
Ordnance BL 15 pounder
Encyclopedia
The Ordnance BL 15 pounder, otherwise known as the 15 pounder 7 cwt, was the British Army
's field gun
in the Second Boer War
and some remained in limited use in minor theatres of World War I
.
of 1883. When the modern smokeless propellant cordite
replaced gunpowder in 1892 it was decided that the 12 pounder was capable of firing a heavier shell up to 15 lb (6.8 kg). A 14 pound shell was adopted and the gun was renamed a 15 pounder.
Mk I carriage : recoil was controlled by drag-shoes. These were placed under the wheels, and were connected by chains and cables to the wheel hubs and the trail.
Mk II carriage : this had the same drag-shoe system and also a hydraulic buffer. This only allowed a short recoil, and was not successful.
Mk III carriage : In 1899 a rudimentary recoil system was added, consisting of a "spade" beneath the axle which dug in when the gun recoiled, connected by a steel wire to a spring in a cylinder on the trail. Mk I and II carriages fitted with these were known as Mk 1* and Mk II*. The latter retained the hydraulic buffer.
Although the whole gun jumped and moved backwards on firing, the spring returned it to firing position and hence still increased the rate of fire compared to the old model without any recoil mechanism. Hogg and Thurston comment ironically : "It is said that it checked it [recoil] so well that the gun usually recoiled 1 foot and jumped forward 2 feet".
Other Mks of carriage followed, all with axle-spades, but without buffers.
From 1904 the BL 15 pounder was superseded by the modern QF 18 pounder
. Remaining BL 15 pounders were upgraded as the BLC 15 pounder
to equip the Territorial Force
with an "ersatz QF gun".
 349 guns were in service in the Second Boer War
349 guns were in service in the Second Boer War
1899 - 1902 and fired 166,548 shells out of the British total of 233,714.
While the gun could fire a shell up to approximately 5800-5900 yards, the No. 56 time and percussion fuze in use in 1899 could only be set for a maximum timed range of 4100 yards because it only burned for 13 seconds. The shrapnel shells in use were usually time-set to burst in the air above and in front of the enemy. Hence the gunners had to get within approximately 4200 yards of the enemy to fire on them. The fuze could be set to explode on contact (percussion) up to the maximum range, but shrapnel exploding on contact was of little use. This was rectified later in the war by the No. 57 "blue fuze" which could be time set up to 5800-5900 yards.
 7th Field Battery (4 guns, originally No. 2 and No. 6 Light Batteries) towed by oxen and known as the Oxo Battery and manned by Mauritian and South African gunners fought in the German East Africa campaign
7th Field Battery (4 guns, originally No. 2 and No. 6 Light Batteries) towed by oxen and known as the Oxo Battery and manned by Mauritian and South African gunners fought in the German East Africa campaign
in World War I
.
British Army
The British Army is the land warfare branch of Her Majesty's Armed Forces in the United Kingdom. It came into being with the unification of the Kingdom of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England...
's field gun
Field gun
A field gun is an artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march and when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances, as to opposed guns installed in a fort, or to siege cannon or mortars which...
in the Second Boer War
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War was fought from 11 October 1899 until 31 May 1902 between the British Empire and the Afrikaans-speaking Dutch settlers of two independent Boer republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State...
and some remained in limited use in minor theatres of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
.
History
The gun was a modified version of the previous BL 12 pounder 7 cwt gunOrdnance BL 12 pounder 7 cwt
The Ordnance BL 12 pounder 7cwt was the British Army's field gun, which succeed the RML 13 pounder 8 cwt in 1885.-History:The gun was initially adopted by both the Royal Field Artillery and Royal Horse Artillery, and was in full service by 1885...
of 1883. When the modern smokeless propellant cordite
Cordite
Cordite is a family of smokeless propellants developed and produced in the United Kingdom from 1889 to replace gunpowder as a military propellant. Like gunpowder, cordite is classified as a low explosive because of its slow burning rates and consequently low brisance...
replaced gunpowder in 1892 it was decided that the 12 pounder was capable of firing a heavier shell up to 15 lb (6.8 kg). A 14 pound shell was adopted and the gun was renamed a 15 pounder.
Mk I carriage : recoil was controlled by drag-shoes. These were placed under the wheels, and were connected by chains and cables to the wheel hubs and the trail.
Mk II carriage : this had the same drag-shoe system and also a hydraulic buffer. This only allowed a short recoil, and was not successful.
Mk III carriage : In 1899 a rudimentary recoil system was added, consisting of a "spade" beneath the axle which dug in when the gun recoiled, connected by a steel wire to a spring in a cylinder on the trail. Mk I and II carriages fitted with these were known as Mk 1* and Mk II*. The latter retained the hydraulic buffer.
Although the whole gun jumped and moved backwards on firing, the spring returned it to firing position and hence still increased the rate of fire compared to the old model without any recoil mechanism. Hogg and Thurston comment ironically : "It is said that it checked it [recoil] so well that the gun usually recoiled 1 foot and jumped forward 2 feet".
Other Mks of carriage followed, all with axle-spades, but without buffers.
From 1904 the BL 15 pounder was superseded by the modern QF 18 pounder
Ordnance QF 18 pounder
The Ordnance QF 18 pounder, or simply 18-pounder Gun, was the standard British Army field gun of the World War I era. It formed the backbone of the Royal Field Artillery during the war, and was produced in large numbers. It was also used by British and Commonwealth Forces in all the main theatres,...
. Remaining BL 15 pounders were upgraded as the BLC 15 pounder
Ordnance BLC 15 pounder
The Ordnance BLC 15 pounder gun was a modernised version of the obsolete BL 15 pounder 7 cwt gun, incorporating a recoil and recuperator mechanism above the barrel and modified quicker-opening breech...
to equip the Territorial Force
Territorial Force
The Territorial Force was the volunteer reserve component of the British Army from 1908 to 1920, when it became the Territorial Army.-Origins:...
with an "ersatz QF gun".
Second Boer War

Second Boer War
The Second Boer War was fought from 11 October 1899 until 31 May 1902 between the British Empire and the Afrikaans-speaking Dutch settlers of two independent Boer republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State...
1899 - 1902 and fired 166,548 shells out of the British total of 233,714.
While the gun could fire a shell up to approximately 5800-5900 yards, the No. 56 time and percussion fuze in use in 1899 could only be set for a maximum timed range of 4100 yards because it only burned for 13 seconds. The shrapnel shells in use were usually time-set to burst in the air above and in front of the enemy. Hence the gunners had to get within approximately 4200 yards of the enemy to fire on them. The fuze could be set to explode on contact (percussion) up to the maximum range, but shrapnel exploding on contact was of little use. This was rectified later in the war by the No. 57 "blue fuze" which could be time set up to 5800-5900 yards.
World War I

East African Campaign (World War I)
The East African Campaign was a series of battles and guerrilla actions which started in German East Africa and ultimately affected portions of Mozambique, Northern Rhodesia, British East Africa, Uganda, and the Belgian Congo. The campaign was effectively ended in November 1917...
in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
.
Ammunition
 |
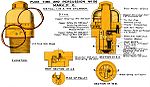 |
 |
 |
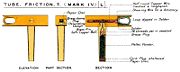 |
as used in Second Boer War |

