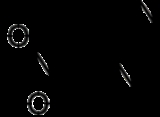
Nitroimidazole
Encyclopedia
4-Nitroimidazole is an imidazole
derivative
that contains a nitro group.
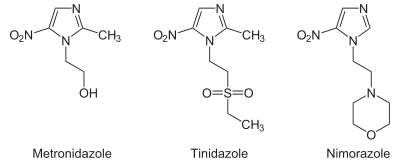
Several derivatives of nitroimidazole constitute the class of nitroimidazole antibiotics that have been used to combat anaerobic
bacterial and parasitic infection
s. Perhaps the most common example is metronidazole
(Flagyl). Other heterocycles such as nitrothiazoles (thiazole
) are also used for this purpose. Nitroheterocycles may be reductively
activated in hypoxic
cells, and then undergo redox
recycling or decompose
to toxic products.
Imidazole
Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents...
derivative
Analog (chemistry)
In chemistry, a structural analog , also known as chemical analog or simply analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another one, but differing from it in respect of a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced...
that contains a nitro group.
Several derivatives of nitroimidazole constitute the class of nitroimidazole antibiotics that have been used to combat anaerobic
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
bacterial and parasitic infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
s. Perhaps the most common example is metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
(Flagyl). Other heterocycles such as nitrothiazoles (thiazole
Thiazole
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen; the term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS...
) are also used for this purpose. Nitroheterocycles may be reductively
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
activated in hypoxic
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
cells, and then undergo redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
recycling or decompose
Chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction...
to toxic products.


