has finite volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
and useful spectral characteristics (the first several eigenvalues of the Laplacian are computed and in good accord with observation). In this model one end of the figure curves finitely into the bell of the horn. The curve along any side of horn is considered to be a negative curve
Hyperbola
In mathematics a hyperbola is a curve, specifically a smooth curve that lies in a plane, which can be defined either by its geometric properties or by the kinds of equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, which are mirror...
. The other end extends to infinity.

