
P-ANCA
Encyclopedia
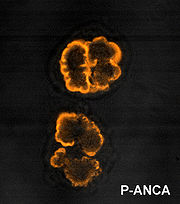
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies are a group of autoantibodies, mainly of the IgG type, against antigens in the cytoplasm of neutrophil granulocytes and monocytes...
, show a perinuclear staining pattern.
This pattern occurs because the vast majority of the antigens targeted by ANCAs are highly cationic (Positively charged) at pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
7.00. During ethanol fixation, antigens which are more cationic migrate and localize around the nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
, attracted by its negatively charged DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
content. Antibody staining therefore results in fluorescence of the region around the nucleus.
Targets
By far the most common p-ANCA target is myeloperoxidaseMyeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase is a peroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MPO gene. Myeloperoxidase is most abundantly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes . It is a lysosomal protein stored in azurophilic granules of the neutrophil...
(MPO), a neutrophil granule protein whose primary role in normal metabolic processes is generation of oxygen radicals.
ANCA will less commonly form against alternative antigens that may also result in a p-ANCA pattern. These include lactoferrin
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin , also known as lactotransferrin , is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions...
; elastase
Elastase
In molecular biology, elastase is an enzyme from the class of proteases that break down proteins.- Forms and classification:There exist eight human genes for elastase:Bacterial forms: Organisms such as P...
; and cathepsin G
Cathepsin G
Cathepsin G is an enzymatic protein belonging to the peptidase or protease families. In humans, it is coded by the CTSG gene.The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the peptidase S1 protein family, is found in azurophil granules of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes...
.
When the condition is a vasculitis
Vasculitis
Vasculitis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders that are characterized by inflammatory destruction of blood vessels. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis...
, the target is usually MPO. However, the proportion of p-ANCA sera with anti-MPO antibodies has been reported to be as low as 12%.
Medical conditions
p-ANCA is associated with several medical conditions:- It is fairly specific, but not sensitiveSensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
for ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease . Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the colon , that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores. The main symptom of active disease is usually constant diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset...
, so is not useful as a sole diagnostic test. When measured together with Anti-saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodiesAnti-saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodiesAnti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies , along with perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies , are among the two most useful and often discriminating markers for colitis...
(ASCA), p-ANCA has been estimated to have a specificity of 97% and a sensitivity of 48% in differentiating patients with ulcerative colitis from normal controls. - about 50% of cases of Churg-Strauss syndromeChurg-Strauss syndromeChurg–Strauss syndrome is a medium and small vessel autoimmune vasculitis, leading to necrosis. It involves mainly the blood vessels of the lungs , gastrointestinal system, and peripheral nerves, but also affects the heart, skin and kidneys. It is a rare disease that is non-inheritable and...
- A majority of primary sclerosing cholangitisPrimary sclerosing cholangitisPrimary sclerosing cholangitis is a chronic liver disease caused by progressive inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts of the liver. The inflammation impedes the flow of bile to the gut, which can ultimately lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer...
- sometimes polyarteritis nodosaPolyarteritis nodosaPolyarteritis nodosa is a vasculitis of medium & small-sized arteries, which become swollen and damaged from attack by rogue immune cells. Polyarteritis nodosa is also called Kussmaul disease or Kussmaul-Maier disease...
(only in the variant microscopic polyangitis, usually negative in typical polyarteritis nodosa) - microscopic polyangiitisMicroscopic polyangiitisMicroscopic polyangiitis is an ill-defined autoimmune disease characterized by pauci-immune, necrotizing, small-vessel vasculitis without clinical or pathological evidence of necrotizing granulomatous inflammation.-Presentation:Because many different organ systems may be involved, a wide range of...
- Focal necrotising and crescentic glomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis, also known as glomerular nephritis, abbreviated GN, is a renal disease characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, or small blood vessels in the kidneys...
- Rheumatoid arthritisRheumatoid arthritisRheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...

