
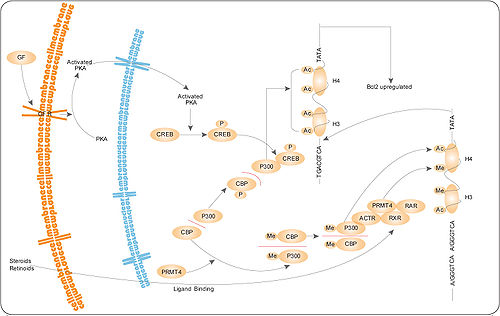
PRMT4 pathway
Encyclopedia
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
N-methyltransferase
Methyltransferase
A methyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that transfers a methyl group from a donor to an acceptor.Methylation often occurs on nucleic bases in DNA or amino acids in protein structures...
-4 (PRMT4/CARM1) methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
of arginine
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
residues within proteins plays a critical key role in transcriptional regulation (see the PRMT4 pathway on the left). PRMT4 binds to the classes of transcriptional activators known as p160 and CBP/p300. The modified forms of these proteins are involved in stimulation of gene expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
via steroid hormone receptor
Hormone receptor
A hormone receptor is a receptor protein on the surface of a cell or in its interior that binds to a specific hormone. The hormone causes many changes to take place in the cell....
s. Significantly, PRMT4 methylates core histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
s H3 and H4, which are also targets of the histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
acetylase activity of CBP/p300 coactivators. PRMT4 recruitment of chromatin
Chromatin
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are; to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene...
by binding to coactivators increases histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
and enhances the accessibility of promoter regions for transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
. Methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
of the transcriptional coactivator CBP by PRMT4 inhibits binding to CREB and thereby partitions the limited cellular pool of CBP for steroid hormone
Steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into five groups by the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, and progestogens...
receptor interaction.
See also
- DNA methyltransferaseDNA methyltransferaseIn biochemistry, the DNA methyltransferase family of enzymescatalyze the transfer of a methyl group to DNA. DNA methylation serves a wide variety of biological functions...
- NucleosomeNucleosomeNucleosomes are the basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound around a histone protein core. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool....
- HistoneHistoneIn biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
- Histone-Modifying EnzymesHistone-Modifying EnzymesThe packaging of the eukaryotic genome into highly condensed chromatin makes it inaccessible to the factors required for gene transcription, DNA replication, recombination and repair. Eukaryotes have developed intricate mechanisms to overcome this repressive barrier imposed by the chromatin...
- ChromatinChromatinChromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are; to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene...
- Diet and cancerDiet and cancerDiet and cancer are associated. While it is not yet possible to provide quantitative estimates of the overall risks, it has been estimated that 35 percent of cancer deaths may be related to dietary factors. Almost all cancers are caused by environmental factors, and of these, 30–40% of cancers are...

