
Numerary nexus
Encyclopedia
Musical tuning
In music, there are two common meanings for tuning:* Tuning practice, the act of tuning an instrument or voice.* Tuning systems, the various systems of pitches used to tune an instrument, and their theoretical bases.-Tuning practice:...
, a numerary nexus is an identity shared by two or more interval ratio
Interval ratio
In music, an interval ratio is a ratio of the frequencies of the pitches in a musical interval. For example, a just perfect fifth is 3:2 , 1.5, and may be approximated by an equal tempered perfect fifth which is 27/12, 1.498...
s in their numerator or denominator, with different identities in the other. For example, in the Otonality the denominator is always 1, thus 1 is the numerary nexus:
1 2 3 4 5
- - - - - etc.
1 1 1 1 1
3 5
(-) (-)
2 4
In the Utonality the numerator is always 1 and the numerary nexus is thus also 1:
1 1 1 1 1
- - - - - etc.
1 2 3 4 5
4 8
(-) (-)
3 5
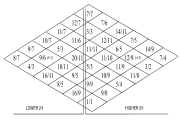
For example, in a tonality diamond
Tonality diamond
In music theory and tuning, a tonality diamond is a two-dimensional diagram of ratios in which one dimension is the Otonality and one the Utonality...
, such as Harry Partch
Harry Partch
Harry Partch was an American composer and instrument creator. He was one of the first twentieth-century composers to work extensively and systematically with microtonal scales, writing much of his music for custom-made instruments that he built himself, tuned in 11-limit just intonation.-Early...
's 11-limit diamond to the right, each ratio of a right slanting row shares a numerator and each ratio of a left slanting row shares an denominator. Each ratio of the upper left row has 7 as a denominator, while each ratio of the upper right row has 7 (or 14) as a numerator.

