
Phred quality score
Encyclopedia

Phred base calling
Phred base-calling is a computer program for identifying a base sequence from a fluorescence "trace" data generated by an automated DNA sequencer that uses electrophoresis and 4-fluorescent dye method. When originally developed, Phred produced significantly fewer errors in the data sets examined...
to help in the automation of DNA sequencing in the Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project is an international scientific research project with a primary goal of determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up DNA, and of identifying and mapping the approximately 20,000–25,000 genes of the human genome from both a physical and functional...
. Phred quality scores are assigned to each base call in automated sequencer traces. Phred quality scores have become widely accepted to characterize the quality of DNA sequences, and can be used to compare the efficacy of different sequencing methods. Perhaps the most important use of Phred quality scores is the automatic determination of accurate, quality-based consensus sequences.
History
The idea of sequence quality scores can be traced back to the original description of the SCF file format by Staden's group in 1992. In 1995, Bonfield and Staden proposed a method to use base-specific quality scores to improve the accuracy of consensus sequences in DNA sequencing projects.However, early attempts to develop base-specific quality scores had only limited success.
The first program to develop accurate and powerful base-specific quality scores was the program Phred
Phred
Phred may refer to:*Phred base calling, a program used in molecular biology*Phred quality score, a term used in molecular biology*Phred , a character from the comic strip Doonesbury*The Phred on Your Head Show, a children's television show...
. Phred was able to calculate highly accurate quality scores that were logarithmically linked to the error probabilities. Phred was quickly adapted by all major genome sequencing centers and many other laboratories; the vast majority of the DNA sequences produced during the Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project is an international scientific research project with a primary goal of determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up DNA, and of identifying and mapping the approximately 20,000–25,000 genes of the human genome from both a physical and functional...
were processed with Phred.
After Phred quality scores had become a required standard in DNA sequencing, other manufacturers of DNA sequencing instruments developed similar quality scoring methods for their base calling software, including Li-Cor and ABI.
Methods
Phred's approach to base calling and calculating quality scores was outlined by Ewing et al.. To determine quality scores, Phred first calculates several parameters related to peak shape and peak resolution at each base. Phred then uses these parameters to look up a corresponding quality score in huge lookup tables. These lookup tables were generated from sequence traces where the correct sequence was known, and are hard coded in Phred; different lookup tables are used for different sequencing chemistries and machines. An evaluation of the accuracy of Phred quality scores for a number of variations in sequencing chemistry and instrumentation showed that Phred quality scores are highly accurate.Phred was originally developed for "slab gel" sequencing machines like the ABI373. When originally developed, Phred had a lower base calling error rate than the manufacturer's base calling software, which also did not provide quality scores. However, Phred was only partially adapted to the capillary DNA sequencers that became popular later. In contrast, instrument manufacturers like ABI continued to adapt their base calling software changes in sequencing chemistry, and have included the ability to create Phred-like quality scores. Therefore, the need to use Phred for base calling of DNA sequencing traces has diminished, and using the manufacturer's current software versions can often give more accurate results.
Applications
Phred quality scores are used for:- Assessment of sequence quality
- Recognition and removal of low-quality sequence (end clipping)
- Determination of accurate consensus sequences
Originally, Phred quality scores were primarily used by the sequence assembly program Phrap
Phrap
Phrap is a widely used program for DNA sequence assembly. It is part of the Phred-Phrap-Consed package.- History :Phrap was originally developed by Prof. Phil Green for the assembly of cosmids in large-scale cosmid shotgun sequencing within the Human Genome Project...
. Phrap was routinely used in some of the largest sequencing projects in the Human Genome Sequencing Project and is currently one of the most widely used DNA sequence assembly programs in the biotech industry. Phrap uses Phred quality scores to determine highly accurate consensus sequences and to estimate the quality of the consensus sequences. Phrap also uses Phred quality scores to estimate whether discrepancies between two overlapping sequences are more likely to arise from random errors, or from different copies of a repeated sequence.
Within the Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project is an international scientific research project with a primary goal of determining the sequence of chemical base pairs which make up DNA, and of identifying and mapping the approximately 20,000–25,000 genes of the human genome from both a physical and functional...
, the most important use of Phred quality scores was for automatic determination of consensus sequences. Before Phred and Phrap, scientists had to carefully look at discrepancies between overlapping DNA fragments; often, this involved manual determination of the highest-quality sequence, and manual editing of any errors. Phrap's use of Phred quality scores effectively automated finding the highest-quality consensus sequence; in most cases, this completely circumvents the need for any manual editing. As a result, the estimated error rate in assemblies that were created automatically with Phred and Phrap is typically substantially lower than the error rate of manually edited sequence.
In 2009, many commonly used software packages make use of Phred quality scores, albeit to a different extent. Some programs like Sequencher use quality scores only for display and end clipping, but not for consensus determination; other programs like CodonCode Aligner also implement quality-based consensus methods.
Reliability
Phred quality scores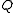 are defined as a property which is logarithmically related to the base-calling error probabilities
are defined as a property which is logarithmically related to the base-calling error probabilities  .
.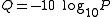
or
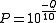
For example, if Phred assigns a quality score of 30 to a base, the chances that this base is called incorrectly are 1 in 1000. The most commonly used method is to count the bases with a quality score of 20 and above. The high accuracy of Phred quality scores make them an ideal tool to assess the quality of sequences.
| Phred Quality Score | Probability of incorrect base call | Base call accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1 in 10 | 90 % |
| 20 | 1 in 100 | 99 % |
| 30 | 1 in 1000 | 99.9 % |
| 40 | 1 in 10000 | 99.99 % |
| 50 | 1 in 100000 | 99.999 % |
External links
- Long Reads with the KB Basecaller Comparison of Phred accuracy with a competing program, ABI's KB Basecaller
- The Laboratory of Phil Green Phrap's homepage.

