
Northwestern Bulgarian dialects
Encyclopedia
Bulgarian language
Bulgarian is an Indo-European language, a member of the Slavic linguistic group.Bulgarian, along with the closely related Macedonian language, demonstrates several linguistic characteristics that set it apart from all other Slavic languages such as the elimination of case declension, the...
, which are located west of the yat
Yat
Yat or Jat is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet. Its name in Old Church Slavonic is jěd’ or iad’ . In the common scientific Latin transliteration for old Slavic languages, the letter is represented by e with caron: .The yat represented a Common Slavic long vowel...
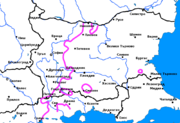
boundary and thus are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. The range of the dialects includes most of northwestern Bulgaria, to the west of the line between Nikopol
Nikopol, Bulgaria
Nikopol is a town in northern Bulgaria, the administrative center of Nikopol municipality, part of Pleven Province, on the right bank of the Danube river, 4 km downstream from the mouth of the Osam river. It spreads at the foot of steep chalk cliffs along the Danube and up a narrow valley...
, Pleven
Pleven
Pleven is the seventh most populous city in Bulgaria. Located in the northern part of the country, it is the administrative centre of Pleven Province, as well as of the subordinate Pleven municipality...
and Mezdra
Mezdra
Mezdra is a town in northwestern Bulgaria, part of Vratsa Province. It is located on the left bank of the Iskar River just north of its gorge through the Balkan Mountains....
and to the north of the line between Vratsa
Vratsa
Vratsa is a city in northwestern Bulgaria, at the foothills of the Balkan Mountains. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Vratsa Province. As of February 2011, the town has a population of 60,482 inhabitants....
and Belogradchik
Belogradchik
Belogradchik is a town in Vidin Province, Northwestern Bulgaria, the administrative centre of the homonymous Belogradchik Municipality. The town, whose name literally means "small white town," is situated in the foothills of the Balkan Mountains just east of the Serbian border and about 50 km...
. They bear strong resemblance to their neighbouring Eastern Bulgarian dialects and with some exceptions, mainly the pronunciation of yat
Yat
Yat or Jat is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet. Its name in Old Church Slavonic is jěd’ or iad’ . In the common scientific Latin transliteration for old Slavic languages, the letter is represented by e with caron: .The yat represented a Common Slavic long vowel...
, have the same phonological and morphological features as the neighbouring subdialects of the Eastern Bulgarian Central Balkan dialect
Central Balkan dialect
The Central Balkan dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes most of north-central Bulgaria , as well as the regions of Karlovo, Kazanlak and Plovdiv in southern Bulgaria, all the way down to the northernmost ridges of...
.
Phonological and morphological characteristics

- Old Church Slavonic (yat) is always pronounced as ɛ instead of formal Bulgarian я/е (ʲa~ɛ) – бел/бели
- Vocalic r and l for Old Church Slavonic ръ/рь and лъ/ль instead of the combinations ръ/ър (rə~ər) and лъ/ъл (lə~əl) in Standard Bulgarian - дрво, слза instead of дърво, сълза (tree, tear). However, there are words where the schwaSchwaIn linguistics, specifically phonetics and phonology, schwa can mean the following:*An unstressed and toneless neutral vowel sound in some languages, often but not necessarily a mid-central vowel...
(ə) is pronounced as in Standard Bulgarian - връх, слънце (summit, sun) - ending e instead of formal Bulgarian i for plural past active aorist participles (биле instead of били)
- The masculine definite article is (ə) (in a stressed syllable) and slightly reduced a (in an unstressed syllable) - гърбъ́, сто́ла (the back, the chair)
Most other phonological and morphological features of the Northwestern Bulgarian dialects are similar to the characteristics of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects and the formal language: щ~жд (ʃt~ʒd) for Proto-Slavic *tʲ~*dʲ and Old Church Slavonic щ~жд (ʃt~ʒd), ъ (ə) for both Old Church Slavonic (yus) and ъ (ə), vowel reduction, etc.

