Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia
Encyclopedia
Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED) is an autosomal recessive disorder of bone
growth that results in skeletal abnormalities, severe hearing loss, and distinctive facial features. The name of the condition indicates that it affects hearing (oto-) and the bones of the spine (spondylo-), and enlarges the ends of bones (megaepiphyses).
The features of OSMED are similar to those of another skeletal disorder, Weissenbacher-Zweymüller syndrome
. Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI
.
that begins early in life. Severe high-tone hearing loss is common. Typical facial features include protruding eyes; a sunken nasal bridge; an upturned nose with a large, rounded tip; and a small lower jaw. Some affected infants are born with an opening in the roof of the mouth, which is called a cleft palate.
 Mutations in the COL11A2
Mutations in the COL11A2
gene
cause otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia. The protein made by the COL11A2 gene is involved in the production of type XI collagen
. This type of collagen is important for the normal development of bone and other connective tissue
s. Mutations in the COL11A2 gene lead to a loss of function of this type of collagen, resulting in the signs and symptoms of OSMED.
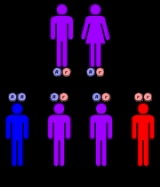
OSMED is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a person to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected but are carriers of one copy of the altered gene. A recessive pattern of inheritance makes OSMED unique among the type II and type XI collagenopathies.
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
growth that results in skeletal abnormalities, severe hearing loss, and distinctive facial features. The name of the condition indicates that it affects hearing (oto-) and the bones of the spine (spondylo-), and enlarges the ends of bones (megaepiphyses).
The features of OSMED are similar to those of another skeletal disorder, Weissenbacher-Zweymüller syndrome
Weissenbacher-Zweymüller syndrome
Weissenbacher–Zweymuller syndrome , also called Pierre-Robin syndrome with fetal chondrodysplasia, is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder, linked to mutations in the COL11A2 gene , which codes for the α2 strand of collagen type XI...
. Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI
Collagenopathy, types II and XI
The type II and XI collagenopathies are a group of disorders that affect connective tissue, the tissue that supports the body's joints and organs. These disorders are caused by defects in type II or type XI collagen. Collagens are complex molecules that provide structure, strength, and elasticity ...
.
Diagnosis
The distinctive characteristics of OSMED include severe bone and joint problems and very severe hearing loss. This disorder affects the epiphyses, the parts of the bone where growth occurs. People with the condition are often shorter than average because the bones in their arms and legs are unusually short. Other skeletal signs include enlarged joints, short hands and fingers, and flat bones of the spine (vertebrae). People with the disorder often experience back and joint pain, limited joint movement, and arthritisArthritis
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
that begins early in life. Severe high-tone hearing loss is common. Typical facial features include protruding eyes; a sunken nasal bridge; an upturned nose with a large, rounded tip; and a small lower jaw. Some affected infants are born with an opening in the roof of the mouth, which is called a cleft palate.
Pathophysiology

COL11A2
COL11A2 is a human gene that is one of several genes that provide instructions for the production of type XI collagen. The COL11A2 gene produces one component of this type of collagen, called the pro-alpha2 chain...
gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
cause otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia. The protein made by the COL11A2 gene is involved in the production of type XI collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
. This type of collagen is important for the normal development of bone and other connective tissue
Connective tissue
"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
s. Mutations in the COL11A2 gene lead to a loss of function of this type of collagen, resulting in the signs and symptoms of OSMED.
OSMED is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a person to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected but are carriers of one copy of the altered gene. A recessive pattern of inheritance makes OSMED unique among the type II and type XI collagenopathies.

