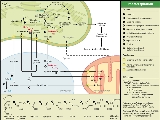
Photorespiration
Overview
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
(rubisco
RuBisCO
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, commonly known by the shorter name RuBisCO, is an enzyme involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. RuBisCo is an abbreviation...
), instead of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
during normal photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
. This is the beginning step of the Calvin-Benson cycle. This process reduces efficiency of photosynthesis in C3 plants.
Rubisco favors carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
as a ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
to oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, however, photorespiration occurs when there is a high concentration of oxygen relative to carbon dioxide.
Unanswered Questions

