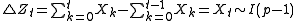Order of integration
Encyclopedia
Order of integration, denoted I(p), is a summary statistic
for a time series
. It reports the minimum number of differences required to obtain a stationary series.
is integrated of order 0 if it admits a moving average representation with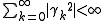
This is a necessary, but not sufficient condition for a stationary process
. Therefore, all stationary processes are I(0), but not all I(0) processes are stationary.
is integrated of order P if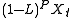
is integrated of order 0, where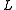 is the lag operator and
is the lag operator and  is the first difference, ie:
is the first difference, ie:  .
.
In other words, a process is integrated to order P if taking repeated differences P times yields a stationary process.
Summary statistics
In descriptive statistics, summary statistics are used to summarize a set of observations, in order to communicate the largest amount as simply as possible...
for a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
. It reports the minimum number of differences required to obtain a stationary series.
Integration of order zero
A time seriesTime series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
is integrated of order 0 if it admits a moving average representation with
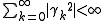
This is a necessary, but not sufficient condition for a stationary process
Stationary process
In the mathematical sciences, a stationary process is a stochastic process whose joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time or space...
. Therefore, all stationary processes are I(0), but not all I(0) processes are stationary.
Integration of order P
A time seriesTime series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
is integrated of order P if
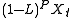
is integrated of order 0, where
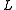 is the lag operator and
is the lag operator and  is the first difference, ie:
is the first difference, ie:  .
.In other words, a process is integrated to order P if taking repeated differences P times yields a stationary process.
Constructing an integrated series
An I(p) process can be constructed by summing an I(p−1) process:- Suppose
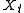 is I(p-1)
is I(p-1) - Now construct a series
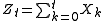
- Show that Z is I(p) by observing its first-differences are I(p-1):