
Paley–Zygmund inequality
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the Paley–Zygmund inequality bounds the
probability that a positive random variable is small, in terms of
its mean
and variance
(i.e., its first two moments
). The inequality was
proved by Raymond Paley
and Antoni Zygmund
.
Theorem: If Z ≥ 0 is a random variable
with
finite variance, and if 0 < θ < 1, then
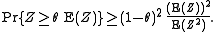
Proof: First,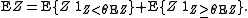
Obviously, the first addend is at most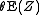 . The second one is at most
. The second one is at most
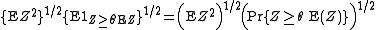
according to the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality
. ∎
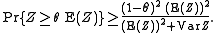
The one-sided Chebyshev inequality gives a slightly better bound:
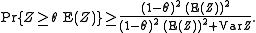
The latter is sharp.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the Paley–Zygmund inequality bounds the
probability that a positive random variable is small, in terms of
its mean
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
and variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
(i.e., its first two moments
Moment (mathematics)
In mathematics, a moment is, loosely speaking, a quantitative measure of the shape of a set of points. The "second moment", for example, is widely used and measures the "width" of a set of points in one dimension or in higher dimensions measures the shape of a cloud of points as it could be fit by...
). The inequality was
proved by Raymond Paley
Raymond Paley
Raymond Edward Alan Christopher Paley was an English mathematician. Paley was born in Bournemouth, England. He was educated at Eton. From there he entered Trinity College, Cambridge where he showed himself the most brilliant student among a remarkable collection of fellow undergraduates...
and Antoni Zygmund
Antoni Zygmund
Antoni Zygmund was a Polish-born American mathematician.-Life:Born in Warsaw, Zygmund obtained his PhD from Warsaw University and became a professor at Stefan Batory University at Wilno...
.
Theorem: If Z ≥ 0 is a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
with
finite variance, and if 0 < θ < 1, then
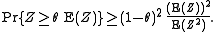
Proof: First,
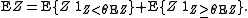
Obviously, the first addend is at most
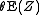 . The second one is at most
. The second one is at most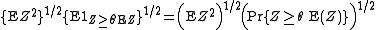
according to the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality
Cauchy–Schwarz inequality
In mathematics, the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality , is a useful inequality encountered in many different settings, such as linear algebra, analysis, probability theory, and other areas...
. ∎
Related inequalities
The right-hand side of the Paley–Zygmund inequality can be written as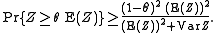
The one-sided Chebyshev inequality gives a slightly better bound:
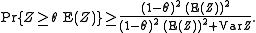
The latter is sharp.

