
Minimum-shift keying
Encyclopedia
Continuous phase modulation
Continuous phase modulation is a method for modulation of data commonly used in wireless modems. In contrast to other coherent digital phase modulation techniques where the carrier phase...
frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
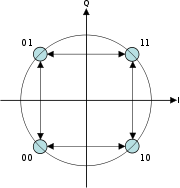
that was developed in the late 1950s and 1960s. Similar to OQPSK, MSK is encoded with bits alternating between quadrature components, with the Q component delayed by half the symbol period. However, instead of square pulses as OQPSK uses, MSK encodes each bit as a half sinusoid. This results in a constant-modulus signal, which reduces problems caused by non-linear distortion. In addition to being viewed as related to OQPSK, MSK can also be viewed as a continuous phase frequency shift keyed (CPFSK) signal with a frequency separation of one-half the bit rate.
Mathematical representation
The resulting signal is represented by the formula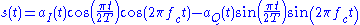
where
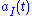 and
and 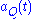 encode the even and odd information respectively with a sequence of square pulses of duration 2T.
encode the even and odd information respectively with a sequence of square pulses of duration 2T.Using the trigonometric identity, this can be rewritten in a form where the phase and frequency modulation are more obvious,

where bk(t) is +1 when
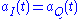 and -1 if they are of opposite signs, and
and -1 if they are of opposite signs, and 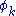 is 0 if
is 0 if 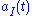 is 1, and
is 1, and  otherwise. Therefore, the signal is modulated in frequency and phase, and the phase changes continuously and linearly.
otherwise. Therefore, the signal is modulated in frequency and phase, and the phase changes continuously and linearly.Gaussian minimum-shift keying
In digital communication, Gaussian minimum shift keying or GMSK is a continuous-phase frequency-shift keyingFrequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
modulation scheme
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
. It is similar to standard minimum-shift keying (MSK); however the digital data stream is first shaped with a Gaussian filter
Gaussian filter
In electronics and signal processing, a Gaussian filter is a filter whose impulse response is a Gaussian function. Gaussian filters are designed to give no overshoot to a step function input while minimizing the rise and fall time. This behavior is closely connected to the fact that the Gaussian...
before being applied to a frequency modulator. This has the advantage of reducing sideband
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier...
power, which in turn reduces out-of-band interference between signal carriers in adjacent frequency channels. However, the Gaussian filter increases the modulation memory in the system and causes intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
, making it more difficult to discriminate between different transmitted data values and requiring more complex channel equalization algorithms such as an adaptive equalizer
Adaptive equalizer
An adaptive equalizer is an equalizer that automatically adapts to time-varying properties of the communication channel. It is frequently used with coherent modulations such as phase shift keying, mitigating the effects of multipath propagation and Doppler spreading.Many adaptation strategies exist...
at the receiver. GMSK has high spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
, but it needs a higher power level than QPSK, for instance, in order to reliably transmit the same amount of data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
.
GMSK is most notably used in the Global System for Mobile Communications
Global System for Mobile Communications
GSM , is a standard set developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute to describe technologies for second generation digital cellular networks...
(GSM).

