
Non-configurational language
Encyclopedia
In generative grammar
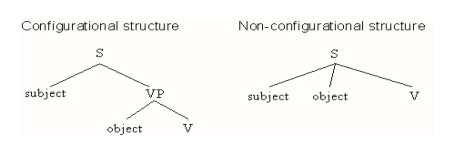
, non-configurational languages are languages in which there is no verb phrase
constituent (VP below). In configurational languages, the subject of a sentence is outside the VP (directly under S
below) and the object is inside; in non-configurational languages, since there is no VP constituent, there is no structural difference between subject and object.
More generally, it has been proposed that non-configurational languages have the following characteristics:
However, it is not clear that these properties all cluster together.
Languages that have been classified as non-configurational include Mohawk
, Warlpiri
, Nahuatl and O'odham
(Papago).
has attempted to show that they are in fact configurational. On the other hand, it has been argued in Lexical Functional Grammar
that these attempts are flawed, and that truly non-configurational languages exist. From the perspective of syntactic theory, the existence of non-configurational languages bears on the question of whether grammatical functions like subject
and object
are independent of structure. If they are not, no language can be truly non-configurational.
Generative grammar
In theoretical linguistics, generative grammar refers to a particular approach to the study of syntax. A generative grammar of a language attempts to give a set of rules that will correctly predict which combinations of words will form grammatical sentences...
, non-configurational languages are languages in which there is no verb phrase
Verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase or VP is a syntactic unit composed of at least one verb and the dependents of that verb. One can distinguish between two types of VPs, finite VPs and non-finite VPs . While phrase structure grammars acknowledge both, dependency grammars reject the existence of a...
constituent (VP below). In configurational languages, the subject of a sentence is outside the VP (directly under S
Sentence (linguistics)
In the field of linguistics, a sentence is an expression in natural language, and often defined to indicate a grammatical unit consisting of one or more words that generally bear minimal syntactic relation to the words that precede or follow it...
below) and the object is inside; in non-configurational languages, since there is no VP constituent, there is no structural difference between subject and object.

More generally, it has been proposed that non-configurational languages have the following characteristics:
- free (or more accurately, pragmatically determined) word orderWord orderIn linguistics, word order typology refers to the study of the order of the syntactic constituents of a language, and how different languages can employ different orders. Correlations between orders found in different syntactic subdomains are also of interest...
- null anaphoraAnaphora (linguistics)In linguistics, anaphora is an instance of an expression referring to another. Usually, an anaphoric expression is represented by a pro-form or some other kind of deictic--for instance, a pronoun referring to its antecedent...
- syntacticallySyntaxIn linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
discontinuous expressions
However, it is not clear that these properties all cluster together.
Languages that have been classified as non-configurational include Mohawk
Mohawk language
Mohawk is an Iroquoian language spoken by around 2,000 people of the Mohawk nation in the United States and Canada . Mohawk has the largest number of speakers of the Northern Iroquoian languages; today it is the only one with greater than a thousand remaining...
, Warlpiri
Warlpiri language
The Warlpiri language is spoken by about 3000 of the Warlpiri people in Australia's Northern Territory. It is one of the Ngarrkic languages of the large Southwest branch of the Pama–Nyungan family, and is one of the largest aboriginal languages in Australia in terms of number of speakers.-...
, Nahuatl and O'odham
O'odham language
O'odham is an Uto-Aztecan language of southern Arizona and northern Sonora where the Tohono O'odham and Pima reside. As of the year 2000, there were estimated to be approximately 9750 speakers in the United States and Mexico combined, although there may be more due to underreporting...
(Papago).
Controversy
The analysis of non-configurational languages has been very controversial in theoretical syntax. On the one hand, much recent work on these languages in Principles and ParametersPrinciples and parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general principles and specific parameters that for particular languages are either turned on or off...
has attempted to show that they are in fact configurational. On the other hand, it has been argued in Lexical Functional Grammar
Lexical functional grammar
Lexical functional grammar is a grammar framework in theoretical linguistics, a variety of generative grammar. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to...
that these attempts are flawed, and that truly non-configurational languages exist. From the perspective of syntactic theory, the existence of non-configurational languages bears on the question of whether grammatical functions like subject
Subject (grammar)
The subject is one of the two main constituents of a clause, according to a tradition that can be tracked back to Aristotle and that is associated with phrase structure grammars; the other constituent is the predicate. According to another tradition, i.e...
and object
Object (grammar)
An object in grammar is part of a sentence, and often part of the predicate. It denotes somebody or something involved in the subject's "performance" of the verb. Basically, it is what or whom the verb is acting upon...
are independent of structure. If they are not, no language can be truly non-configurational.
W-type
W-type languages have the following (Jelinek 1984):- predicate-AUX complex that constitutes a finite sentence
- optional, non-argumental NPsNoun phraseIn grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
- split case-marking (on clitics and NPs)
- independent pronounPronounIn linguistics and grammar, a pronoun is a pro-form that substitutes for a noun , such as, in English, the words it and he...
s used for contrastive emphasis - zero 3rd person marking
- adjoined clauses with two interpretations:
- temporal reading
- relative reading
External links
- Non-configurational language (Lexicon of Linguistics)
- Configurational language (Lexicon of Linguistics)
- Scrambling (Lexicon of Linguistics)
- Cartoon Theories of Linguistics: Non-Configurational Languages A simplification of the basic idea of non-configurational languages into a cartoon.

