Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding
Encyclopedia
In cryptography
, Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP) is a padding scheme
often used together with RSA encryption. OAEP was introduced by Bellare
and Rogaway
.
The OAEP algorithm is a form of Feistel network which uses a pair of random oracle
s G and H to process the plaintext prior to asymmetric encryption. When combined with any secure trapdoor one-way permutation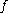 , this processing is proved in the random oracle model to result in a combined scheme which is semantically secure
, this processing is proved in the random oracle model to result in a combined scheme which is semantically secure
under chosen plaintext attack (IND-CPA). When implemented with certain trapdoor permutations (e.g., RSA), OAEP is also proved secure against chosen ciphertext attack. OAEP can be used to build an all-or-nothing transform.
OAEP satisfies the following two goals:
The original version of OAEP (Bellare/Rogaway, 1994) showed a form of "plaintext awareness
" (which they claimed implies security against chosen ciphertext attack) in the random oracle model when OAEP is used with any trapdoor permutation. Subsequent results contradicted this claim, showing that OAEP was only IND-CCA1 secure. However, the original scheme was proved in the random oracle model to be IND-CCA2 secure when OAEP is used with the RSA permutation using standard encryption exponents, as in the case of RSA-OAEP.
An improved scheme (called OAEP+) that works with any trapdoor one-way permutation was offered by Victor Shoup
to solve this problem.
More recent work has shown that in the standard model (that is, when hash functions are not modelled as random oracles), that it is impossible to prove the IND-CCA2 security of RSA-OAEP under the assumed hardness of the RSA problem
.
 In the diagram,
In the diagram,
To encode,
To decode,
The "all-or-nothing
" security is from the fact that to recover m, you must recover the entire X and the entire Y; X is required to recover r from Y, and r is required to recover m from X. Since any bit of a cryptographic hash completely changes the result, the entire X, and the entire Y must both be completely recovered.
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
, Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP) is a padding scheme
Padding (cryptography)
-Classical cryptography:Official messages often start and end in predictable ways: My dear ambassador, Weather report, Sincerely yours, etc. The primary use of padding with classical ciphers is to prevent the cryptanalyst from using that predictability to find cribs that aid in breaking the...
often used together with RSA encryption. OAEP was introduced by Bellare
Mihir Bellare
Mihir Bellare is a cryptographer and professor at the University of California, San Diego. He has published several seminal papers in the field of cryptography , many coauthored with Phillip Rogaway. Bellare has published a number of papers in the field of Format-Preserving Encryption...
and Rogaway
Phillip Rogaway
Phillip Rogaway is a professor of computer science at the University of California, Davis. He graduated with an BA in computer science from UC Berkeley and completed his PhD in cryptography at MIT, in the Theory of Computation group. He has taught at UC Davis since 1994.Dr...
.
The OAEP algorithm is a form of Feistel network which uses a pair of random oracle
Random oracle
In cryptography, a random oracle is an oracle that responds to every query with a random response chosen uniformly from its output domain, except that for any specific query, it responds the same way every time it receives that query...
s G and H to process the plaintext prior to asymmetric encryption. When combined with any secure trapdoor one-way permutation
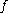 , this processing is proved in the random oracle model to result in a combined scheme which is semantically secure
, this processing is proved in the random oracle model to result in a combined scheme which is semantically secureSemantic security
Semantic security is a widely used definition for security in an asymmetric key encryption algorithm. For a cryptosystem to be semantically secure, it must be infeasible for a computationally bounded adversary to derive significant information about a message when given only its ciphertext and...
under chosen plaintext attack (IND-CPA). When implemented with certain trapdoor permutations (e.g., RSA), OAEP is also proved secure against chosen ciphertext attack. OAEP can be used to build an all-or-nothing transform.
OAEP satisfies the following two goals:
- Add an element of randomness which can be used to convert a deterministic encryptionDeterministic encryptionA deterministic encryption scheme is a cryptosystem which always produces the same ciphertext for a given plaintext and key, even over separate executions of the encryption algorithm...
scheme (e.g., traditional RSA) into a probabilisticProbabilistic encryptionProbabilistic encryption is the use of randomness in an encryption algorithm, so that when encrypting the same message several times it will, in general, yield different ciphertexts...
scheme. - Prevent partial decryption of ciphertexts (or other information leakage) by ensuring that an adversary cannot recover any portion of the plaintext without being able to invert the trapdoor one-way permutation
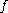 .
.
The original version of OAEP (Bellare/Rogaway, 1994) showed a form of "plaintext awareness
Plaintext-aware encryption
Plaintext-awareness is a notion of security for public-key encryption. A cryptosystem is plaintext-aware if it is difficult for any efficient algorithm to come up with a valid ciphertext without being aware of the corresponding plaintext....
" (which they claimed implies security against chosen ciphertext attack) in the random oracle model when OAEP is used with any trapdoor permutation. Subsequent results contradicted this claim, showing that OAEP was only IND-CCA1 secure. However, the original scheme was proved in the random oracle model to be IND-CCA2 secure when OAEP is used with the RSA permutation using standard encryption exponents, as in the case of RSA-OAEP.
An improved scheme (called OAEP+) that works with any trapdoor one-way permutation was offered by Victor Shoup
Victor Shoup
Victor Shoup is a computer scientist and mathematician. He obtained a PhD in computer science from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1989, and he did his undergraduate work at the University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire. He is currently a professor at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences...
to solve this problem.
More recent work has shown that in the standard model (that is, when hash functions are not modelled as random oracles), that it is impossible to prove the IND-CCA2 security of RSA-OAEP under the assumed hardness of the RSA problem
RSA problem
In cryptography, the RSA problem summarizes the task of performing an RSA private-key operation given only the public key. The RSA algorithm raises a message to an exponent, modulo a composite number N whose factors are not known. As such, the task can be neatly described as finding the eth roots...
.
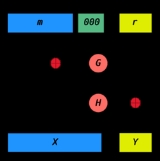
Diagram of OAEP

- n is the number of bits in the RSA modulus.
- k0 and k1 are integers fixed by the protocol.
- m is the plaintext message, an (n − k0 − k1 )-bit string
- G and H are typically some cryptographic hash functionCryptographic hash functionA cryptographic hash function is a deterministic procedure that takes an arbitrary block of data and returns a fixed-size bit string, the hash value, such that an accidental or intentional change to the data will change the hash value...
s fixed by the protocol.
To encode,
- messages are padded with k1 zeros to be n − k0 bits in length.
- r is a random k0-bit string
- G expands the k0 bits of r to n − k0 bits.
- X = m00..0 ⊕ G(r)
- H reduces the n − k0 bits of X to k0 bits.
- Y = r ⊕ H(X)
- The output is X || Y where X is shown in the diagram as the leftmost block and Y as the rightmost block.
To decode,
- recover the random string as r = Y ⊕ H(X)
- recover the message as m00..0 = X ⊕ G(r)
The "all-or-nothing
All-or-nothing transform
In cryptography, an all-or-nothing transform , also known as an all-or-nothing protocol, is an encryption mode which allows the data to be understood only if all of it is known. AONTs are not encryption, but frequently make use of symmetric ciphers and may be applied before encryption...
" security is from the fact that to recover m, you must recover the entire X and the entire Y; X is required to recover r from Y, and r is required to recover m from X. Since any bit of a cryptographic hash completely changes the result, the entire X, and the entire Y must both be completely recovered.

