
Operating margin
Encyclopedia
In business
, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales (ROS) — is the ratio of operating income ("operating profit" in the UK
) divided by net sales
, usually presented in percent.
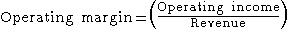
Net profit
measures the profitability
of ventures after accounting for all costs.
Return on sales (ROS) is net profit as a percentage of sales revenue
. ROS is an indicator of profitability and is often used to compare the profitability of companies and industries of differing sizes. Significantly, ROS does not account for the capital
(investment
) used to generate the profit. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 69 percent responded that they found the "return on sales" metric very useful.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA)
is a rough measure of operating cash flow, which reduces the effect of accounting, financing, and tax policies on reported profits.
. How does a company decide whether it is successful or not? Probably the most common way is to look at the net profits
of the business. Given that companies are collections of projects and markets, individual areas can be judged on how successful they are at adding to the corporate net profit. Not all projects are of equal size, however, and one way to adjust for size is to divide the profit by sales revenue
. The resulting ratio is return on sales (ROS), the percentage of sales revenue that gets “returned” to the company as net profits after all the related costs of the activity are deducted.
Net profit: To calculate net profit for a unit (such as a company or division), subtract all costs, including a fair share of total corporate overheads, from the gross revenues.
Return on sales (ROS): Net profit as a percentage of sales revenue.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA)
is a very popular measure of financial performance. It is used to assess the "operating" profit of the business. It is a rough way of calculating how much cash the business is generating and is even sometimes called the "operating cash flow." It can be useful because it removes factors that change the view of performance depending upon the accounting and financing policies of the business. Supporters argue it reduces management's ability to change the profits they report by their choice of accounting rules and the way they generate financial backing for the company. This metric excludes from consideration expenses related to decisions such as how to finance the business (debt or equity) and over what period they depreciate fixed assets. EBITDA is typically closer to actual cash flow than is NOPAT
. EBITDA can be calculated by adding back the costs of interest, depreciation, and amortization charges and any taxes incurred. EBITDA ($) = Net profit ($) + Interest Payments ($) + Taxes Incurred ($) + Depreciation and Amortization Charges ($)
Example: The Coca Cola Company
(Relevant figures in italics)
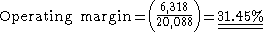
It is a measurement of what proportion of a company's revenue is left over, before taxes and other indirect costs (such as rent, bonus, interest, etc.), after paying for variable costs of production as wages, raw materials, etc. A good operating margin is needed for a company to be able to pay for its fixed costs, such as interest on debt. A higher operating margin means that the company has less financial risk.
Operating margin can be considered total revenue from product sales less all costs before adjustment for taxes, dividends to shareholders, and interest on debt.
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales (ROS) — is the ratio of operating income ("operating profit" in the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
) divided by net sales
Revenue
In business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
, usually presented in percent.
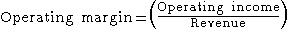
Net profit
Net profit
Net profit or net revenue is a measure of the profitability of a venture after accounting for all costs. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 91 percent responded that they found the "net profit" metric very useful...
measures the profitability
Profit (accounting)
In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
of ventures after accounting for all costs.
Return on sales (ROS) is net profit as a percentage of sales revenue
Revenue
In business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
. ROS is an indicator of profitability and is often used to compare the profitability of companies and industries of differing sizes. Significantly, ROS does not account for the capital
Capital (economics)
In economics, capital, capital goods, or real capital refers to already-produced durable goods used in production of goods or services. The capital goods are not significantly consumed, though they may depreciate in the production process...
(investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
) used to generate the profit. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 69 percent responded that they found the "return on sales" metric very useful.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA)
EBITDA
EBITDA is an acronym for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is a non-GAAP metric that is measured exactly as stated. All interest, tax, depreciation and amortization entries in the income statement are reversed out from the bottom-line net income...
is a rough measure of operating cash flow, which reduces the effect of accounting, financing, and tax policies on reported profits.
Purpose
These financial metrics measure levels and rates of profitabilityProfit (accounting)
In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
. How does a company decide whether it is successful or not? Probably the most common way is to look at the net profits
Net profit
Net profit or net revenue is a measure of the profitability of a venture after accounting for all costs. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 91 percent responded that they found the "net profit" metric very useful...
of the business. Given that companies are collections of projects and markets, individual areas can be judged on how successful they are at adding to the corporate net profit. Not all projects are of equal size, however, and one way to adjust for size is to divide the profit by sales revenue
Revenue
In business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
. The resulting ratio is return on sales (ROS), the percentage of sales revenue that gets “returned” to the company as net profits after all the related costs of the activity are deducted.
Construction
Net profit measures the fundamental profitability of the business. It is the revenues of the activity less the costs of the activity. The main complication is in more complex businesses when overhead needs to be allocated across divisions of the company. Almost by definition, overheads are costs that cannot be directly tied to any specific product or division. The classic example would be the cost of headquarters staff.Net profit: To calculate net profit for a unit (such as a company or division), subtract all costs, including a fair share of total corporate overheads, from the gross revenues.
- Net profit ($) = Sales revenue ($) - Total costs ($)
Return on sales (ROS): Net profit as a percentage of sales revenue.
- Return on sales (%) = Net profit ($) / Sales revenue ($)
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA)
EBITDA
EBITDA is an acronym for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is a non-GAAP metric that is measured exactly as stated. All interest, tax, depreciation and amortization entries in the income statement are reversed out from the bottom-line net income...
is a very popular measure of financial performance. It is used to assess the "operating" profit of the business. It is a rough way of calculating how much cash the business is generating and is even sometimes called the "operating cash flow." It can be useful because it removes factors that change the view of performance depending upon the accounting and financing policies of the business. Supporters argue it reduces management's ability to change the profits they report by their choice of accounting rules and the way they generate financial backing for the company. This metric excludes from consideration expenses related to decisions such as how to finance the business (debt or equity) and over what period they depreciate fixed assets. EBITDA is typically closer to actual cash flow than is NOPAT
NOPAT
In corporate finance, net operating profit after tax or NOPAT is a company's after-tax operating profit for all investors, including shareholders and debt holders. It is equal to NOPLAT and is defined as follows:An alternative formula is as follows...
. EBITDA can be calculated by adding back the costs of interest, depreciation, and amortization charges and any taxes incurred. EBITDA ($) = Net profit ($) + Interest Payments ($) + Taxes Incurred ($) + Depreciation and Amortization Charges ($)
Example: The Coca Cola Company
| Net Operating Revenues | $ 20,088 |
| Gross Profit Gross profit In accounting, gross profit or sales profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of making a product or providing a service, before deducting overhead, payroll, taxation, and interest payments... |
$ 15,924 |
| Operating Income | $ 6,318 |
| Income Before Income Taxes | $ 6,578 |
| Net Income Net income Net income is the residual income of a firm after adding total revenue and gains and subtracting all expenses and losses for the reporting period. Net income can be distributed among holders of common stock as a dividend or held by the firm as an addition to retained earnings... |
$ 5,080 |
(Relevant figures in italics)
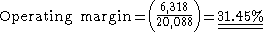
It is a measurement of what proportion of a company's revenue is left over, before taxes and other indirect costs (such as rent, bonus, interest, etc.), after paying for variable costs of production as wages, raw materials, etc. A good operating margin is needed for a company to be able to pay for its fixed costs, such as interest on debt. A higher operating margin means that the company has less financial risk.
Operating margin can be considered total revenue from product sales less all costs before adjustment for taxes, dividends to shareholders, and interest on debt.

