Organisation-based access control
Encyclopedia
In computer security
, organization-based access control (OrBAC) is an access control
model first presented in 2003. The current approaches of the access control
rest on the three entities (subject, action, object) to control the access the policy specifies that some subject has the permission to realize some action on some object.
OrBAC allows the policy designer to define a security policy independently of the implementation. The chosen method to fulfill this goal is the introduction of an abstract level.
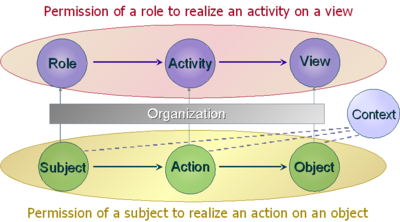 Each security policy is defined for and by an organization. Thus, the specification of the security policy is completely parameterized by the organization so that it is possible to handle simultaneously several security policies associated with different organizations. The model is not restricted to permissions, but also includes the possibility to specify prohibitions and obligations. From the three abstract entities (roles, activities, views), abstract privileges are defined. And from theses abstract privileges, concrete privileges are derived.
Each security policy is defined for and by an organization. Thus, the specification of the security policy is completely parameterized by the organization so that it is possible to handle simultaneously several security policies associated with different organizations. The model is not restricted to permissions, but also includes the possibility to specify prohibitions and obligations. From the three abstract entities (roles, activities, views), abstract privileges are defined. And from theses abstract privileges, concrete privileges are derived.
OrBAC is context sensitive, so the policy could be expressed dynamically. Furthermore, OrBAC owns concepts of hierarchy (organization, role, activity, view, context) and separation constraints. To design and implement security policies using the OrBAC model, the MotOrBAC tool has been developed. His simulation mode can be used to test a security policy. MotOrBAC also features a conflict detection function which helps the designer to find and solve conflicts.
Computer security
Computer security is a branch of computer technology known as information security as applied to computers and networks. The objective of computer security includes protection of information and property from theft, corruption, or natural disaster, while allowing the information and property to...
, organization-based access control (OrBAC) is an access control
Access control
Access control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
model first presented in 2003. The current approaches of the access control
Access control
Access control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
rest on the three entities (subject, action, object) to control the access the policy specifies that some subject has the permission to realize some action on some object.
OrBAC allows the policy designer to define a security policy independently of the implementation. The chosen method to fulfill this goal is the introduction of an abstract level.
- Subjects are abstracted into roles. A role is a set of subjects to which the same security rule apply.
- Similarly, an activity is a set of actions to which the same security rule apply.
- And, a view is a set of objects to which the same security rule apply.

OrBAC is context sensitive, so the policy could be expressed dynamically. Furthermore, OrBAC owns concepts of hierarchy (organization, role, activity, view, context) and separation constraints. To design and implement security policies using the OrBAC model, the MotOrBAC tool has been developed. His simulation mode can be used to test a security policy. MotOrBAC also features a conflict detection function which helps the designer to find and solve conflicts.
See also
- Mandatory access controlMandatory access controlIn computer security, mandatory access control refers to a type of access control by which the operating system constrains the ability of a subject or initiator to access or generally perform some sort of operation on an object or target...
- MAC - Discretionary access controlDiscretionary access controlIn computer security, discretionary access control is a kind of access control defined by the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria "as a means of restricting access to objects based on the identity of subjects and/or groups to which they belong...
- DAC - Role-based access controlRole-Based Access ControlIn computer systems security, role-based access control is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is used by the majority of enterprises with more than 500 employees, and can be implemented via mandatory access control or discretionary access control...
- RBAC - Bell–LaPadula model

