
Moisture advection
Encyclopedia
Moisture advection is the horizontal transport of water vapor
by the wind
. Measurement and knowledge of atmospheric water vapor, or "moisture", is crucial in the prediction of all weather
elements, especially cloud
s, fog
, temperature
, humidity
thermal comfort indices and precipitation
.
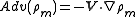
in which V is the horizontal wind vector, and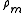 is the density of water vapor. However, water vapor content is usually measured in terms of mixing ratio
is the density of water vapor. However, water vapor content is usually measured in terms of mixing ratio
(mass fraction) in reanalyses
or dew point
(temperature to partial vapor pressure saturation
, i.e. relative humidity
to 100%) in operational forecasting
. The advection of dew point itself can be thought as moisture advection:
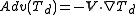
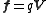
in which q is the mixing ratio. The value can integrated throughout the atmosphere to total transport of moisture through the vertical:
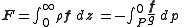
which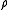 is the density of air, P is pressure at the ground surface. For the far right definition, we have used Hydrostatic equilibrium
is the density of air, P is pressure at the ground surface. For the far right definition, we have used Hydrostatic equilibrium
approximation.
and its divergence (convergence) imply net evapotranspiration
(precipitation
) is adding (removing) moisture from the column:
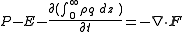
which P, E, and the integral term are precipitation, evapotranspiration, and time rate of change of Precipitable water; all represented in terms of mass per unit area (one can convert to more typical units in length such as mm by multiplying the density of liquid water and the correct length unit conversion factor).
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
by the wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
. Measurement and knowledge of atmospheric water vapor, or "moisture", is crucial in the prediction of all weather
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
elements, especially cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
s, fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
thermal comfort indices and precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
.
Definition
Using the classical definition of advection, moisture advection is defined as: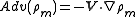
in which V is the horizontal wind vector, and
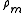 is the density of water vapor. However, water vapor content is usually measured in terms of mixing ratio
is the density of water vapor. However, water vapor content is usually measured in terms of mixing ratioMixing ratio
In chemistry and physics, the dimensionless mixing ratio is defined as the abundance of one component of a mixture relative to that of all other components...
(mass fraction) in reanalyses
Meteorological reanalysis
A meteorological reanalysis is a meteorological data assimilation project which aims to assimilate historical observational data spanning an extended period, using a single consistent assimilation scheme throughout....
or dew point
Dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which a given parcel of humid air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to condense into liquid water. The condensed water is called dew when it forms on a solid surface. The dew point is a saturation temperature.The dew point is...
(temperature to partial vapor pressure saturation
Saturation (chemistry)
In chemistry, saturation has six different meanings, all based on reaching a maximum capacity...
, i.e. relative humidity
Relative humidity
Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture, given as a percentage of the saturated vapor pressure under those conditions...
to 100%) in operational forecasting
Weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
. The advection of dew point itself can be thought as moisture advection:
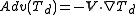
Moisture Flux
In terms of mixing ratio, horizontal transport/advection can be represented in terms moisture flux: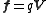
in which q is the mixing ratio. The value can integrated throughout the atmosphere to total transport of moisture through the vertical:
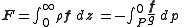
which
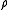 is the density of air, P is pressure at the ground surface. For the far right definition, we have used Hydrostatic equilibrium
is the density of air, P is pressure at the ground surface. For the far right definition, we have used Hydrostatic equilibriumHydrostatic equilibrium
Hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance is the condition in fluid mechanics where a volume of a fluid is at rest or at constant velocity. This occurs when compression due to gravity is balanced by a pressure gradient force...
approximation.
and its divergence (convergence) imply net evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is a term used to describe the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies...
(precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
) is adding (removing) moisture from the column:
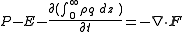
which P, E, and the integral term are precipitation, evapotranspiration, and time rate of change of Precipitable water; all represented in terms of mass per unit area (one can convert to more typical units in length such as mm by multiplying the density of liquid water and the correct length unit conversion factor).

