
Natural experiment
Encyclopedia
A natural experiment is an observational study
in which the assignment of treatments
to subjects has been haphazard: That is, the assignment of treatments has been made "by nature", but not by experimenters. Thus, a natural experiment is not a controlled experiment. Natural experiments are most useful when there has been a clearly defined and large change in the treatment (or exposure) to a clearly defined subpopulation, so that changes in responses may be plausibly attributed to the change in treatments (or exposure).
Natural experiments are considered for study design
s whenever controlled experimentation is difficult, such as in many problems in epidemiology
and economics
.
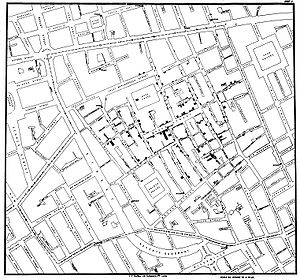
in London
, England.
On 31 August 1854, a major outbreak of cholera
struck Soho
. Over the next three days 127 people near Broad Street died. By the end of the outbreak 616 people died. The physician John Snow
identified the source of the outbreak as the nearest public water pump, which he identified using a map of deaths and illness.
In this example, Snow discovered a strong association between the use of the water and deaths and illnesses due to cholera. Snow found that the water company (the Southwark and Vauxhall Company) that supplied water to districts with high attack rates obtained the water from the Thames downstream from where raw sewage was discharged into the river. By contrast, districts that were supplied water by the Lambeth Company, which obtained water upstream from the points of sewage discharge, had low attack rates. Given the near-haphazard patchwork development of the water supply in mid-Nineteenth Century London, Snow viewed the developments as "an experiment...on the grandest scale." Of course, the exposure to the polluted water was not under the control of any scientist. Therefore, this exposure has been recognized as being a natural experiment.
during the six-month period from June 2002 to December 2002 when a smoking ban
was in effect in all public spaces in Helena including bars and restaurants. Helena is geographically isolated and served by only one hospital. It was observed that the rate of heart attacks
dropped by 60% while the smoking ban was in effect. Opponents of the law prevailed in getting the enforcement of the law suspended after six months, after which the rate of heart attacks went back up. Note, however, that while this may have been a good example of a natural experiment (called a case-crossover experiment, where the exposure is removed for a time period and then returned), it is also a good example of how confounding variables can result in faulty conclusions being made. For instance, many smoking ban-heart attack studies fail to indicate that heart attack rates were already on the decline before the smoking ban was in place, or fail to take into account seasonal fluxes in heart attacks (highest in the winter months and lowest in the summer). For the Helena study in particular, the claim that 40% of pre-ban heart attacks were caused by passive smoking is not believable, considering that only 10-15% of coronary heart disease cases are thought to be caused by active smoking.
Observational study
In epidemiology and statistics, an observational study draws inferences about the possible effect of a treatment on subjects, where the assignment of subjects into a treated group versus a control group is outside the control of the investigator...
in which the assignment of treatments
Design of experiments
In general usage, design of experiments or experimental design is the design of any information-gathering exercises where variation is present, whether under the full control of the experimenter or not. However, in statistics, these terms are usually used for controlled experiments...
to subjects has been haphazard: That is, the assignment of treatments has been made "by nature", but not by experimenters. Thus, a natural experiment is not a controlled experiment. Natural experiments are most useful when there has been a clearly defined and large change in the treatment (or exposure) to a clearly defined subpopulation, so that changes in responses may be plausibly attributed to the change in treatments (or exposure).
Natural experiments are considered for study design
Study design
Clinical study design is the formulation of trials and experiments in medical and epidemiological research, sometimes known as clinical trials. Many of the considerations here are shared under the more general topic of design of experiments but there can be others, in particular related to patient...
s whenever controlled experimentation is difficult, such as in many problems in epidemiology
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
and economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
.

History
One of the most famous early natural experiments was the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak
The Broad Street cholera outbreak was a severe outbreak of cholera that occurred near Broad Street in Soho district of London, England in 1854...
in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, England.
On 31 August 1854, a major outbreak of cholera
Cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine that is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. The main symptoms are profuse watery diarrhea and vomiting. Transmission occurs primarily by drinking or eating water or food that has been contaminated by the diarrhea of an infected person or the feces...
struck Soho
Soho
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster and part of the West End of London. Long established as an entertainment district, for much of the 20th century Soho had a reputation for sex shops as well as night life and film industry. Since the early 1980s, the area has undergone considerable...
. Over the next three days 127 people near Broad Street died. By the end of the outbreak 616 people died. The physician John Snow
John Snow
John Snow or Jon Snow may refer to:* Jon Snow, British newscaster* John Snow , founder of epidemiology and a major contributor to the development of anaesthesia* John W. Snow, 73rd United States Secretary of the Treasury...
identified the source of the outbreak as the nearest public water pump, which he identified using a map of deaths and illness.
In this example, Snow discovered a strong association between the use of the water and deaths and illnesses due to cholera. Snow found that the water company (the Southwark and Vauxhall Company) that supplied water to districts with high attack rates obtained the water from the Thames downstream from where raw sewage was discharged into the river. By contrast, districts that were supplied water by the Lambeth Company, which obtained water upstream from the points of sewage discharge, had low attack rates. Given the near-haphazard patchwork development of the water supply in mid-Nineteenth Century London, Snow viewed the developments as "an experiment...on the grandest scale." Of course, the exposure to the polluted water was not under the control of any scientist. Therefore, this exposure has been recognized as being a natural experiment.
Family size
An example of a natural experiment was discussed in Angrist and Evans (1998). The authors wish to estimate the effect of family size on the labor market outcomes of the mother. The correlations between family size and various outcomes do not tell us how family size causally affects labor market outcomes because both labor market outcomes and family size may be affected by unobserved variables such as preferences and because labor market outcomes may itself affect family size (called "reverse causality", for example, a woman may defer having a child if she gets a raise at work). The study notes that two-children families with either two boys or two girls are substantially more likely to have a third child than two-children families with one boy and one girl. The sex of the first two children, then, forms a natural experiment: it is as if an experimenter has randomly assigned some families to have two children and others to have three or more. The authors are then able to credibly estimate the causal effect of having a third child on labor market outcomes.Game shows
Within economics, game shows are a frequently studied form of natural experiment. While game shows might seem as artificial contexts, they can be considered as natural experiment due to the fact that the context arises without interference of the scientist. Game shows have been used to study a wide range of different types of economic behavior, such as decision making under risk and cooperative behavior.Smoking ban
An example of a natural experiment occurred in Helena, MontanaHelena, Montana
Helena is the capital city of the U.S. state of Montana and the county seat of Lewis and Clark County. The 2010 census put the population at 28,180. The local daily newspaper is the Independent Record. The Helena Brewers minor league baseball and Helena Bighorns minor league hockey team call the...
during the six-month period from June 2002 to December 2002 when a smoking ban
Smoking ban
Smoking bans are public policies, including criminal laws and occupational safety and health regulations, which prohibit tobacco smoking in workplaces and/or other public spaces...
was in effect in all public spaces in Helena including bars and restaurants. Helena is geographically isolated and served by only one hospital. It was observed that the rate of heart attacks
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
dropped by 60% while the smoking ban was in effect. Opponents of the law prevailed in getting the enforcement of the law suspended after six months, after which the rate of heart attacks went back up. Note, however, that while this may have been a good example of a natural experiment (called a case-crossover experiment, where the exposure is removed for a time period and then returned), it is also a good example of how confounding variables can result in faulty conclusions being made. For instance, many smoking ban-heart attack studies fail to indicate that heart attack rates were already on the decline before the smoking ban was in place, or fail to take into account seasonal fluxes in heart attacks (highest in the winter months and lowest in the summer). For the Helena study in particular, the claim that 40% of pre-ban heart attacks were caused by passive smoking is not believable, considering that only 10-15% of coronary heart disease cases are thought to be caused by active smoking.

