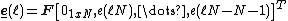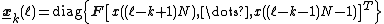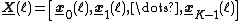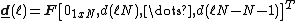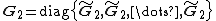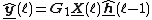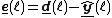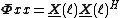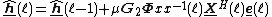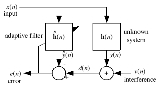
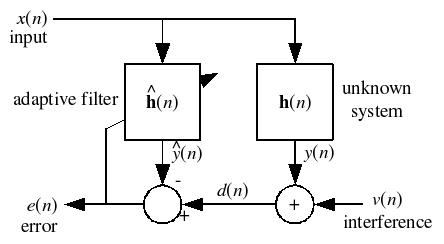
Multidelay block frequency domain adaptive filter
Encyclopedia
The Multidelay block frequency domain adaptive filter (MDF) algorithm is a block-based frequency domain implementation of the (normalised) Least mean squares filter (LMS)
algorithm.
). However, the algorithm differs from the Fast LMS algorithm in that block size it uses may be smaller than the filter length. If both are equal, then MDF reduces to the FLMS algorithm.
The advantages of MDF over the (N)LMS algorithm are:
Let be the length of the processing blocks,
be the length of the processing blocks, 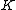 be the number of blocks and
be the number of blocks and 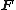 denote the 2Nx2N Fourier transform matrix. The variables are defined as:
denote the 2Nx2N Fourier transform matrix. The variables are defined as:
With normalisation matrices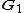 and
and 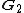 :
:
Least mean squares filter
Least mean squares algorithms are a class of adaptive filter used to mimic a desired filter by finding the filter coefficients that relate to producing the least mean squares of the error signal . It is a stochastic gradient descent method in that the filter is only adapted based on the error at...
algorithm.
Introduction
The MDF algorithm is based on the fact that convolutions may be efficiently computed in the frequency domain (thanks to the Fast Fourier TransformFast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform is an efficient algorithm to compute the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. "The FFT has been called the most important numerical algorithm of our lifetime ." There are many distinct FFT algorithms involving a wide range of mathematics, from simple...
). However, the algorithm differs from the Fast LMS algorithm in that block size it uses may be smaller than the filter length. If both are equal, then MDF reduces to the FLMS algorithm.
The advantages of MDF over the (N)LMS algorithm are:
- Lower algorithmic complexity
- Partial de-correlation of the input (which 'may' lead to faster convergence)
Variable definitions

Let
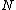 be the length of the processing blocks,
be the length of the processing blocks, 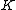 be the number of blocks and
be the number of blocks and 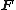 denote the 2Nx2N Fourier transform matrix. The variables are defined as:
denote the 2Nx2N Fourier transform matrix. The variables are defined as:With normalisation matrices
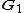 and
and 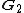 :
:-
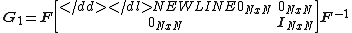
-
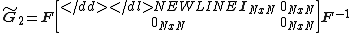
In practice, when multiplying a column vector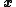 by
by 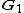 , we take the inverse FFT of
, we take the inverse FFT of 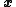 , set the first
, set the first 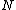 values in the result to zero and then take the FFT. This is meant to remove the effects of the circular convolution.
values in the result to zero and then take the FFT. This is meant to remove the effects of the circular convolution.
Algorithm description
For each block, the MDF algorithm is computed as:
It is worth noting that, while the algorithm is more easily expressed in matrix form, the actual implementation requires no matrix multiplications. For instance the normalisation matrix computation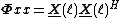 reduces to an element-wise vector multiplication because
reduces to an element-wise vector multiplication because 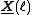 is block-diagonal. The same goes for other multiplications.
is block-diagonal. The same goes for other multiplications.
See also
- Adaptive filterAdaptive filterAn adaptive filter is a filter that self-adjusts its transfer function according to an optimization algorithm driven by an error signal. Because of the complexity of the optimization algorithms, most adaptive filters are digital filters. By way of contrast, a non-adaptive filter has a static...
- Recursive least squares
- For statistical techniques relevant to LMS filter see Least squaresLeast squaresThe method of least squares is a standard approach to the approximate solution of overdetermined systems, i.e., sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns. "Least squares" means that the overall solution minimizes the sum of the squares of the errors made in solving every...
.
-
-