Phonological history of English consonant clusters
Encyclopedia
The phonological history of English consonant clusters is part of the phonological history of the English language
in terms of changes in the phonology
of consonant clusters.
involving consonant clusters beginning with /h/ that have lost the /h/ in certain varieties of English.
found mainly in accents of Philadelphia and New York City
; also in Cork
accents of Hiberno-English
. In some dialects of English, the cluster /hj/ (phonetically [çj]) has been reduced to [ç] so that hew and yew differ only by the initial consonant sound (i.e. [çuː] and [juː]).
of the sound [j]. The term comes from the Hebrew
letter yod
, which represents [j].
Yod dropping before [uː] occurs in most varieties of English
in the following environments:
There are accents, for example Welsh English
, in which pairs like chews/choose, yew/you, threw/through are distinct: the first member of each pair has the diphthong [ɪu] while the second member has [uː].
Many varieties of English have extended yod dropping to the following environments, on condition that the [j] be in the same syllable as the preceding consonant:
Yod dropping in the above environments was formerly considered nonstandard in England, but today it is heard even among well-educated RP
speakers. In General American
yod dropping is found not only in the above environments but also:
Glide retention in these contexts has occasionally been held to be a shibboleth distinguishing Canadians from Americans. However, in a survey conducted in the Golden Horseshoe
area of Southern Ontario in 1994, over 80% of respondents under the age of 40 pronounced student and news without yod.
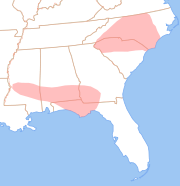 General American thus undergoes yod dropping after all alveolar consonant
General American thus undergoes yod dropping after all alveolar consonant
s. Some accents of Southern American English
preserve the distinction in pairs like loot/lute and do/dew by using a diphthong /ɪu/ in words where RP has /juː/, thus [lut]/[lɪut], [du]/[dɪu], etc.
However, in words like annual, menu, volume, Matthew, continue, etc., where there is a syllable break before the /j/, there is no yod dropping.
Some East Anglian accents such as Norfolk dialect
extend yod dropping not only to the position after /t/, /d/ or /n/, but to the position after nonalveolar consonants as well, so that pairs like pure/poor, beauty/booty, mute/moot, cute/coot are homophonous. Watchers of UK television are likely to be familiar with Bernard Matthews
's description of his turkeys in his television advertisements as bootiful for beautiful.
In yod-pronouncing dialects, the spellings eu, ew, uCV (where C is any consonant and V is any vowel), ue and ui, as in feud, few, mute, cue and suit generally indicate /juː/ or /ɪu/, while the spellings oo and ou, as in moon and soup generally indicate /uː/.
This occurs in unstressed syllables in many varieties of English. Occurring in unstressed syllables, it leads to pronunciations such as the following:
It also occurs in some accents in stressed syllables as in tune and dune. Yod coalescence in stressed syllables occurs in Australian
, Cockney, Estuary English
, Newfoundland English
, and to a certain extent in New Zealand English
, resulting in further examples as follows:
This can lead to additional homophony; for instance, in the case of /dʒ/, dew, due, and Jew come to be pronounced identically. Yod coalescence has traditionally been considered non-RP.
See also
Old English had a contrast between /wr/ and /r/, the former characterized by lip rounding. In Middle English, the contrast disappeared and all cases of initial /r/ came to be rounded.
All of the kn words stem from Old English forms beginning with cn-, and at the time all were pronounced with an initial /k/ before the /n/. These words were common to the Germanic languages, most of which still pronounce the initial /k/. Thus, for example, the Old English ancestor of knee was cnēo, pronounced /kne͡oː/, and the cognate word in Modern German is Knie, pronounced /kniː/.
Most dialects of English reduced the initial cluster /kn/ to /n/ relatively recently; the change seems to have taken place in educated English during the seventeenth century, meaning that Shakespeare did not have the reduction.
, words spelt with gn like gnat, gnostic, gnome, etc. had the cluster /ɡn/. The humorous song The Gnu
jokes about this, even though the g in gnu may actually have always been silent in English, since this loanword did not enter the language until the late 18th century. The trumpeter Kenny Wheeler
wrote a composition titled "Gnu High", a pun on "New High".
. After the initial /s/ is removed, the plosive is aspirated
in the new word-initial environment, resulting in pronunciations such as:
and Caribbean English
. The new final consonant may be slightly lengthened as an effect.
Examples are:
The plurals of test and desk may become tesses and desses by the same English rule that gives us plural messes from singular mess.
These vowel clusters may also merge: and /ndz/ as in "bans", "pens" and "Hans" sounding the same as "bands", "pends" and "hands". The merged form being [nz] and /ntʃ/ as in "pinscher" sounding the same as "pincher". The merged form being [ntʃ]. and /mpt/ as in "dreamt" and "attempt". The merged form being [mpt]. and /mps/ as in "camps" and "hamster". The merged form being [mps].
of final consonant clusters starting with /s/ occurring in African American Vernacular English
as well as many other varieties of English.
For AAVE speakers with S-cluster metathesis the following words can undergo the following changes:
S-cluster metathesis is lexically determined.
The above pronunciations in fact have a long history, and all the metathesised forms have existed in English for around as long as the words themselves, with varying degrees of acceptance.
For example, the Old English verb áscian also appeared as acsian, and both forms continued into Middle English. The two forms co-existed and evolved separately in various regions of England, and later America. The variant ascian gives us the modern standard English ask, but the form "axe", probably derived from Old English acsian, appears in Chaucer: "I axe, why the fyfte man Was nought housband to the Samaritan?" (Wife of Bath's Prologue, 1386.) It was considered acceptable in literary English until about 1600 and can still be found in some dialects of English including African American Vernacular English
. It is, however, one of the most stigmatized features of AAVE, often commented on by teachers. It also persists in Ulster Scots
as /ˈaks/ and Jamaican English as /ˈaːks/, from where it has entered the London
dialect of British English as /ˈɑːks/.
/str/ as /skr/ occurring for some speakers of African American Vernacular English
making "scream" and "stream" homophonous as /ˈskriːm/.
This phonological pattern in AAVE is a phonological pattern that's been mentioned from time to time, often by speech pathologists. Presumably the speech pathologists were concerned about this use of "skr" in place of standard English "str" because it was not clear whether the combination of sounds was an indication of a disorder or dialectal pattern. Still the scream–stream merger has not been observed or recorded in the literature nearly as often as other sound patterns. There are three possible reasons for this: (1) One is that because "skr" only occurs in positions where "str" can occur in general American English
, there will be limited opportunity to produce the sound. (2) Secondly, the scream–stream merger may be viewed as a feature of the speech of young AAVE speakers that is not maintained in adult AAVE. (3) Thirdly, the scream–stream merger may be associated with AAVE spoken in certain regions of the United States.
In summarizing her research on the cluster, Dandy (1991) notes that the form is found in Gullah
and in the speech of some young African Americans born in the Southern United States. She explains that the stream–scream merger is a highly stigmatized feature and that many of the students in her study who used it were referred to speech pathologists. She goes on to note the following about her research: "I also found a continuum that may indicate sound change in progress. If children said skretch for stretch, they probably have used the skr alternation in other words that contained the feature: skreet for street, skrong for strong, skrike for strike, skranger/deskroy for stranger/destroy. There were some who said skreet for street but did not make alteration on other words with that sound". (p. 44). Also, although Dandy does not make this point, it is important to note that the students' use of /skr/ may have been affected by the training they were getting from the speech pathologists.
Phonological history of the English language
The phonological history of English describes changing phonology of the English language over time, starting from its roots in proto-Germanic to diverse changes in different dialects of modern English....
in terms of changes in the phonology
Phonology
Phonology is, broadly speaking, the subdiscipline of linguistics concerned with the sounds of language. That is, it is the systematic use of sound to encode meaning in any spoken human language, or the field of linguistics studying this use...
of consonant clusters.
H-cluster reductions
The h-cluster reductions are various consonant reductions that have occurred in the history of EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
involving consonant clusters beginning with /h/ that have lost the /h/ in certain varieties of English.
Wh-cluster reductions
- The hole–whole merger is the replacement of /hw/ with /h/ before the vowels /oː/ and /uː/ which occurred in Old English. This is due to the effect that rounded back vowels have on /h/, giving it velar and labial characteristics making /hw/ an allophone of /h/ before these vowels; the true phonetic /hw/ then eventually became perceived as this allophone of /h/ and no longer a phonologically distinct speech sound.
- The wine–whine merger is the merger of /hw/ (spelled wh) with /w/. It occurs in the speech of the great majority of English speakers. Notable dialects that retain the distinction include Irish English, Scottish EnglishScottish EnglishScottish English refers to the varieties of English spoken in Scotland. It may or may not be considered distinct from the Scots language. It is always considered distinct from Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic language....
, and Southern American EnglishSouthern American EnglishSouthern American English is a group of dialects of the English language spoken throughout the Southern region of the United States, from Southern and Eastern Maryland, West Virginia and Kentucky to the Gulf Coast, and from the Atlantic coast to most of Texas and Oklahoma.The Southern dialects make...
. This occurred after the hole–whole merger meaning that wh- is usually /w/ before orthographic a, e, i and y, but /h/ before orthographic o. (Orthographic a is usually phonologically /ɒ/ or /ɔː/ after /w/ in some varieties of English.)
Yew–hew merger
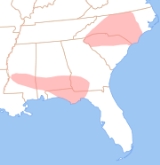
The yew–hew merger is a process that occurs in some dialects of English that causes the cluster /hj/ to be reduced to /j/. It leads to pronunciations like /juːdʒ/ for huge and /juːmən/ for human; hew and yew become homophonous. It is sometimes considered a type of glide-cluster reduction, but is much less widespread than wh-reduction, and is generally stigmatized where it is found. Aside from accents with h dropping, this reduction is in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
found mainly in accents of Philadelphia and New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
; also in Cork
County Cork
County Cork is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and is also part of the province of Munster. It is named after the city of Cork . Cork County Council is the local authority for the county...
accents of Hiberno-English
Hiberno-English
Hiberno-English is the dialect of English written and spoken in Ireland .English was first brought to Ireland during the Norman invasion of the late 12th century. Initially it was mainly spoken in an area known as the Pale around Dublin, with Irish spoken throughout the rest of the country...
. In some dialects of English, the cluster /hj/ (phonetically [çj]) has been reduced to [ç] so that hew and yew differ only by the initial consonant sound (i.e. [çuː] and [juː]).
hl-cluster, hr-cluster and hn-cluster reductions
The hl-cluster, hr-cluster and hn-cluster reductions are three reductions that occurred in Middle English that caused the consonant clusters /hl/, /hr/ and /hn/ to be reduced to /l/, /r/, and /n/. For example, Old English hlāf, hring and hnutu became loaf, ring and nut in Modern English.Yod dropping
Yod dropping is the elisionElision
Elision is the omission of one or more sounds in a word or phrase, producing a result that is easier for the speaker to pronounce...
of the sound [j]. The term comes from the Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
letter yod
Yodh
Yodh is the tenth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Yud , Syriac and Arabic...
, which represents [j].
Yod dropping before [uː] occurs in most varieties of English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
in the following environments:
- After [tʃ, dʒ, j], for example chew [ˈtʃuː], juice [ˈdʒuːs], yew [juː]
- After /ɹ/, for example rude [ɹuːd]
- After consonant+/l/ clusters, for example blue [ˈbluː]
There are accents, for example Welsh English
Welsh English
Welsh English, Anglo-Welsh, or Wenglish refers to the dialects of English spoken in Wales by Welsh people. The dialects are significantly influenced by Welsh grammar and often include words derived from Welsh...
, in which pairs like chews/choose, yew/you, threw/through are distinct: the first member of each pair has the diphthong [ɪu] while the second member has [uː].
Many varieties of English have extended yod dropping to the following environments, on condition that the [j] be in the same syllable as the preceding consonant:
- After /s/, for example suit [ˈsuːt]
- After /l/, for example lute [ˈluːt]
- After /z/, for example Zeus [ˈzuːs]
- After /θ/, for example enthusiasm [ɛnˈθuːziæzəm]
Yod dropping in the above environments was formerly considered nonstandard in England, but today it is heard even among well-educated RP
Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation , also called the Queen's English, Oxford English or BBC English, is the accent of Standard English in England, with a relationship to regional accents similar to the relationship in other European languages between their standard varieties and their regional forms...
speakers. In General American
General American
General American , also known as Standard American English , is a major accent of American English. The accent is not restricted to the United States...
yod dropping is found not only in the above environments but also:
- After /t/, /d/ and /n/, for example tune [ˈtuːn], dew [ˈduː], new [ˈnuː]
Glide retention in these contexts has occasionally been held to be a shibboleth distinguishing Canadians from Americans. However, in a survey conducted in the Golden Horseshoe
Golden Horseshoe
The Golden Horseshoe is a densely populated and industrialized region centred around the Greater Toronto Area at the western end of Lake Ontario in Southern Ontario, Canada, with outer boundaries stretching south to Lake Erie and north to Georgian Bay. Most of it is also part of the Quebec City...
area of Southern Ontario in 1994, over 80% of respondents under the age of 40 pronounced student and news without yod.

Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
s. Some accents of Southern American English
Southern American English
Southern American English is a group of dialects of the English language spoken throughout the Southern region of the United States, from Southern and Eastern Maryland, West Virginia and Kentucky to the Gulf Coast, and from the Atlantic coast to most of Texas and Oklahoma.The Southern dialects make...
preserve the distinction in pairs like loot/lute and do/dew by using a diphthong /ɪu/ in words where RP has /juː/, thus [lut]/[lɪut], [du]/[dɪu], etc.
However, in words like annual, menu, volume, Matthew, continue, etc., where there is a syllable break before the /j/, there is no yod dropping.
Some East Anglian accents such as Norfolk dialect
Norfolk dialect
The Norfolk dialect, also known as Broad Norfolk, is a dialect that was once, and to a great extent, still is spoken by those living in the county of Norfolk in England...
extend yod dropping not only to the position after /t/, /d/ or /n/, but to the position after nonalveolar consonants as well, so that pairs like pure/poor, beauty/booty, mute/moot, cute/coot are homophonous. Watchers of UK television are likely to be familiar with Bernard Matthews
Bernard Trevor Matthews
Bernard Trevor Matthews CVO, CBE was the founder of Bernard Matthews Farms Limited, a company that is best-known for farming turkeys and producing turkey products.-Early life:...
's description of his turkeys in his television advertisements as bootiful for beautiful.
In yod-pronouncing dialects, the spellings eu, ew, uCV (where C is any consonant and V is any vowel), ue and ui, as in feud, few, mute, cue and suit generally indicate /juː/ or /ɪu/, while the spellings oo and ou, as in moon and soup generally indicate /uː/.
| Homophonous pairs after cj/j/r/sh/w/y |
|---|
| Homophonous pairs after l/s/th/z |
|---|
| Homophonous pairs after d/n/t |
|---|
| Homophonous pairs after other consonants |
|---|
Yod coalescence
Yod coalescence is a process that changes the clusters [dj], [tj], [sj] and [zj] into [dʒ], [tʃ], [ʃ] and [ʒ] respectively.This occurs in unstressed syllables in many varieties of English. Occurring in unstressed syllables, it leads to pronunciations such as the following:
| educate | → /ˈɛdʒuːkeɪt/ |
| nature | → /ˈneɪtʃər/ |
| pressure | → /ˈprɛʃər/ |
| measure | → /ˈmɛʒər/ |
| azure | → /ˈæʒər/ |
It also occurs in some accents in stressed syllables as in tune and dune. Yod coalescence in stressed syllables occurs in Australian
Australian English phonology
Australian English is a non-rhotic variety of English spoken by most native-born Australians. Phonologically, it is one of the most regionally homogeneous language varieties in the world...
, Cockney, Estuary English
Estuary English
Estuary English is a dialect of English widely spoken in South East England, especially along the River Thames and its estuary. Phonetician John C. Wells defines Estuary English as "Standard English spoken with the accent of the southeast of England"...
, Newfoundland English
Newfoundland English
Newfoundland English is a name for several accents and dialects thereof the English found in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Most of these differ substantially from the English commonly spoken elsewhere in Canada...
, and to a certain extent in New Zealand English
New Zealand English
New Zealand English is the dialect of the English language used in New Zealand.The English language was established in New Zealand by colonists during the 19th century. It is one of "the newest native-speaker variet[ies] of the English language in existence, a variety which has developed and...
, resulting in further examples as follows:
| dew | → /ˈdʒuː/ |
| tune | → /ˈtʃuːn/ |
| resume | → /rəˈʒuːm/ |
| assume | → /əˈʃuːm/ |
This can lead to additional homophony; for instance, in the case of /dʒ/, dew, due, and Jew come to be pronounced identically. Yod coalescence has traditionally been considered non-RP.
| Homophonous pairs |
|---|
See also
- List of yod dropping and coalescence homophones on WiktionaryWiktionaryWiktionary is a multilingual, web-based project to create a free content dictionary, available in 158 languages...
.
Rap–wrap merger
The rap–wrap merger is a reduction that causes the initial cluster /wr/ to be reduced to /r/, making rap and wrap, rite and write etc. homophones.Old English had a contrast between /wr/ and /r/, the former characterized by lip rounding. In Middle English, the contrast disappeared and all cases of initial /r/ came to be rounded.
Not–knot merger
The not–knot merger is a reduction that occurs in modern English where the historical cluster /kn/ is reduced to /n/ making knot and not homophones.All of the kn words stem from Old English forms beginning with cn-, and at the time all were pronounced with an initial /k/ before the /n/. These words were common to the Germanic languages, most of which still pronounce the initial /k/. Thus, for example, the Old English ancestor of knee was cnēo, pronounced /kne͡oː/, and the cognate word in Modern German is Knie, pronounced /kniː/.
Most dialects of English reduced the initial cluster /kn/ to /n/ relatively recently; the change seems to have taken place in educated English during the seventeenth century, meaning that Shakespeare did not have the reduction.
Nome–gnome merger
The nome–gnome merger is the reduction of the initial cluster /ɡn/ to /n/. In Middle EnglishMiddle English
Middle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
, words spelt with gn like gnat, gnostic, gnome, etc. had the cluster /ɡn/. The humorous song The Gnu
The Gnu
"The Gnu" is a humorous song about a talking gnu by Flanders and Swann.The word gnu is consistently pronounced with two syllables as "g-noo", with the g clearly enunciated, and the n unpalatalised...
jokes about this, even though the g in gnu may actually have always been silent in English, since this loanword did not enter the language until the late 18th century. The trumpeter Kenny Wheeler
Kenny Wheeler
Kenneth Vincent John Wheeler, OC is a Canadian composer and trumpet and flugelhorn player, based in the U.K. since the 1950s....
wrote a composition titled "Gnu High", a pun on "New High".
S-cluster reduction
S-cluster reduction is the dropping of /s/ from the initial consonant clusters with voiceless plosives (environments /sp/, /st/, and /sk(ʷ)/) occurring in Caribbean EnglishCaribbean English
Caribbean English is a broad term for the dialects of the English language spoken in the Caribbean, most countries on the Caribbean coast of Central America, and Guyana. Caribbean English is influenced by the English-based Creole varieties spoken in the region, but they are not the same. In the...
. After the initial /s/ is removed, the plosive is aspirated
Aspiration (phonetics)
In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of air that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. To feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say pin ...
in the new word-initial environment, resulting in pronunciations such as:
| spit | → 'pit | ([ˈspɪt] | → [ˈpʰɪt]) |
| stomach | → 'tomach | ([ˈstɐmək] | → [ˈtʰɐmək]) |
| spend | → 'pen | ([ˈspɛnd] | → [ˈpʰɛn]) (also affected by final consonant-cluster reduction) |
| squeeze | → 'queeze | ([ˈskwiːz] | → [ˈkʰwiz]) |
Final-consonant-cluster reduction
Reduction of final consonant clusters occurs in African American Vernacular EnglishAfrican American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English —also called African American English; less precisely Black English, Black Vernacular, Black English Vernacular , or Black Vernacular English —is an African American variety of American English...
and Caribbean English
Caribbean English
Caribbean English is a broad term for the dialects of the English language spoken in the Caribbean, most countries on the Caribbean coast of Central America, and Guyana. Caribbean English is influenced by the English-based Creole varieties spoken in the region, but they are not the same. In the...
. The new final consonant may be slightly lengthened as an effect.
Examples are:
| test | → tes' | ([tʰɛst] | → [tʰɛs]) |
| desk | → des' | ([ˈdɛsk] | → [ˈdɛs]) |
| hand | → han' | ([ˈhænd] | → [ˈhæn]) |
| send | → sen' | ([ˈsɛnd] | → [ˈsɛn]) |
| left | → lef' | ([ˈlɛft] | → [ˈlɛf]) |
| wasp | → was' | ([ˈwɑːsp] | → [ˈwɑːs]) |
The plurals of test and desk may become tesses and desses by the same English rule that gives us plural messes from singular mess.
Plum–plumb merger
The plum–plumb merger is the reduction of the final cluster /mb/ to /m/ that occurs in all dialects of present English. In early Middle English, words spelled with mb like plumb, lamb etc. had the cluster /mb/.Prince-prints merger
The prince-prints merger is a merger of /ns/ and /nts/ occurring for many speakers of English. For them, "prince" and "prints" are homonyms as [prɪnts]. A [t] is inserted between the [n] and the [t]. Likewise the fricative [ʃ] often becomes [tʃ] after [n], so that "pinscher" and "pincher" are homophones.These vowel clusters may also merge: and /ndz/ as in "bans", "pens" and "Hans" sounding the same as "bands", "pends" and "hands". The merged form being [nz] and /ntʃ/ as in "pinscher" sounding the same as "pincher". The merged form being [ntʃ]. and /mpt/ as in "dreamt" and "attempt". The merged form being [mpt]. and /mps/ as in "camps" and "hamster". The merged form being [mps].
Yod rhotacization
Yod rhotacization is a process that occurs for some Southern AAVE speakers where /j/ is rhotacized to /r/ in consonant clusters causing pronunciations like:| beautiful | → /ˈbruːtɪfəl/ |
| cute | → /ˈkruːt/ |
| music | → /ˈmruːzɪk/ |
S-cluster metathesis
S-cluster metathesis is the metathesisMetathesis (linguistics)
Metathesis is the re-arranging of sounds or syllables in a word, or of words in a sentence. Most commonly it refers to the switching of two or more contiguous sounds, known as adjacent metathesis or local metathesis:...
of final consonant clusters starting with /s/ occurring in African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English —also called African American English; less precisely Black English, Black Vernacular, Black English Vernacular , or Black Vernacular English —is an African American variety of American English...
as well as many other varieties of English.
For AAVE speakers with S-cluster metathesis the following words can undergo the following changes:
| ask | → /ˈæks/ |
| grasp | → /ˈɡræps/ |
| wasp | → /ˈwɑːps/ |
| gasp | → /ˈɡæps/ |
S-cluster metathesis is lexically determined.
The above pronunciations in fact have a long history, and all the metathesised forms have existed in English for around as long as the words themselves, with varying degrees of acceptance.
For example, the Old English verb áscian also appeared as acsian, and both forms continued into Middle English. The two forms co-existed and evolved separately in various regions of England, and later America. The variant ascian gives us the modern standard English ask, but the form "axe", probably derived from Old English acsian, appears in Chaucer: "I axe, why the fyfte man Was nought housband to the Samaritan?" (Wife of Bath's Prologue, 1386.) It was considered acceptable in literary English until about 1600 and can still be found in some dialects of English including African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English —also called African American English; less precisely Black English, Black Vernacular, Black English Vernacular , or Black Vernacular English —is an African American variety of American English...
. It is, however, one of the most stigmatized features of AAVE, often commented on by teachers. It also persists in Ulster Scots
Ulster Scots language
Ulster Scots or Ulster-Scots generally refers to the dialects of Scots spoken in parts of Ulster in Ireland. Some definitions of Ulster Scots may also include Standard English spoken with an Ulster Scots accent...
as /ˈaks/ and Jamaican English as /ˈaːks/, from where it has entered the London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
dialect of British English as /ˈɑːks/.
Scream–stream merger
The scream–stream merger is the pronunciation of the consonant clusterConsonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word splits....
/str/ as /skr/ occurring for some speakers of African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English
African American Vernacular English —also called African American English; less precisely Black English, Black Vernacular, Black English Vernacular , or Black Vernacular English —is an African American variety of American English...
making "scream" and "stream" homophonous as /ˈskriːm/.
This phonological pattern in AAVE is a phonological pattern that's been mentioned from time to time, often by speech pathologists. Presumably the speech pathologists were concerned about this use of "skr" in place of standard English "str" because it was not clear whether the combination of sounds was an indication of a disorder or dialectal pattern. Still the scream–stream merger has not been observed or recorded in the literature nearly as often as other sound patterns. There are three possible reasons for this: (1) One is that because "skr" only occurs in positions where "str" can occur in general American English
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
, there will be limited opportunity to produce the sound. (2) Secondly, the scream–stream merger may be viewed as a feature of the speech of young AAVE speakers that is not maintained in adult AAVE. (3) Thirdly, the scream–stream merger may be associated with AAVE spoken in certain regions of the United States.
-
-
- Common words in which the /sk/ sequence occurs are given below:
-
| street | → /ˈskriːt/ |
| stretch | → /ˈskrɛtʃ/ |
| straight | → /ˈskreɪt/ |
In summarizing her research on the cluster, Dandy (1991) notes that the form is found in Gullah
Gullah
The Gullah are African Americans who live in the Lowcountry region of South Carolina and Georgia, which includes both the coastal plain and the Sea Islands....
and in the speech of some young African Americans born in the Southern United States. She explains that the stream–scream merger is a highly stigmatized feature and that many of the students in her study who used it were referred to speech pathologists. She goes on to note the following about her research: "I also found a continuum that may indicate sound change in progress. If children said skretch for stretch, they probably have used the skr alternation in other words that contained the feature: skreet for street, skrong for strong, skrike for strike, skranger/deskroy for stranger/destroy. There were some who said skreet for street but did not make alteration on other words with that sound". (p. 44). Also, although Dandy does not make this point, it is important to note that the students' use of /skr/ may have been affected by the training they were getting from the speech pathologists.
See also
- Phonological history of the English languagePhonological history of the English languageThe phonological history of English describes changing phonology of the English language over time, starting from its roots in proto-Germanic to diverse changes in different dialects of modern English....
- Phonological history of English consonantsPhonological history of English consonantsThe phonological history of English consonants is part of the phonological history of the English language in terms of changes in the phonology of consonants.-H-cluster reductions:* The wine–whine merger is the merger of with...
- G dropping
- Phonological history of English fricatives
- H dropping

