
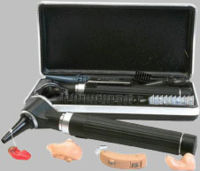
Otoscope
Encyclopedia
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
device which is used to look into the ear
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system....
s. Health care providers use otoscopes to screen for illness during regular check-ups and also to investigate when a symptom involves the ears. With an otoscope, it is possible to see the outer ear and middle ear.
Otoscopes consist of a handle and a head. The head contains a light source and a simple low-power magnifying lens
Magnifying glass
A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle ....
, typically around 8 diopters. The distal (front) end of the otoscope has an attachment for disposable plastic ear specula
Speculum (medical)
A speculum is a medical tool for investigating body cavities, with a form dependent on the body cavity for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra...
. The examiner first straightens the ear canal
Ear canal
The ear canal , is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 35 mm in length and 5 to 10 mm in diameter....
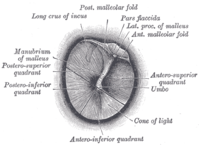
by pulling on the pinna and then inserts the ear speculum side of the otoscope into the external ear. It is important to brace the hand holding the otoscope against the patient's head to avoid injury to the ear canal by placing the index finger or little finger. The examiner can then look through a lens on the rear of the instrument and see inside the ear canal. In many models, the lens can be removed, which allows the examiner to insert instruments through the otoscope into the ear canal, such as for removing earwax
Earwax
Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a yellowish waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. It protects the skin of the human ear canal, assists in cleaning and lubrication, and also provides some protection from bacteria, fungi, insects and water...
(cerumen). Most models also have an insertion point for a bulb capable of pushing air through the speculum which is called pneumatic otoscope
Pneumatic otoscopy
The pneumatic otoscope is the standard tool used in diagnosing otitis media. In addition to the pneumatic head, a surgical head also is useful. The pneumatic head contains a lens, an enclosed light source, and a nipple for attachment of a rubber bulb and tubing...
. This puff of air allows an examiner to test the mobility of the tympanic membrane.
Many otoscopes used in doctors offices are wall-mounted, while others are portable. Wall-mounted otoscopes are attached by a flexible power cord to a base, which serves to hold the otoscope when it's not in use and also serves as a source of electric power, being plugged into an electric outlet
Domestic AC power plugs and sockets
AC power plugs and sockets are devices for removably connecting electrically operated devices to the power supply. Electrical plugs and sockets differ by country in rating, shape, size and type of connectors...
. Portable models are powered by batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
in the handle; these batteries are usually rechargeable and can be recharged from a base unit. Otoscopes are often sold with ophthalmoscopes as a diagnostic set.
Diseases which may be diagnosed by an otoscope include otitis media
Otitis media
Otitis media is inflammation of the middle ear, or a middle ear infection.It occurs in the area between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear, including a duct known as the eustachian tube. It is one of the two categories of ear inflammation that can underlie what is commonly called an earache,...
and otitis externa
Otitis externa
Otitis externa is an inflammation of the outer ear and ear canal. Along with otitis media, external otitis is one of the two human conditions commonly called "earache". It also occurs in many other species. Inflammation of the skin of the ear canal is the essence of this disorder...
, infection of the middle and outer parts of the ear, respectively.
Otoscopes are also frequently used for examining patients' noses (avoiding the need for a separate nasal speculum) and (with the speculum removed) upper throats.
External links
- An article detailing the use of otoscopes from one of the first issues of the Student BMJ available online published in July 1995. This archived version of a similar page from wisc.edu contains images.
- This archived page from indstate.edu gives another overview with images.
- Phisick Pictures and information about antique otoscopes

