
Panel analysis
Encyclopedia
Panel analysis is statistical method, widely used in social science, epidemiology
, and econometrics
, which deals with two-dimensional panel data
. The data are usually collected over time and over the same individuals and then a regression
is run over these two dimensions. Multidimensional analysis
is an econometric
method in which data are collected over more than two dimensions (typically, time, individuals, and some third dimension).
A common panel data
regression model looks like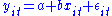 , where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variable
, where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variable
, a and b are coefficients, i and t are indices
for individuals and time. The error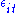 is very important in this analysis. Assumptions about the error term determine whether we speak of fixed effects or random effects. In a fixed effects model,
is very important in this analysis. Assumptions about the error term determine whether we speak of fixed effects or random effects. In a fixed effects model, 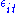 is assumed to vary non-stochastically over
is assumed to vary non-stochastically over 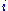 or
or  making the fixed effects model analogous to a dummy variable model in one dimension. In a random effects model,
making the fixed effects model analogous to a dummy variable model in one dimension. In a random effects model, 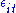 is assumed to vary stochastically over
is assumed to vary stochastically over 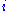 or
or  requiring special treatment of the error variance matrix.
requiring special treatment of the error variance matrix.
Panel data analysis has three more-or-less independent approaches:
The selection between these methods depends upon the objective of our analysis, and the problems concerning the exogeneity of the explanatory variables.
There are no unique attributes of individuals within the measurement set, and no universal effects across time.
There are unique attributes of individuals that are not the results of random variation and that do not vary across time. Adequate, if we want to draw inferences only about the examined individuals.
There are unique, time constant attributes of individuals that are the results of random variation and do not correlate with the individual regressors. This model is adequate, if we want to draw inferences about the whole population, not only the examined sample.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
, and econometrics
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, which deals with two-dimensional panel data
Panel data
In statistics and econometrics, the term panel data refers to multi-dimensional data. Panel data contains observations on multiple phenomena observed over multiple time periods for the same firms or individuals....
. The data are usually collected over time and over the same individuals and then a regression
Linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
is run over these two dimensions. Multidimensional analysis
Multidimensional analysis
In statistics, econometrics, and related fields, multidimensional analysis is a data analysis process that groups data into two or more categories: data dimensions and measurements. For example, a data set consisting of the number of wins for a single football team at each of several years is a...
is an econometric
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
method in which data are collected over more than two dimensions (typically, time, individuals, and some third dimension).
A common panel data
Panel data
In statistics and econometrics, the term panel data refers to multi-dimensional data. Panel data contains observations on multiple phenomena observed over multiple time periods for the same firms or individuals....
regression model looks like
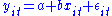 , where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variable
, where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variableIndependent variable
The terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
, a and b are coefficients, i and t are indices
Index (mathematics)
The word index is used in variety of senses in mathematics.- General :* In perhaps the most frequent sense, an index is a number or other symbol that indicates the location of a variable in a list or array of numbers or other mathematical objects. This type of index is usually written as a...
for individuals and time. The error
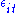 is very important in this analysis. Assumptions about the error term determine whether we speak of fixed effects or random effects. In a fixed effects model,
is very important in this analysis. Assumptions about the error term determine whether we speak of fixed effects or random effects. In a fixed effects model, 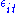 is assumed to vary non-stochastically over
is assumed to vary non-stochastically over 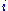 or
or  making the fixed effects model analogous to a dummy variable model in one dimension. In a random effects model,
making the fixed effects model analogous to a dummy variable model in one dimension. In a random effects model, 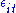 is assumed to vary stochastically over
is assumed to vary stochastically over 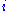 or
or  requiring special treatment of the error variance matrix.
requiring special treatment of the error variance matrix.Panel data analysis has three more-or-less independent approaches:
- independently pooled panels;
- random effects models;
- fixed effects modelsFixed effects estimatorIn econometrics and statistics, a fixed effects model is a statistical model that represents the observed quantities in terms of explanatory variables that are treated as if the quantities were non-random. This is in contrast to random effects models and mixed models in which either all or some of...
or first differenced models.
The selection between these methods depends upon the objective of our analysis, and the problems concerning the exogeneity of the explanatory variables.
Independently pooled panels
Key Assumption:There are no unique attributes of individuals within the measurement set, and no universal effects across time.
Fixed effect models
Key Assumption:There are unique attributes of individuals that are not the results of random variation and that do not vary across time. Adequate, if we want to draw inferences only about the examined individuals.
Random effect models
Key Assumption:There are unique, time constant attributes of individuals that are the results of random variation and do not correlate with the individual regressors. This model is adequate, if we want to draw inferences about the whole population, not only the examined sample.
See also
- Panel study
- Hausman testHausman testThe Hausman test or Hausman specification test is a statistical test in econometrics named after Jerry A. Hausman. The test evaluates the significance of an estimator versus an alternative estimator...
- Factor analysisFactor analysisFactor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved, uncorrelated variables called factors. In other words, it is possible, for example, that variations in three or four observed variables...

