Microphotonics
Encyclopedia
Microphotonics is a branch of technology
that deals with directing light on a microscopic scale. It is used in optical networking
.
Microphotonics employs at least two different materials with a large differential index of refraction to squeeze the light down to a small size. Generally speaking virtually all of microphotonics relies on Fresnel reflection to guide the light. If the photons reside mainly in the higher index material, the confinement is due to total internal reflection
. If the confinement is due many distributed Fresnel reflections, the device is termed a photonic crystal
. There are many different types of geometries used in microphotonics including optical waveguides
, optical microcavities
, and Arrayed waveguide grating
s.
s are non-conducting materials that reflect various wavelengths of light almost perfectly. Such a crystal can be referred to as a perfect mirror
. Other devices employed in microphotonics include micromirrors and photonic wire waveguides. These tools are used to "mold the flow of light", a famous phrase for describing the goal of microphotonics.
Currently microphotonics technology is being developed to replace electronics devices. For instance, the long-standing goal of an all-optical router would eliminate electronic bottlenecks, speeding up the network. Perfect mirrors are being developed for use in fiber optic cables.
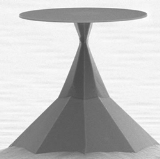
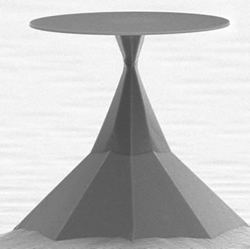 An optical microdisk, optical microtoroid, or optical microsphere
An optical microdisk, optical microtoroid, or optical microsphere
uses internal reflection in a circular geometry to hold onto the photons. This type of circularly symmetric optical resonance is called a Whispering Gallery Mode, after Lord Rayleigh coined the term.
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
that deals with directing light on a microscopic scale. It is used in optical networking
Optical networking
Optical networking can refer to:* Optical communication* Fiber-optic communication* Synchronous optical networking* Optical Transport Network * Passive optical network...
.
Microphotonics employs at least two different materials with a large differential index of refraction to squeeze the light down to a small size. Generally speaking virtually all of microphotonics relies on Fresnel reflection to guide the light. If the photons reside mainly in the higher index material, the confinement is due to total internal reflection
Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
. If the confinement is due many distributed Fresnel reflections, the device is termed a photonic crystal
Photonic crystal
Photonic crystals are periodic optical nanostructures that are designed to affect the motion of photons in a similar way that periodicity of a semiconductor crystal affects the motion of electrons...
. There are many different types of geometries used in microphotonics including optical waveguides
Waveguide (optics)
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber and rectangular waveguides....
, optical microcavities
Optical microcavity
An optical microcavity is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium. The name microcavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range...
, and Arrayed waveguide grating
Arrayed waveguide grating
Arrayed waveguide gratings are commonly used as optical multiplexers in wavelength division multiplexed systems. These devices are capable of multiplexing a large number of wavelengths into a single optical fiber, thereby increasing the transmission capacity of optical networks considerably.The...
s.
Photonic crystals
Photonic crystalPhotonic crystal
Photonic crystals are periodic optical nanostructures that are designed to affect the motion of photons in a similar way that periodicity of a semiconductor crystal affects the motion of electrons...
s are non-conducting materials that reflect various wavelengths of light almost perfectly. Such a crystal can be referred to as a perfect mirror
Perfect mirror
A perfect mirror is a theoretical mirror that reflects light perfectly, and doesn't transmit or absorb it.Domestic mirrors are not perfect mirrors as they absorb a significant portion of the light which falls on them....
. Other devices employed in microphotonics include micromirrors and photonic wire waveguides. These tools are used to "mold the flow of light", a famous phrase for describing the goal of microphotonics.
Currently microphotonics technology is being developed to replace electronics devices. For instance, the long-standing goal of an all-optical router would eliminate electronic bottlenecks, speeding up the network. Perfect mirrors are being developed for use in fiber optic cables.
Microdisks, microtoroids, and microspheres

Optical microsphere
Optical microspheres are high quality factor optical resonators used for active and passive photonic applications such as microlaser cavities and filters....
uses internal reflection in a circular geometry to hold onto the photons. This type of circularly symmetric optical resonance is called a Whispering Gallery Mode, after Lord Rayleigh coined the term.

