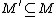Multi-track Turing machine
Encyclopedia
A Multitrack Turing machine
is a specific type of Multi-tape Turing machine. In a standard n-tape Turing machine, n heads move independently along n tracks. In a n-track Turing machine, one head reads and writes on all tracks simultaneously. A tape position in a n-track Turing Machine contains n symbols from the tape alphabet. It is equivalent to the standard Turing machine and therefore accepts precisely the recursively enumerable languages.
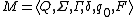 , where
, where
where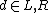
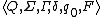 be standard Turing machine that accepts L. Let M' is a two-track Turing machine. To prove M=M' it must be shown that M
be standard Turing machine that accepts L. Let M' is a two-track Turing machine. To prove M=M' it must be shown that M 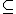 M' and M'
M' and M' 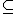 M.
M.
If all but the first track is ignored than M and M' are clearly equivalent.
The tape alphabet of a one-track Turing machine equivalent to a two-track Turing machine consists of an ordered pair. The input symbol a of a Turing machine M' can be identified as an ordered pair [x,y] of Turing machine M. The one-track Turing machine is:
M=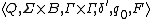 with the transition function
with the transition function 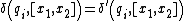
This machine also accepts L.
Turing machine
A Turing machine is a theoretical device that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite its simplicity, a Turing machine can be adapted to simulate the logic of any computer algorithm, and is particularly useful in explaining the functions of a CPU inside a...
is a specific type of Multi-tape Turing machine. In a standard n-tape Turing machine, n heads move independently along n tracks. In a n-track Turing machine, one head reads and writes on all tracks simultaneously. A tape position in a n-track Turing Machine contains n symbols from the tape alphabet. It is equivalent to the standard Turing machine and therefore accepts precisely the recursively enumerable languages.
Formal definition
A multitape Turing machine can be formally defined as a 6-tuple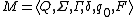 , where
, where-
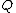 is a finite set of states
is a finite set of states -
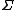 is a finite set of symbols called the tape alphabet
is a finite set of symbols called the tape alphabet 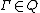
-
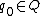 is the initial state
is the initial state -
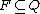 is the set of final or accepting states.
is the set of final or accepting states. 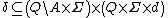 is a relation on states and symbols called the transition relation.
is a relation on states and symbols called the transition relation.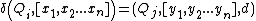
where
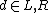
Proof of equivalency to standard Turing machine
This will prove that a two-track Turing machine is equivalent to a standard Turing machine. This can be generalized to a n-track Turing machine. Let L be a recursively enumerable language. Let M=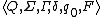 be standard Turing machine that accepts L. Let M' is a two-track Turing machine. To prove M=M' it must be shown that M
be standard Turing machine that accepts L. Let M' is a two-track Turing machine. To prove M=M' it must be shown that M 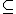 M' and M'
M' and M' 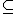 M.
M.If all but the first track is ignored than M and M' are clearly equivalent.
The tape alphabet of a one-track Turing machine equivalent to a two-track Turing machine consists of an ordered pair. The input symbol a of a Turing machine M' can be identified as an ordered pair [x,y] of Turing machine M. The one-track Turing machine is:
M=
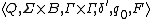 with the transition function
with the transition function 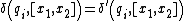
This machine also accepts L.