
Oldroyd-B model
Encyclopedia
The Oldroyd B model is a constitutive model used to describe the flow of viscoelastic fluids.
This model can be regarded as an extension of the Upper Convected Maxwell model and is equivalent to a fluid filled with elastic bead and spring dumbbells.
The model is named after its creator James G. Oldroyd
.
The model can be written as:
where:
The model can also be written split into polymeric (viscoelastic) part separately from the solvent part:
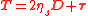 .
.
where
Whilst the model gives good approximations of viscoelastic fluids in shear flow, it has an unphysical singularity in extensional flow, where the dumbbells are infinitely stretched;
If the solvent viscosity is zero then the Oldroyd-B becomes the Upper Convected Maxwell model.
This model can be regarded as an extension of the Upper Convected Maxwell model and is equivalent to a fluid filled with elastic bead and spring dumbbells.
The model is named after its creator James G. Oldroyd
James G. Oldroyd
James Gardner Oldroyd was British mathematician and noted rheologist. He formulated the Oldroyd-B model to describe the viscoelastic behaviour of non-Newtonian fluids.-Life:...
.
The model can be written as:

where:
-
 is the stressStress (physics)In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
is the stressStress (physics)In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
tensorTensorTensors are geometric objects that describe linear relations between vectors, scalars, and other tensors. Elementary examples include the dot product, the cross product, and linear maps. Vectors and scalars themselves are also tensors. A tensor can be represented as a multi-dimensional array of...
; -
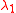 is the relaxation time;
is the relaxation time; -
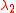 is the retardation time =
is the retardation time = 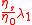 ;
; -
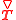 is the Upper convected time derivative of stress tensor:
is the Upper convected time derivative of stress tensor: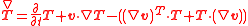
 is the fluid velocity
is the fluid velocity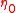 is the total viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
is the total viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
composed of solvent and polymer components,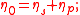 ;
; is the deformation rate tensor.
is the deformation rate tensor.
The model can also be written split into polymeric (viscoelastic) part separately from the solvent part:
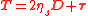 .
.where

Whilst the model gives good approximations of viscoelastic fluids in shear flow, it has an unphysical singularity in extensional flow, where the dumbbells are infinitely stretched;
If the solvent viscosity is zero then the Oldroyd-B becomes the Upper Convected Maxwell model.

