
New fuchsine
Encyclopedia
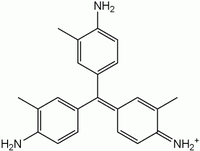
Dye
A dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and requires a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber....
having chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
22243. It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine
Fuchsine
Fuchsine or rosaniline hydrochloride is a magenta dye with chemical formula C20H19N3·HCl. There are other similar chemical formulations of products sold as fuchsine, and several dozen other synonyms of this molecule....
, and one of the two that are available as single dyes. (The other is pararosaniline
Pararosaniline
Pararosaniline, Basic Red 9, or C.I. 42500 is a magenta dye having chemical formula 19183. It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine. Pararosaniline, which is sold as a single dye, may make the best Schiff's reagent...
.) New fuchsine can be used for staining
Staining (biology)
Staining is an auxiliary technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in the microscopic image. Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology and medicine to highlight structures in biological tissues for viewing, often with the aid of different microscopes...
acid fast organism, e.g. by Ziehl-Neelsen stain
Ziehl-Neelsen stain
The Ziehl–Neelsen stain, also known as the acid-fast stain, was first described by two German doctors; Franz Ziehl , a bacteriologist and Friedrich Neelsen , a pathologist. It is a special bacteriological stain used to identify acid-fast organisms, mainly Mycobacteria...
, and for making Schiff's reagent. As a primary amine, the dye can be diazotized in the laboratory, and the resulting diazonium salt used as a trapping agent in enzyme histochemistry.

