.gif)
Parental notification (abortion)
Encyclopedia
Canada
In Canada, abortion care is subject to general medical legislation, as there are no special laws regulating abortion. Access varies by province and by region; though there are no legal restrictions to abortion. Most medical care facilities in Canada observe a minor's ethical right to medical confidentiality, and they do not share medical information with a parent without consent of the patient. In 1989, the Supreme Court ruled that the woman's partner has no right to veto her decision to undergo an abortion. Abortion care, as with the rest of medical care, is funded by the government.United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
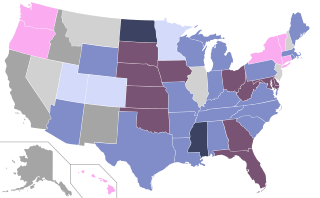
, most states typically require one of two types of parental involvement– consent and/or notification, New Hampshire's abortion law allows a minor to get an abortion without parental consent or notification. 35 states required some type of parental involvement in a minor's decision to have an abortion– 22 states require one or both parents to consent to the procedure, 11 require one or both parents be notified and 2 require both consent and notification before an elective abortion can occur.
Parental involvement laws played a key role in forcing the Court to clarify its position on abortion regulation. The Court ruled, in essence, that parental involvement laws (and all other abortion regulation) can legally make it more difficult for a female to acquire an abortion. But there is a threshold beyond which the increased difficulties become unconstitutional. Requiring spousal involvement before a woman can acquire an abortion has been interpreted as falling on the unconstitutional side of that threshold, while parental involvement has been interpreted as falling on the constitutional side. Or, to use the language of Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992), spousal notification laws place an "undue burden" on a woman's ability to get an abortion, whereas parental involvement laws do not.
Parental involvement laws have three basic features. First, they are binding on minors, not adults. Second, they require, at minimum, that minors notify their parents before an abortion is performed, and in some cases consent from the parents. And third, they allow minors to acquire a judicial bypass if consent cannot be acquired. These regulations are but one example of the detailed fabric of abortion legislation and regulation that has evolved since the Supreme Court's decision to legalize abortion in its 1973 Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade, , was a controversial landmark decision by the United States Supreme Court on the issue of abortion. The Court decided that a right to privacy under the due process clause in the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution extends to a woman's decision to have an abortion,...
and Doe v. Bolton
Doe v. Bolton
Doe v. Bolton, 410 U.S. 179 , was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court overturning the abortion law of Georgia. The Supreme Court's decision was released on January 22, 1973, the same day as the decision in the better-known case of Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S...
.
The first major case involving parental involvement legislation was decided in 1976 in Planned Parenthood of Central Missouri v. Danforth
Planned Parenthood of Central Missouri v. Danforth
Planned Parenthood v. Danforth, 428 U.S. 52 was a case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States in which the constitutionality of several Missouri state regulations regarding abortion was challenged...
. This case involved a Missouri law that required consent from various parties before an abortion could be performed– written consent by the patient, spousal consent for married individuals, and parental consent for minors, specifically. The court ruled that the parental consent provision was unconstitutional due to its universal enforcement.
The ability of a minor to acquire an abortion against her parent's wishes became a recurring theme in several more cases following Planned Parenthood of Central Missouri v. Danforth
Planned Parenthood of Central Missouri v. Danforth
Planned Parenthood v. Danforth, 428 U.S. 52 was a case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States in which the constitutionality of several Missouri state regulations regarding abortion was challenged...
. Bellotti v. Baird
Bellotti v. Baird
Bellotti v. Baird can refer to* Bellotti v. Baird * Bellotti v. Baird...
(1979) addressed a Massachusetts law that required a minor to acquire parental consent before an abortion was performed. But, unlike the Danforth case, this law allowed for judicial bypass if consent could not be acquired. Similar reasoning can be found in H.L. v. Matheson (1981). This case ruled on the relatively milder regulation of parental notification as opposed to parental consent. In this case, the Court ruled that parental notification is constitutional since the parent could not veto the adolescent's final decision to acquire an abortion. In Planned Parenthood of Kansas City v. Ashcroft (1983), the Supreme Court ruled conclusively on the constitutionality of parental consent laws– parental consent was found to be constitutional so long as it also allowed a judicial bypass if such consent could not be acquired. In Planned Parenthood of S.E. Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992), the Court placed parental involvement firmly within a broader set of legal principles governing a woman's constitutional right to an abortion. Parental involvement, and other regulations, were constitutional so long that they did not place an "undue burden" on a woman's ability to acquire an abortion.
According to the Chicago Tribune
Chicago Tribune
The Chicago Tribune is a major daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, and the flagship publication of the Tribune Company. Formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" , it remains the most read daily newspaper of the Chicago metropolitan area and the Great Lakes region and is...
online edition, the Illinois Supreme Court, on Wednesday, November 30, 2011, "agreed to consider a dispute over whether the state must begin enforcing a
(1995, never enforced) law requiring parents to be notified before their children can obtain an abortion."
South Africa
In South Africa, any woman of any age can get an abortion on request with no reasons given if she is less than 13 weeks pregnant. A woman under the age of 18 will be advised to consult her parents, but she can decide not to inform or consult them if she so chooses. However, she must give informed consentInformed consent
Informed consent is a phrase often used in law to indicate that the consent a person gives meets certain minimum standards. As a literal matter, in the absence of fraud, it is redundant. An informed consent can be said to have been given based upon a clear appreciation and understanding of the...
, meaning that if she is unable to understand the consequences of an abortion she cannot consent to one without the assistance of her parents or guardian.
Spain
In 2009, the Socialist government started to liberalize current abortion laws, sending a new law through the lower house of Parliament which would allow abortion on-demand for pregnancies through the fourteenth week. The government almost succeeded in lowering the age of consent for abortions to 16, but in the end the bill states that girls aged 16 and 17 must inform her parents (but does not need parental consent) for an abortion except if the girl comes from an abusive household and such news will cause more strife.India
All women coming to a health facility seeking termination of pregnancy up to 7 weeks period of gestation (49 days from the first day of the last menstrual period in women with regular cycle of 28 days) provided certain aspects have been assessed and found appropriate, one being permission of guardian in case of minor (as per MTP Act 1971).Poland
Parental consent is always required if the woman seeking abortion is a minor.Sweden
The current legislation is the Abortion Act of 1974. This states that up until the end of the eighteenth week of the pregnancy the choice of an abortion is entirely up to the woman, for any reason whatsoever. The law makes no distinction with regards to the age of the pregnant woman.Australia
A minor does not require parental consent or notification except in Western Australia, where in the event of the woman being under 16 years of age one of her parents must be notified, except where permission has been granted by the Children's Court or the woman does not live with her parents.New Zealand
New Zealand has no parental notification restrictions on under-sixteen access for abortion. A recent attempt to introduce such restrictions into the Care of Children Act 2004 was heavily defeated in New Zealand's Parliament.Japan
There are social pressures to protect women’s confidentiality, especially that of young women who are junior high or high school students. This may be taken to mean that there are no laws in Japan regarding this aspect of abortion.Greece
Girls under the age of 18 must get written permission from a parent or guardian before being allowed an abortion.France
According to this website, a pregnant girl under the age of 16 may ask for an abortion without consulting her parents first, but she has to be accompanied to the clinic by an adult of her choice.Italy
Parental authorisation is required if the woman is under 18.United Kingdom
Parental involvement laws are liberal in the UK; if the girl is seen as competent by medical staff no disclosure to parents is allowed. In most cases, girls aged 13 or above will be covered by this provision but pre-teenagers will not and parents, social workers and police can become involved to protect the child. Around 120 12-year-olds, at least five 11-year-olds and two nine year olds have had legal abortions since 1996. In 2005, Sue Axon, of Manchester, wanted the law changed to prevent girls under 16 getting confidential advice. However, the High Court had rejected a review of guidelines which state that terminations do not need parents' consent and doctors should respect girls' confidentiality. Parents can however be informedArguments in support
Advocacy groups have made a number of arguments in favor of parental notification.- Minors must have parental approval for most types of medical proceduresSurgerySurgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
. - A study by the Heritage FoundationHeritage FoundationThe Heritage Foundation is a conservative American think tank based in Washington, D.C. Heritage's stated mission is to "formulate and promote conservative public policies based on the principles of free enterprise, limited government, individual freedom, traditional American values, and a strong...
stated that overall, parental involvement laws reduce the number of teenage abortions. - The pregnant minor might be pressured into having an abortion by an older boyfriend, so as to conceal the fact that he is guilty of statutory rapeStatutory rapeThe phrase statutory rape is a term used in some legal jurisdictions to describe sexual activities where one participant is below the age required to legally consent to the behavior...
. - Currently, the parents of the minor are financially responsible for any complications resulting from the abortion, unless said minor has been legally emancipated. (However, this is also true for any complications that result from illegal abortions, which are typically more risky)
- Notification and consent laws give parents a chance to counsel their teenage daughters about the possible consequences of abortion.
Arguments in opposition
Advocacy groups on the other side have also made a number of arguments against parental notification:- Parental notification and consent laws increase the numbers of back alley abortions:
-
-
- Women's health organizations believe that in states that have notification or consent laws, there has been an increase in unsafe, illegal, "back alley" abortions. In 2005, the Detroit News reported that a 16-year-old boy beat his pregnant, under-age girlfriend with a bat at her request to abort a fetus. The young couple avoided getting parental permission to receive an abortion. In Indiana, where there are also parental consent laws, a young woman by the name of Becky BellBecky BellRebecca "Becky" Suzanne Bell was an American teenage girl who died as a result of a back-alley abortion in 1988. She lived in Indianapolis, Indiana....
died from a back-alley abortion rather than discuss her pregnancy and wish for an abortion with her parents. In Idaho, 13-year-old Spring Adams was shot to death by her father when he found out that she was planning to abort a pregnancy caused by his incestuous rape. - Many young women feel they cannot talk to their parents about their sex lives or about rape or incest that they may have suffered, and may seek illegal abortions as a result.
- In states that have notification or consent laws, minors will sometimes travel to a nearby state to have an abortion. Delays mean increased risks:
- Delaying an abortion even if only by a couple of days, increases the likelihood of complications arising from abortion procedures. In fact, legal abortions before the third trimester are less dangerous than childbirth for teens as they are 24 times more likely to die from childbirth complications than from a legal abortion performed in the first trimester. However, the risk of death or major complications significantly increases for each week into pregnancy, particularly if the abortion is delayed until the third trimester.
- Judge Nixon of The District Court in Tennessee estimated "that even under the best of circumstances, the [judicial] waiver process would take twenty-two days to complete– a significant problem given the time-sensitive nature of pregnancy and the increased risk involved in later abortions."
- The American Academy of Pediatrics stated that "Legislation mandating parental involvement does not achieve the intended benefit of promoting family communication, but it does increase the risk of harm to the adolescent by delaying access to appropriate medical care...[M]inors should not be compelled or required to involve their parents in their decisions to obtain abortions, although they should be encouraged to discuss their pregnancies with their parents and other responsible adults."
- An American Medical Association study in 1992 showed that mandatory parental involvement laws "increase the gestational age at which the induced pregnancy termination occurs, thereby also increasing the risk associated with the procedure."
- A study of abortions by researchers at Baruch College at City University of New York showed that Texas teens who were between 17 years, 6 months old and 18 years old were 34% more likely to have an abortion in the much riskier second trimester than young women who were 18 or older when they became pregnant.
- Lawrence Finer, spokesperson for the Guttmacher Institute said: "It just shows how laws like this can lead to health risks for teens. Abortion is a safe procedure, but it's less safe later in the pregnancy." He suggest that parental involvement laws have a small effect on abortion rates compared with improved sexual education and birth control access and usage.
- Many minors of childbearing age are sufficiently mature to make abortion decisions by themselves.
- Other Reproductive Health issues such as STD testing and treatment do not require parental consent.
- Women's health organizations believe that in states that have notification or consent laws, there has been an increase in unsafe, illegal, "back alley" abortions. In 2005, the Detroit News reported that a 16-year-old boy beat his pregnant, under-age girlfriend with a bat at her request to abort a fetus. The young couple avoided getting parental permission to receive an abortion. In Indiana, where there are also parental consent laws, a young woman by the name of Becky Bell
-
Debate within the Roman Catholic Church
In 2009, Archbishop José Cardoso SobrinhoJosé Cardoso Sobrinho
José Cardoso Sobrinho is the Archbishop Emeritus of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of the cities of Olinda and Recife in the Brazilian state of Pernambuco....
excommunicated, or rather declared excommunicated (since the canon law invoked imposes the excommunication automatically), the mother and doctors of a 9-year-old girl for carrying out an abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
on the girl's twin fetuses, after she was raped by her own stepfather, something that had been happening since she was six years old. The affair shocked the Brazilian government and provoked disgust from President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva , known popularly as Lula, served as the 35th President of Brazil from 2003 to 2010.A founding member of the Workers' Party , he ran for President three times unsuccessfully, first in the 1989 election. Lula achieved victory in the 2002 election, and was inaugurated as...
.
Pope Benedict XVI later gave a controversial speech
Speech
Speech is the human faculty of speaking.It may also refer to:* Public speaking, the process of speaking to a group of people* Manner of articulation, how the body parts involved in making speech are manipulated...
in Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
where he appeared to blur the distinction between indirect abortion
Indirect abortion
Indirect abortion is the name given by Catholic theologians to an abortion procedure which has a therapeutic medical effect, presumably to save the life of a pregnant woman....
and direct abortion. He condemned all forms of abortion, even those considered to be therapeutic. This raised the eyebrows of the Vatican communications department, which re-iterated the distinction between direct and indirect abortion.
See also
|
Gillick competence Gillick competence is a term originating in England and is used in medical law to decide whether a child is able to consent to his or her own medical treatment, without the need for parental permission or knowledge.... Informed consent Informed consent is a phrase often used in law to indicate that the consent a person gives meets certain minimum standards. As a literal matter, in the absence of fraud, it is redundant. An informed consent can be said to have been given based upon a clear appreciation and understanding of the... Paternal rights and abortion The paternal rights and abortion issue is an extension of both the abortion debate and the fathers' rights movement. Countries recognizing father's legal rights on abortion have laws requiring that the male who impregnated the pregnant female either consent or be informed before she has an... Parental consent Parental consent laws in some countries require that one or more parents consent to or be notified before their minor child can legally engage in certain activities.... Legal protection of access to abortion Governments sometimes take measures designed to afford legal protection of access to abortion. Such legislation often seeks to guard facilities which provide induced abortion against obstruction, vandalism, picketing, and other actions, or to protect patients and employees of such facilities from... Teenage pregnancy Teenage pregnancy is a pregnancy of a female under the age of 20 when the pregnancy ends. It generally refers to a female who is unmarried and usually refers to an unplanned pregnancy... Youth rights Youth rights refers to a set of philosophies intended to enhance civil rights for young people. They are a response to the oppression of young people, with advocates challenging ephebiphobia, adultism and ageism through youth participation, youth/adult partnerships, and promoting, ultimately,... |
External links
In support- Why We Need The Child Custody Protection Act– NRLC
- Analyzing the Effect of State Legislation on the Incidence of Abortion Among Minors– Heritage Foundation
In opposition
- Restrictions on Young Women's Access to Abortion– NARAL
- Laws Requiring Parental Consent or Notification for Minors' Abortions– Planned Parenthood
Neutral
- HealthVote.org– Non-partisan Analysis of California's Proposition 85 (Parental Notification & Waiting Period for Minors' Abortions– November 2006 Election)

