
Optimal matching
Encyclopedia
Optimal matching is a sequence analysis method used in social science, to assess the dissimilarity of ordered arrays of tokens that usually represent a time-ordered sequence of socio-economic states two individuals have experienced. Once such distances have been calculated for a set of observations (e.g. individuals in a cohort
) classical tools (such as cluster analysis) can be used. The method was tailored to social sciences from a technique originally introduced to study molecular biology (protein or genetic) sequences (see sequence alignment
).
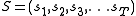 be a sequence of states
be a sequence of states 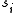 belonging to a finite set of possible states. Let us denote
belonging to a finite set of possible states. Let us denote 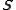 the sequence space, i.e. the set of all possible sequences of states.
the sequence space, i.e. the set of all possible sequences of states.
Optimal matching algorithms work by defining simple operator algebras that manipulate sequences, i.e. a set of operators . In the most simple approach, a set composed of only three basic operations to transform sequences is used:
. In the most simple approach, a set composed of only three basic operations to transform sequences is used:
Imagine now that a cost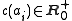 is associated
is associated
to each operator. Given two sequences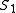 and
and 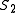 ,
,
the idea is to measure the cost of obtaining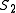 from
from 
using operators from the algebra. Let be a sequence of operators such that the application of all the operators of this sequence
be a sequence of operators such that the application of all the operators of this sequence 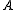 to the first sequence
to the first sequence 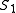 gives the second sequence
gives the second sequence 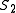 :
:
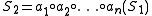 where
where 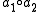 denotes the compound operator.
denotes the compound operator.
To this set we associate the cost , that
, that
represents the total cost of the transformation. One should consider at this point that there might exist different such sequences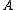 that transform
that transform 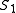 into
into  ; a reasonable choice is to select the cheapest of such sequences. We thus
; a reasonable choice is to select the cheapest of such sequences. We thus
call distance
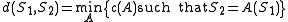
that is, the cost of the less expensive set of transformations that turn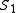 into
into  . Notice that
. Notice that 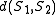 is by definition nonnegative since it is the sum of positive costs, and trivially
is by definition nonnegative since it is the sum of positive costs, and trivially 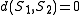 if and only if
if and only if 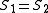 , that is there is no cost. The distance function is symmetric if insertion and deletion costs are equal
, that is there is no cost. The distance function is symmetric if insertion and deletion costs are equal  ; the term indel cost usually refers to the common cost of insertion and deletion.
; the term indel cost usually refers to the common cost of insertion and deletion.
Considering a set composed of only the three basic operations described above, this proximity measure satisfies the triangular inequality. Transitivity
however, depends on the definition of the set of elementary operations.
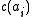 .
.
Cohort (statistics)
In statistics and demography, a cohort is a group of subjects who have shared a particular time together during a particular time span . Cohorts may be tracked over extended periods in a cohort study. The cohort can be modified by censoring, i.e...
) classical tools (such as cluster analysis) can be used. The method was tailored to social sciences from a technique originally introduced to study molecular biology (protein or genetic) sequences (see sequence alignment
Sequence alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are...
).
Algorithm
Let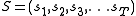 be a sequence of states
be a sequence of states 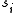 belonging to a finite set of possible states. Let us denote
belonging to a finite set of possible states. Let us denote 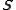 the sequence space, i.e. the set of all possible sequences of states.
the sequence space, i.e. the set of all possible sequences of states.Optimal matching algorithms work by defining simple operator algebras that manipulate sequences, i.e. a set of operators
 . In the most simple approach, a set composed of only three basic operations to transform sequences is used:
. In the most simple approach, a set composed of only three basic operations to transform sequences is used:
- one state
 is inserted in the sequence
is inserted in the sequence 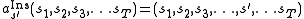
- one state is deleted from the sequence
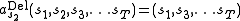 and
and - a state
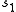 is replaced (substituted) by state
is replaced (substituted) by state 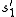 ,
, 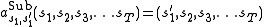 .
.
Imagine now that a cost
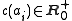 is associated
is associatedto each operator. Given two sequences
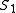 and
and 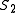 ,
,the idea is to measure the cost of obtaining
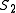 from
from 
using operators from the algebra. Let
 be a sequence of operators such that the application of all the operators of this sequence
be a sequence of operators such that the application of all the operators of this sequence 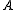 to the first sequence
to the first sequence 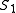 gives the second sequence
gives the second sequence 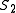 :
: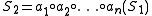 where
where 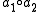 denotes the compound operator.
denotes the compound operator.To this set we associate the cost
 , that
, thatrepresents the total cost of the transformation. One should consider at this point that there might exist different such sequences
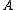 that transform
that transform 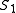 into
into  ; a reasonable choice is to select the cheapest of such sequences. We thus
; a reasonable choice is to select the cheapest of such sequences. We thuscall distance
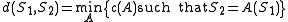
that is, the cost of the less expensive set of transformations that turn
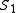 into
into  . Notice that
. Notice that 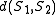 is by definition nonnegative since it is the sum of positive costs, and trivially
is by definition nonnegative since it is the sum of positive costs, and trivially 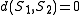 if and only if
if and only if 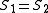 , that is there is no cost. The distance function is symmetric if insertion and deletion costs are equal
, that is there is no cost. The distance function is symmetric if insertion and deletion costs are equal  ; the term indel cost usually refers to the common cost of insertion and deletion.
; the term indel cost usually refers to the common cost of insertion and deletion.Considering a set composed of only the three basic operations described above, this proximity measure satisfies the triangular inequality. Transitivity
Transitivity
-In grammar:* Intransitive verb* Transitive verb, when a verb takes an object* Transitivity -In logic and mathematics:* Arc-transitive graph* Edge-transitive graph* Ergodic theory, a group action that is metrically transitive* Vertex-transitive graph...
however, depends on the definition of the set of elementary operations.
Criticism
Although widely used in sociology, demography, several critics that have been moved to optimal matching techniques. As was pointed out by several authors (see for example), the main problem in the application of optimal matching concerns the definition of the costs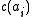 .
.Optimal matching in causal modelling
Optimal matching is also a term used in statistical modelling of causal effects. In this context it refers to matching "cases" with "controls", and is completely separate from the sequence-analytic sense.Software
- Abbott's original program is available. The source code and windows binary are available.
- TDA is a powerful program, offering access to some of the latest developments in transition data analysis.
- STATA has implemented a package to run optimal matching analysis.
- TraMineR is an open source RR (programming language)R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....
-package for analysing and visualizing states and events sequences, including optimal matching analysis.

