
MorphOS
Encyclopedia
MorphOS is an Amiga
-compatible computer operating system
. It is a mixed proprietary
and open source
OS produced for the Pegasos
PowerPC
processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale development boards that use the Genesi
firmware, including the EFIKA
and mobileGT
. Since MorphOS 2.4 Apple, Inc. Mac Mini
G4 is supported as well, with the release of MorphOS 2.5 and MorphOS 2.6 the eMac and PowerMac G4 models are respectively supported. The core, based on the Quark
microkernel
, is proprietary, although several libraries and other parts are open source, such as Ambient
desktop
.
s from Freescale and IBM
while supporting the original AmigaOS
MC680x0
applications via proprietary task-based emulation, and most AmigaOS/PPC applications via API wrappers. It is API
compatible with AmigaOS 3.1 and has a GUI
based on MUI
.
Besides the Pegasos version of MorphOS, there is a version for Amiga computers equipped with PowerUP
accelerator cards produced by Phase5
. This version is free, although it does slow down after each two hour session if it has not been registered. Registration is free. PowerUP MorphOS was most recently updated on 23 February 2006; however, it does not exceed the feature set or advancement of the Pegasos release.
A version of MorphOS for the EFIKA
, a very small mainboard based on the ultra-low wattage MPC5200B processor from Freescale, has been shown at exhibitions and user-gatherings in Germany
. Current (since 2.0) release of MorphOS supports the EFIKA.
formats of Amiga PPC executables. ABox is based in part on AROS Research Operating System
. ABox includes Trance JIT
code translator for 68k
native Amiga applications.
 The project started in 1999, based on the Quark
The project started in 1999, based on the Quark
microkernel
. The earliest versions of MorphOS ran only via PPC accelerator cards on the Amiga computers, and required portions of AmigaOS
to fully function. A collaborative effort between the companies bPlan (of which the lead MorphOS developer is a partner) and Thendic-France in 2002 resulted in the first regular, non-prototype production of bPlan-engineered Pegasos computers capable of running MorphOS or Linux. A busy promotional year followed in 2003, with appearances at conventions and exhibitions in several places around the world, including CES
in Las Vegas. Thendic-France had financial problems and folded; however, the collaboration continued under the new banner of "Genesi
".
After some bitter disagreements within the MorphOS development team in 2003 and 2004 culminating with accusations by a MorphOS developer that he and others had not been paid, the Ambient desktop
interface was released under GPL and is now actively developed by the Ambient development team. Subject to GPL rules, Ambient continues to be included in the commercial MorphOS product. An alternative MorphOS desktop system is Scalos.
On April 1, 2008 the MorphOS team announced that MorphOS 2.0 would be released within Q2/2008. This promise was only kept by a few seconds, with the release of MorphOS 2.0 occurring on June 30, 2008 23:59 CET. MorphOS 2 is commercially available at a price of 150 EUR per machine (111,11 EUR as a special promotion within the first two weeks of its release). A fully functional demo of MorphOS is available, but without a keyfile, its speed is decreased significantly after 30 minutes of use.
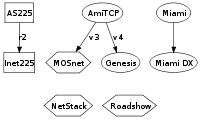
MorphOS 2.x includes a native TCP/IP stack ("Netstack") and two web browsers, Sputnik
and Origyn Web Browser
. Sputnik was begun under a user community bounty system that also resulted in MOSNet, a free, separate TCP/IP stack for MorphOS 1 users. Sputnik is a port of the KHTML rendering engine, which WebKit
is also based on.
Version 2.0
MorphOS 2.0 was released on June 30, 2008. The new version included (along other improvements) the previously missing native TCP/IP stack, an updated Sputnik release, AltiVec support, alpha compositing 3D layers
for the graphical user interface, new USB components (including USB 2.0 support), new screenblankers, and Reggae, a new, modular, streaming multimedia framework. MorphOS 2.0 also included support for the EFIKA, Pegasos I and Pegasos II machines.
Version 2.1
On September 5, 2008 MorphOS 2.1 was released, fixing numerous bugs and adding support for the EFIKA's audio.
Version 2.2
On December 20, 2008 MorphOS 2.2 was released, fixing numerous bugs, adding a TrueCrypt-compatible disk encryption suite and several small items.
Version 2.3
On August 6, 2009 MorphOS 2.3 was released, fixing numerous bugs, adding Origyn Web Browser as the default browser, read only HFS+ filesystem support and several small items.
Version 2.4
On October 12, 2009 MorphOS 2.4 was released, adding support for Mac Mini G4 platform, as well as fixing various bugs and adding new features. Write support for Mac HFS disks were added and new charsets.library was included to provide better multilingual application support.
Version 2.5
On June 4th, 2010 MorphOS 2.5 was released, adding support for eMac G4 platforms and drivers for SiI3x1x based 2-port Serial ATA
PCI cards.
Version 2.6
On October 10th, 2010 MorphOS 2.6 was released, adding support for Power Mac G4 platforms and 2D drivers for Rage 128 Pro graphics cards., Released at precisely 10.10.10 10:10
Version 2.7
On December 2nd, 2010 MorphOS 2.7 was released, improving support for Power Mac G4 platforms and fixing various bugs.
Amiga
The Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
-compatible computer operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
. It is a mixed proprietary
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
and open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
OS produced for the Pegasos
Pegasos
Pegasos is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC 7447 microprocessor, featuring three PCI slots, one AGP slot, two Ethernet ports , USB, DDR, AC'97 sound, and FireWire...
PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
processor based computer, PowerUP accelerator equipped Amiga computers, and a series of Freescale development boards that use the Genesi
Genesi
Genesi is computer company focused on building Power Architecture and ARM architecture computers. The organization is split into two units, Genesi USA, Inc. working out of Texas operating as the primary front-end for sales, customers and developers, and bplan GmbH based in Germany as the primary...
firmware, including the EFIKA
EFIKA
Efika are a line of mobile computing Power Architecture and ARM architecture based computers manufactured by Genesi.In Esperanto efika means "efficacious, effective, or efficient".-Efika 5200B:...
and mobileGT
MobileGT
The mobileGT name refers to both a computing platform and an alliance of vendors in the navigation, infotainment and telematics industries. It focuses on automotive, industrial and consumer electronics based on Power Architecture technology...
. Since MorphOS 2.4 Apple, Inc. Mac Mini
Mac Mini
The Mac Mini is a small form factor desktop computer manufactured by Apple Inc. Like earlier mini-ITX PC designs, it is uncommonly small for a desktop computer: 7.7 inches square and 1.4 inches tall. It weighs 2.7 pounds...
G4 is supported as well, with the release of MorphOS 2.5 and MorphOS 2.6 the eMac and PowerMac G4 models are respectively supported. The core, based on the Quark
Quark (kernel)
In computing, Quark is an operating system kernel used in MorphOS. It is a microkernel designed to run totally virtualized computers, called "boxes"...
microkernel
Microkernel
In computer science, a microkernel is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system . These mechanisms include low-level address space management, thread management, and inter-process communication...
, is proprietary, although several libraries and other parts are open source, such as Ambient
Ambient desktop
Ambient is a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS. Its development was started in 2001 by David Gerber. Its main goals were that it should be simple and fast...
desktop
Desktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
.
Characteristics and versions
Developed for PowerPC processorCentral processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s from Freescale and IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
while supporting the original AmigaOS
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is the default native operating system of the Amiga personal computer. It was developed first by Commodore International, and initially introduced in 1985 with the Amiga 1000...
MC680x0
68k
The Motorola 680x0/m68000/68000 is a family of 32-bit CISC microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and were the primary competitors of Intel's x86 microprocessors...
applications via proprietary task-based emulation, and most AmigaOS/PPC applications via API wrappers. It is API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
compatible with AmigaOS 3.1 and has a GUI
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
based on MUI
Magic User Interface
The Magic User Interface is an object-oriented system by Stefan Stuntz to generate and maintain graphical user interfaces. With the aid of a preferences program, the user of an application has the ability to customize the outfit according to personal taste....
.
Besides the Pegasos version of MorphOS, there is a version for Amiga computers equipped with PowerUP
PowerUP (accelerator)
PowerUP boards were dual-processor 68k–PowerPC accelerator boards designed by Phase5 Digital Products for Amiga computers. They had two different processors working in parallel, sharing the complete address space of the Amiga computer system.-History:...
accelerator cards produced by Phase5
Phase5
Phase5 Digital Products was a computer hardware manufacturer that made boards for the Amiga computer. Their best known products were accelerator boards which replaced the CPU with a faster model...
. This version is free, although it does slow down after each two hour session if it has not been registered. Registration is free. PowerUP MorphOS was most recently updated on 23 February 2006; however, it does not exceed the feature set or advancement of the Pegasos release.
A version of MorphOS for the EFIKA
EFIKA
Efika are a line of mobile computing Power Architecture and ARM architecture based computers manufactured by Genesi.In Esperanto efika means "efficacious, effective, or efficient".-Efika 5200B:...
, a very small mainboard based on the ultra-low wattage MPC5200B processor from Freescale, has been shown at exhibitions and user-gatherings in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. Current (since 2.0) release of MorphOS supports the EFIKA.
ABox
ABox is an emulation sandbox featuring a PPC native AmigaOS API clone that is binary compatible with both 68k Amiga applications and both PowerUP and WarpOSWarpOS
WarpOS was a multi-tasking kernel for the PowerPC architecture developed by Haage & Partner for the Amiga computer platform in the late 1990s and early 2000s. It ran on PowerUP accelerator boards developed by phase5 which contained both a Motorola 68000 family CPU and a PowerPC CPU with shared...
formats of Amiga PPC executables. ABox is based in part on AROS Research Operating System
AROS Research Operating System
AROS Research Operating System is a free and open source multi media centric implementation of the AmigaOS 3.1 APIs. Designed to be portable and flexible, ports are currently available for x86-based and PowerPC-based PCs in native and hosted flavors, with other architectures in development...
. ABox includes Trance JIT
Trance JIT
Trance JIT is a MorphOS JIT compiler, or code translator, for running 68k applications within the MorphOS environment. It has been part of the MorphOS operating system since MorphOS 1.4....
code translator for 68k
68k
The Motorola 680x0/m68000/68000 is a family of 32-bit CISC microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and were the primary competitors of Intel's x86 microprocessors...
native Amiga applications.
Other
- AHIAHI (Amiga)AHI is a retargetable audio subsystem for AmigaOS, MorphOS and AROS. It was created by Martin Blom in the mid 1990s to allow standardized operating system support for audio hardware other than just the native Amiga sound chip, for example, 16-bit sound cards.AHI offers improved functionality not...
— audio interface: 6.7 - Ambient desktopAmbient desktopAmbient is a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS. Its development was started in 2001 by David Gerber. Its main goals were that it should be simple and fast...
— the default MorphOS desktop, inspired by Workbench and Directory OpusDirectory OpusDirectory Opus is a popular file manager program, originally written for the Amiga computer system in the early to mid 1990s...
1.43 - CyberGraphXCyberGraphXCyberGraphX , is the standard ReTargetable Graphics API available for the Amiga and compatible systems. It was developed by Thomas Sontowski and Frank Mariak and later adopted by Phase5 for use with their graphics cards...
— graphics interface originally developed for Amiga computers: 5.1 - Magic User InterfaceMagic User InterfaceThe Magic User Interface is an object-oriented system by Stefan Stuntz to generate and maintain graphical user interfaces. With the aid of a preferences program, the user of an application has the ability to customize the outfit according to personal taste....
—primary GUIGraphical user interfaceIn computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
toolkit: 4.0 - Poseidon (USB stack)— the Amiga USB stack developed by Chris Hodges
- TurboPrintTurboPrintTurboPrint is a closed source printer driver system for Linux, AmigaOS and MorphOS. It supports a number of printers that don't yet have a free driver, and fuller printer functionality on some printer models. It integrates with the CUPS printing system....
— the printing system - TinyGL—OpenGLOpenGLOpenGL is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The interface consists of over 250 different function calls which can be used to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL...
implementation and Warp3DWarp3DWarp3D was a project run by Haage & Partner in 1998, that aimed to provide a standard API which would enable programmers to access, and therefore use, 3D hardware on the Amiga....
compatibility is featured via RAVE low-level API: V 51 - QuarkQuark (kernel)In computing, Quark is an operating system kernel used in MorphOS. It is a microkernel designed to run totally virtualized computers, called "boxes"...
—manages the low level systems
Amiga
- Amiga 1200Amiga 1200The Amiga 1200, or A1200 , was Commodore International's third-generation Amiga computer, aimed at the home market...
with Blizzard PPC accelerator card - Amiga 3000Amiga 3000The Commodore Amiga 3000, or A3000, was the third major release in the Amiga computer family. Released in June 1990, it features improved processing speed, improved rendering of graphics, and a new revision of the operating system...
with CyberStorm PPC accelerator card - Amiga 4000Amiga 4000The Commodore Amiga 4000, or A4000, is the successor of the A2000 and A3000 computers. There are two models, the A4000/040 released in October 1992 with a Motorola 68040 CPU, and the A4000/030 released in April 1993 with a Motorola 68EC030....
with CyberStormPPC accelerator card
History

Quark (kernel)
In computing, Quark is an operating system kernel used in MorphOS. It is a microkernel designed to run totally virtualized computers, called "boxes"...
microkernel
Microkernel
In computer science, a microkernel is the near-minimum amount of software that can provide the mechanisms needed to implement an operating system . These mechanisms include low-level address space management, thread management, and inter-process communication...
. The earliest versions of MorphOS ran only via PPC accelerator cards on the Amiga computers, and required portions of AmigaOS
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is the default native operating system of the Amiga personal computer. It was developed first by Commodore International, and initially introduced in 1985 with the Amiga 1000...
to fully function. A collaborative effort between the companies bPlan (of which the lead MorphOS developer is a partner) and Thendic-France in 2002 resulted in the first regular, non-prototype production of bPlan-engineered Pegasos computers capable of running MorphOS or Linux. A busy promotional year followed in 2003, with appearances at conventions and exhibitions in several places around the world, including CES
Consumer Electronics Show
The International Consumer Electronics Show is a major technology-related trade show held each January in the Las Vegas Convention Center, Las Vegas, Nevada, United States. Not open to the public, the Consumer Electronics Association-sponsored show typically hosts previews of products and new...
in Las Vegas. Thendic-France had financial problems and folded; however, the collaboration continued under the new banner of "Genesi
Genesi
Genesi is computer company focused on building Power Architecture and ARM architecture computers. The organization is split into two units, Genesi USA, Inc. working out of Texas operating as the primary front-end for sales, customers and developers, and bplan GmbH based in Germany as the primary...
".
After some bitter disagreements within the MorphOS development team in 2003 and 2004 culminating with accusations by a MorphOS developer that he and others had not been paid, the Ambient desktop
Ambient desktop
Ambient is a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS. Its development was started in 2001 by David Gerber. Its main goals were that it should be simple and fast...
interface was released under GPL and is now actively developed by the Ambient development team. Subject to GPL rules, Ambient continues to be included in the commercial MorphOS product. An alternative MorphOS desktop system is Scalos.
On April 1, 2008 the MorphOS team announced that MorphOS 2.0 would be released within Q2/2008. This promise was only kept by a few seconds, with the release of MorphOS 2.0 occurring on June 30, 2008 23:59 CET. MorphOS 2 is commercially available at a price of 150 EUR per machine (111,11 EUR as a special promotion within the first two weeks of its release). A fully functional demo of MorphOS is available, but without a keyfile, its speed is decreased significantly after 30 minutes of use.
Release history of 2.x series
| Version | Release Date | Information | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0 | June 30, 2008 | MorphOS 2.0 release notes | Added support for Efika 5200B platform |
| 2.1 | September 6, 2008 | MorphOS 2.1 release notes | |
| 2.2 | December 20, 2008 | MorphOS 2.2 release notes | |
| 2.3 | August 6, 2009 | MorphOS 2.3 release notes | |
| 2.4 | October 12, 2009 | MorphOS 2.4 release notes | Added support for Mac mini G4 |
| 2.5 | June 4, 2010 | MorphOS 2.5 release notes | Added support for eMac G4 |
| 2.6 | October 10, 2010 | MorphOS 2.6 release notes | Added support for Power Mac G4 |
| 2.7 | December 2, 2010 | MorphOS 2.7 release notes |
MorphOS 2.x includes a native TCP/IP stack ("Netstack") and two web browsers, Sputnik
Sputnik (web browser)
Sputnik is a web-browser for MorphOS developed by Marcin Kwiatkowski. It is a port of the KHTML browser, which is based on S60 WebCore. Sputnik was first released to the general public on November 11, 2006. The second public release occurred on March 10, 2007....
and Origyn Web Browser
Origyn Web Browser
Origyn Web Browser is a web browser that is synchronized with WebKit and sponsored by web enabler Pleyo. OWB provides a meta-port to an abstract platform with the aim of making porting to embedded or lightweight systems quicker and easier...
. Sputnik was begun under a user community bounty system that also resulted in MOSNet, a free, separate TCP/IP stack for MorphOS 1 users. Sputnik is a port of the KHTML rendering engine, which WebKit
WebKit
WebKit is a layout engine designed to allow web browsers to render web pages. WebKit powers Google Chrome and Apple Safari and by October 2011 held over 33% of the browser market share between them. It is also used as the basis for the experimental browser included with the Amazon Kindle ebook...
is also based on.

Version 2.0
MorphOS 2.0 was released on June 30, 2008. The new version included (along other improvements) the previously missing native TCP/IP stack, an updated Sputnik release, AltiVec support, alpha compositing 3D layers
Compositing window manager
A compositing window manager is a type of window manager. A window manager is software that draws a graphical user interface on a computer display – it positions windows, draws additional elements on windows , and controls how windows interact with each other, and with the rest of the desktop...
for the graphical user interface, new USB components (including USB 2.0 support), new screenblankers, and Reggae, a new, modular, streaming multimedia framework. MorphOS 2.0 also included support for the EFIKA, Pegasos I and Pegasos II machines.
Version 2.1
On September 5, 2008 MorphOS 2.1 was released, fixing numerous bugs and adding support for the EFIKA's audio.
Version 2.2
On December 20, 2008 MorphOS 2.2 was released, fixing numerous bugs, adding a TrueCrypt-compatible disk encryption suite and several small items.
Version 2.3
On August 6, 2009 MorphOS 2.3 was released, fixing numerous bugs, adding Origyn Web Browser as the default browser, read only HFS+ filesystem support and several small items.
Version 2.4
On October 12, 2009 MorphOS 2.4 was released, adding support for Mac Mini G4 platform, as well as fixing various bugs and adding new features. Write support for Mac HFS disks were added and new charsets.library was included to provide better multilingual application support.
Version 2.5
On June 4th, 2010 MorphOS 2.5 was released, adding support for eMac G4 platforms and drivers for SiI3x1x based 2-port Serial ATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
PCI cards.
Version 2.6
On October 10th, 2010 MorphOS 2.6 was released, adding support for Power Mac G4 platforms and 2D drivers for Rage 128 Pro graphics cards., Released at precisely 10.10.10 10:10
Version 2.7
On December 2nd, 2010 MorphOS 2.7 was released, improving support for Power Mac G4 platforms and fixing various bugs.
See also
- Ambient desktopAmbient desktopAmbient is a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS. Its development was started in 2001 by David Gerber. Its main goals were that it should be simple and fast...
- AmigaOS 4AmigaOS 4AmigaOS 4, , is a line of Amiga operating systems which runs on PowerPC microprocessors. It is mainly based on AmigaOS 3.1 source code, and partially on version 3.9 developed by Haage & Partner...
- APUS ComputerAPUS ComputerAPUS stands for "Amiga Power Up System", and describes a computer comprising an Amiga computer with a Phase5 PowerUP PowerPC accelerator board....
- AROSAROS Research Operating SystemAROS Research Operating System is a free and open source multi media centric implementation of the AmigaOS 3.1 APIs. Designed to be portable and flexible, ports are currently available for x86-based and PowerPC-based PCs in native and hosted flavors, with other architectures in development...
- MUIMagic User InterfaceThe Magic User Interface is an object-oriented system by Stefan Stuntz to generate and maintain graphical user interfaces. With the aid of a preferences program, the user of an application has the ability to customize the outfit according to personal taste....

