
Mysterium Cosmographicum
Encyclopedia
Mysterium Cosmographicum, (lit The Cosmographic Mystery, alternately translated Cosmic Mystery, The Secret of the World or some variation) is an astronomy book by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler
, published at Tübingen
in 1596 and in a second edition in 1621. The full title being Forerunner of the Cosmological Essays, Which Contains the Secret of the Universe; on the Marvelous Proportion of the Celestial Spheres, and on the True and Particular Causes of the Number, Magnitude, and Periodic Motions of the Heavens; Established by Means of the Five Regular Geometric Solids (Latin: Prodromus dissertationum cosmographicarum, continens mysterium cosmographicum, de admirabili proportione orbium coelestium, de que causis coelorum numeri, magnitudinis, motuumque periodicorum genuinis & proprijs, demonstratum, per quinque regularia corpora geometrica). Kepler proposed that the distance relationships between the six planets known at that time could be understood in terms of the five Platonic solids, enclosed within a sphere that represented the orbit of Saturn
.
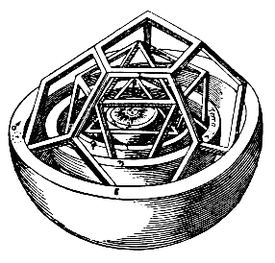
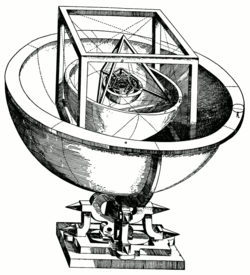 This book explains Kepler's cosmological theory, based on the Copernican system
This book explains Kepler's cosmological theory, based on the Copernican system
, in which the five Pythagorean
regular polyhedra
dictate the structure of the universe and reflect God's plan through geometry.
According to Kepler's account from this text, the ratio was brought to his attention accidentally while demonstrating the calculation of the ratio between a circle and a circle created by a rotated inscribed circle. From this he realized that he had stumbled on the same ratio between the orbits of Saturn and Jupiter. He wrote, “By a certain mere accident I chanced to come closer to the actual state of affairs. I thought it was by divine intervention that I gained fortuitously what I was never able to obtain by any amount of toil.” But after doing further calculations he realized he could not use the two-dimensional polygons to represent all the planets, but instead he had to use the five Platonic solids.
 The reverse side of the coin has a portrait of the contemporary scholar and astronomer, Johannes Kepler, who spent some time teaching in Graz and the surrounding areas. Kepler was acquainted with Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg
The reverse side of the coin has a portrait of the contemporary scholar and astronomer, Johannes Kepler, who spent some time teaching in Graz and the surrounding areas. Kepler was acquainted with Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg
personally, and most probably he knew and influenced the construction of Eggenberg Castle (the main motive of the coin). In front of him on the coin is a model of his master piece, the “Mysterium Cosmographicum”.
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican...
, published at Tübingen
Tübingen
Tübingen is a traditional university town in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, on a ridge between the Neckar and Ammer rivers.-Geography:...
in 1596 and in a second edition in 1621. The full title being Forerunner of the Cosmological Essays, Which Contains the Secret of the Universe; on the Marvelous Proportion of the Celestial Spheres, and on the True and Particular Causes of the Number, Magnitude, and Periodic Motions of the Heavens; Established by Means of the Five Regular Geometric Solids (Latin: Prodromus dissertationum cosmographicarum, continens mysterium cosmographicum, de admirabili proportione orbium coelestium, de que causis coelorum numeri, magnitudinis, motuumque periodicorum genuinis & proprijs, demonstratum, per quinque regularia corpora geometrica). Kepler proposed that the distance relationships between the six planets known at that time could be understood in terms of the five Platonic solids, enclosed within a sphere that represented the orbit of Saturn
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
.

Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism, or heliocentricism, is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around a stationary Sun at the center of the universe. The word comes from the Greek . Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center...
, in which the five Pythagorean
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him...
regular polyhedra
Polyhedron
In elementary geometry a polyhedron is a geometric solid in three dimensions with flat faces and straight edges...
dictate the structure of the universe and reflect God's plan through geometry.
According to Kepler's account from this text, the ratio was brought to his attention accidentally while demonstrating the calculation of the ratio between a circle and a circle created by a rotated inscribed circle. From this he realized that he had stumbled on the same ratio between the orbits of Saturn and Jupiter. He wrote, “By a certain mere accident I chanced to come closer to the actual state of affairs. I thought it was by divine intervention that I gained fortuitously what I was never able to obtain by any amount of toil.” But after doing further calculations he realized he could not use the two-dimensional polygons to represent all the planets, but instead he had to use the five Platonic solids.

In popular culture
The Mysterium Cosmographicum was featured on the Austrian 10 euro Johannes Kepler silver commemorative coin minted in 2002.
Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg
Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg was an Austrian statesman, a son of Seyfried von Eggenberg and great-grandson of Balthasar Eggenberger of the House of Eggenberg.- Biography :...
personally, and most probably he knew and influenced the construction of Eggenberg Castle (the main motive of the coin). In front of him on the coin is a model of his master piece, the “Mysterium Cosmographicum”.
External links
- http://www.uff.br/cdme/kepler/kepler-html/kepler-en.html Mysterium Cosmographicum Interactive 3D JAVA Model

