
Oogamy
Encyclopedia
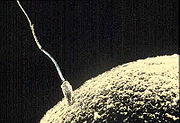
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
. It is a form of anisogamy
Anisogamy
Anisogamy refers to a form of sexual reproduction involving the union or fusion of two dissimilar gametes — anisogamous, anisogamic,...
(heterogamy
Heterogamy
Heterogamy has a number of biological definitions:*In reproductive biology, heterogamy is the alternation of differently organized generations, applied to the alternation between parthenogenetic and a sexual generation...
) in which the female gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
(e.g. egg cell
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
) is significantly larger than the male gamete and is non-motile. The male gametes are typically highly motile spermatozoa
Spermatozoon
A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote...
competing for the fertilization of the immotile egg.
By contrast to isogamy
Isogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of similar morphology , differing only in allele expression in one or more mating-type regions...
, the gametes are specialized. The ovum contains nearly all of the materials that will be needed by the zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
after fertilization, but it typically cannot move. The sperm contains almost nothing but the male genetic contribution to the zygote, but it is usually tasked with all of the travel necessary to bring the respective gametes together. The prevalence of oogamy in higher animals leads to the conclusion that this specialization of the gametes results in their performing their respective tasks better and more efficiently than those tasks could be performed by generalist isogametes, particularly the ability to concentrate high-energy substances in a smaller number of ova.
Oogamy predominantly occurs in animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s, but can also be found in many protist
Protist
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista, which includes mostly unicellular organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms, but this group is contested in modern taxonomy...
s, certain orders of algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
(Ochrophytes, Charophyceans
Charophyta
The Charophyta are a division of green algae, including the closest relatives of the embryophyte plants. In some groups, such as conjugating green algae, flagellate cells do not occur. The latter group does engage in sexual reproduction, and motility does not involve flagella, since they are...
), and some plants such as bryophyte
Bryophyte
Bryophyte is a traditional name used to refer to all embryophytes that do not have true vascular tissue and are therefore called 'non-vascular plants'. Some bryophytes do have specialized tissues for the transport of water; however since these do not contain lignin, they are not considered to be...
s, fern
Fern
A fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s, and some gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s like cycad
Cycad
Cycads are seed plants typically characterized by a stout and woody trunk with a crown of large, hard and stiff, evergreen leaves. They usually have pinnate leaves. The individual plants are either all male or all female . Cycads vary in size from having a trunk that is only a few centimeters...
s and ginkgo
Ginkgo
Ginkgo , also spelled gingko and known as the Maidenhair Tree, is a unique species of tree with no close living relatives...
.
In some algae, most gymnosperms and all angiosperms, a variation of oogamy occurs where the sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
cells are non-motile as well.
It appears that isogamy
Isogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of similar morphology , differing only in allele expression in one or more mating-type regions...
was the first stage of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
. In several lineages, this form of reproduction independently evolved to anisogamy
Anisogamy
Anisogamy refers to a form of sexual reproduction involving the union or fusion of two dissimilar gametes — anisogamous, anisogamic,...
with gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
s of male and female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
types to oogamy. There is a good argument that this pattern was driven by the physical constraints on the mechanisms by which two gametes get together as required for sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
.

