
Offer curve
Encyclopedia
In economics
and particularly in international trade, an offer curve shows the quantity of one type of product that an agent will export ("offer") for each quantity of another type of product that it imports. The offer curve was first derived by English
economists Edgeworth
and Marshall
to help explain international trade.
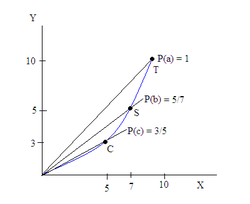
at point C. At point C, country K can produce (and consume) 3 Y for 5 X. As trade begins with another country, and country K begins to specialize
in producing good X. When it produces at point B, it can trade with the other country and consume at point S. We now look at our Offer curve and draw a ray
at the level 5 Y for 7 X. When full specialization occurs, K then produces at point A, trades and then consumes at point T. The price has reduced to 1 Y for 1 X, and the economy is now at equilibrium
An extremely useful link for understanding offer curves can be found at: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~alandear/glossary/figs/OfferCurve/oc.html#

Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and particularly in international trade, an offer curve shows the quantity of one type of product that an agent will export ("offer") for each quantity of another type of product that it imports. The offer curve was first derived by English
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
economists Edgeworth
Francis Ysidro Edgeworth
Francis Ysidro Edgeworth FBA was an Irish philosopher and political economist who made significant contributions to the methods of statistics during the 1880s...
and Marshall
Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall was an Englishman and one of the most influential economists of his time. His book, Principles of Economics , was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years...
to help explain international trade.
Offer Curve Described
The Offer Curve is derived from the country's PPF. We describe a Country named K which enjoys both goods Y and X. It is slightly better at producing good X, but wants to consume both goods. It wants to consume at point C or higher (above the PPF). Country K starts in AutarkyAutarky
Autarky is the quality of being self-sufficient. Usually the term is applied to political states or their economic policies. Autarky exists whenever an entity can survive or continue its activities without external assistance. Autarky is not necessarily economic. For example, a military autarky...
at point C. At point C, country K can produce (and consume) 3 Y for 5 X. As trade begins with another country, and country K begins to specialize
Heckscher-Ohlin model
The Heckscher–Ohlin model is a general equilibrium mathematical model of international trade, developed by Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin at the Stockholm School of Economics. It builds on David Ricardo's theory of comparative advantage by predicting patterns of commerce and production based...
in producing good X. When it produces at point B, it can trade with the other country and consume at point S. We now look at our Offer curve and draw a ray
Line (mathematics)
The notion of line or straight line was introduced by the ancient mathematicians to represent straight objects with negligible width and depth. Lines are an idealization of such objects...
at the level 5 Y for 7 X. When full specialization occurs, K then produces at point A, trades and then consumes at point T. The price has reduced to 1 Y for 1 X, and the economy is now at equilibrium
An extremely useful link for understanding offer curves can be found at: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~alandear/glossary/figs/OfferCurve/oc.html#



