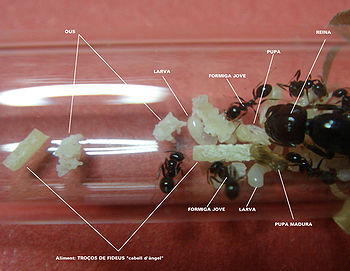
Messor is a
myrmicineMyrmicinae is a subfamily of ants. There are about 140 genera within the group, with the family being cosmopolitan. The pupae lack cocoons. Some species retain a functional sting. The petioles of Myrmicinae consist of two nodes...
genusIn biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of
antAnts are social insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from wasp-like ancestors in the mid-Cretaceous period between 110 and 130 million years ago and diversified after the rise of flowering plants. More than...
s with more than 100
speciesIn biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
, all of which are
harvester antAnts known as Harvester ants include:species*Red harvester ant *Florida harvester ant *Maricopa harvester ant , the most venomous insect in the world....
s; the generic name comes from the Roman god of crops and harvest,
MessorMessor is a myrmicine genus of ants with more than 100 species, all of which are harvester ants; the generic name comes from the Roman god of crops and harvest, Messor. The subterranean colonies tend to be found in open fields and near roadsides, openings are directly to the surface...
. The subterranean colonies tend to be found in open fields and near roadsides, openings are directly to the surface. The
Vessomessor genus was recently added to messor adding 8 more species.
Colonies can achieve huge sizes and are notable for their intricately designed granaries in which seeds are stored in dry conditions, preventing germination. The structure of Messor spp. nests is complex and the genus on the whole is one of very accomplished architects.
Messor spp. are polymorphic and have a distinct caste of macrocephalic dinoergates whose role is of carrying and cutting the large seeds which comprise much of the colonies' subsistence.
Equipped with a tough shining cuticle, Messor spp. are slow moving and form long, seed-carrying runs. Colonies tend to be monogynous and are founded by a single queen alone.
Species

- Messor abdelazizi Santschi, 1921
- Messor aciculatus (Smith, 1874)
- Messor aegyptiacus (Emery, 1878)
- Messor alexandri Tohme, 1981
- Messor andrei (Mayr, 1886)
- Messor angularis Santschi, 1928
- Messor antennatus Emery, 1908
- Messor aphaenogasteroides Pisarski, 1967
- Messor aralocaspius Ruzsky, 1902
- Messor arenarius (Fabricius, 1787)
- Messor atanassovii Atanassov, 1982
- Messor barbarus (Linnaeus, 1767)
- Messor beduinus Emery, 1922
- Messor berbericus Bernard, 1955
- Messor bernardi Cagniant, 1967
- Messor bouvieri Bondroit, 1918
- Messor buettikeri Collingwood, 1985
- Messor caducus (Victor, 1839)
- Messor capensis (Mayr, 1862)
- Messor capitatus (Latreille, 1798)
- Messor carthaginensis Bernard, 1980
- Messor caviceps (Forel, 1902)
- Messor celiae Reyes, 1985
- Messor cephalotes (Emery, 1895)
- Messor ceresis Santschi, 1934
- Messor chamberlini Wheeler, 1915
- Messor clypeatus Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927
- Messor collingwoodi Bolton, 1982
- Messor concolor Santschi, 1927
- Messor decipiens Santschi, 1917
- Messor dentatus Santschi, 1927
- Messor denticornis Forel, 1910
- Messor denticulatus Santschi, 1927
- Messor diabarensis Arnol'di, 1969
- Messor ebeninus Santschi, 1927
- Messor excursionis Ruzsky, 1905
- Messor ferreri Collingwood, 1993
- Messor foreli Santschi, 1923
- Messor fraternus Ruzsky, 1905
- Messor galla (Mayr, 1904)
- Messor hebraeus Santschi, 1927
- Messor hellenius Agosti & Collingwood, 1987
- Messor himalayanus (Forel, 1902)
- Messor hispanicus Santschi, 1919
- Messor ibericus Santschi, 1931
- Messor incisus Stitz, 1923
- Messor incorruptus Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929
- Messor inermis Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1929
- Messor instabilis (Smith, 1858)
- Messor intermedius Santschi, 1927
- Messor julianus (Pergande, 1894)
- Messor kasakorum Arnol'di, 1969
- Messor kisilkumensis Arnol'di, 1969
|
Messor lamellicornis Arnol'di, 1968
Messor lariversi (Smith, 1951)
Messor lobicornis Forel, 1894
Messor lobognathus Andrews, 1916
Messor luebberti Forel, 1910
Messor luridus Santschi, 1927
Messor lusitanicus Tinaut, 1985
Messor maculifrons Santschi, 1927
Messor marikovskii Arnol'di, 1969
Messor marocanus Santschi, 1927
Messor medioruber Santschi, 1910
Messor melancholicus Arnol'di, 1977
Messor minor (Andre, 1883)
Messor nahali Tohme, 1981
Messor niloticus Santschi, 1938
Messor oertzeni Forel, 1910
Messor olegianus Arnol'di, 1969
Messor orientalis (Emery, 1898)
Messor perantennatus Arnol'di, 1969
Messor pergandei (Mayr, 1886)
Messor piceus Stitz, 1923
Messor picturatus Santschi, 1927
Messor planiceps Stitz, 1917
Messor postpetiolatus Santschi, 1917
Messor regalis (Emery, 1892)
Messor reticuliventris Karavaiev, 1910
Messor rufotestaceus (Foerster, 1850)
Messor rufus Santschi, 1923
Messor ruginodis Stitz, 1916
Messor rugosus (Andre, 1881)
Messor sanctus Emery, 1921
Messor sculpturatus Carpenter, 1930
Messor semirufus (Andre, 1883)
Messor semoni (Forel, 1906)
Messor smithi (Cole, 1963)
Messor sordidus (Forel, 1892)
Messor stoddardi (Emery, 1895)
Messor striatellus Arnol'di, 1969
Messor striaticeps (Andre, 1883)
Messor striatifrons Stitz, 1923
Messor striativentris Emery, 1908
Messor structor (Latreille, 1798)
Messor subgracilinodis Arnol'di, 1969
Messor sultanus Santschi, 1917
Messor syriacus Tohme, 1969
Messor tapallatis Batas, 2011
Messor testaceus Donisthorpe, 1950
Messor tropicorum Wheeler, 1922
Messor turcmenochorassanicus Arnol'di, 1977
Messor valentinae Arnol'di, 1969
Messor variabilis Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927
Messor vaucheri Emery, 1908
Messor vicinus Kuznetsov-Ugamsky, 1927
Messor wasmanni Krausse, 1910 |
The source of this article is
wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the
GFDL.