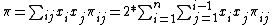Nucleotide diversity
Encyclopedia
Nucleotide diversity is a concept in molecular genetics
which is used to measure the degree of polymorphism
within a population.
One commonly used measure of nucleotide diversity was first introduced by Nei and Li in 1979. This measure is defined as the average number of nucleotide
differences per site between any two DNA
sequences chosen randomly from the sample population, and is denoted by π.
It is given by the formula:
where xi and xj are the respective frequencies of the ith and jth sequences, πij is the number of nucleotide differences per nucleotide site between the ith and jth sequences, and n is the number of sequences in the sample.
Nucleotide diversity is a measure of genetic variation
. It is usually associated with other statistical measures of population diversity, and is similar to expected heterozygosity. This statistic may be used to monitor diversity within or between ecological populations, to examine the genetic variation in crops and related species, or to determine evolutionary relationships.
Nucleotide diversity can be calculated by examining the DNA sequences directly, or may be estimated from molecular marker data, such as Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD
) data and Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP
) data.
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
which is used to measure the degree of polymorphism
Polymorphism (biology)
Polymorphism in biology occurs when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species — in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph...
within a population.
One commonly used measure of nucleotide diversity was first introduced by Nei and Li in 1979. This measure is defined as the average number of nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
differences per site between any two DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
sequences chosen randomly from the sample population, and is denoted by π.
It is given by the formula:
where xi and xj are the respective frequencies of the ith and jth sequences, πij is the number of nucleotide differences per nucleotide site between the ith and jth sequences, and n is the number of sequences in the sample.
Nucleotide diversity is a measure of genetic variation
Genetic variation
Genetic variation, variation in alleles of genes, occurs both within and among populations. Genetic variation is important because it provides the “raw material” for natural selection. Genetic variation is brought about by mutation, a change in a chemical structure of a gene. Polyploidy is an...
. It is usually associated with other statistical measures of population diversity, and is similar to expected heterozygosity. This statistic may be used to monitor diversity within or between ecological populations, to examine the genetic variation in crops and related species, or to determine evolutionary relationships.
Nucleotide diversity can be calculated by examining the DNA sequences directly, or may be estimated from molecular marker data, such as Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD
RAPD
RAPD stands for random amplification of polymorphic DNA. It is a type of PCR reaction, but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random. The scientist performing RAPD creates several arbitrary, short primers , then proceeds with the PCR using a large template of genomic DNA, hoping that...
) data and Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP
Aflp
AFLP may refer to:*amplified fragment length polymorphism, a highly sensitive tool used in molecular biology to detect DNA polymorphisms*acute fatty liver of pregnancy, a life-threatening liver condition that may occur during pregnancy...
) data.
Software
- DnaSP — DNA Sequence Polymorphism, is a software package for the analysis of nucleotide polymorphism from aligned DNA sequence data.
- MEGA, Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, is a software package used for estimating rates of molecular evolution, as well as generating phylogenetic trees, and aligning DNA sequences. Available for Windows, Linux and Mac OSX (since ver. 5.x).
- Arlequin3 software can be used for calculations of nucleotide diversity and a variety of other statistical tests for intra-population and inter-population analyses. Available for Windows.
- Variscan