
Meselson-Stahl experiment
Encyclopedia
The Meselson–Stahl experiment was an experiment by Matthew Meselson
and Franklin Stahl
in 1958 which supported the hypothesis that DNA replication
was semiconservative
. Semiconservative replication means that when the double stranded DNA helix was replicated, each of the two double stranded DNA
helices consisted of one strand coming from the original helix and one newly synthesized. It has been called "the most beautiful experiment in biology."
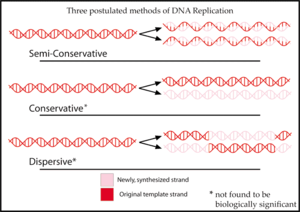 Three hypotheses had been previously proposed for the method of replication of DNA.
Three hypotheses had been previously proposed for the method of replication of DNA.
In the semiconservative hypothesis, proposed by Watson
and Crick
, the two strands of a DNA molecule separate during replication. Each strand then acts as a template for synthesis of a new strand.
The conservative hypothesis proposed that the entire DNA molecule acted as a template for synthesis of an entirely new one. According to this model, histone
proteins bound to the DNA, distorting it in such a way as to expose both strands' bases for hydrogen bonding.
The dispersive hypothesis is exemplified by a model proposed by Max Delbrück
, which attempts to solve the problem of unwinding the two strands of the double helix by a mechanism that breaks the DNA backbone every 10 nucleotides or so, untwists the molecule, and attaches the old strand to the end of the newly synthesized one. This would synthesize the DNA in short pieces alternating from one strand to the other.
Each of these three models makes a different prediction about the distribution of the "old" DNA in molecules formed after replication. In the conservative hypothesis, after replication, one molecule is the entirely conserved "old" molecule, and the other is all newly synthesized DNA. The semiconservative hypothesis predicts that each molecule after replication will contain one old and one new strand. The dispersive model predicts that each strand of each new molecule will contain a mixture of old and new DNA.
is a major constituent of DNA. 14N is by far the most abundant isotope
of nitrogen, but DNA with the heavier (but non-radioactive) 15N isotope is also functional.
E. coli were grown for several generations in a medium with 15N. When DNA is extracted from these cells and centrifuged on a salt density gradient, the DNA separates out at the point at which its density equals that of the salt solution. The DNA of the cells grown in 15N medium had a higher density than cells grown in normal 14N medium. After that, E. coli cells with only 15N in their DNA were transferred to a 14N medium and were allowed to divide; the progress of cell division was monitored by measuring the optical density of the cell suspension.
DNA was extracted periodically and was compared to pure 14N DNA and 15N DNA. After one replication, the DNA was found to have close to the intermediate density. Since conservative replication would result in equal amounts of DNA of the higher and lower densities (but no DNA of an intermediate density), conservative replication was excluded. However, this result was consistent with both semiconservative and dispersive replication. Semiconservative replication would result in double-stranded DNA with one strand of 15N DNA, and one of 14N DNA, while dispersive replication would result in double-stranded DNA with both strands having mixtures of 15N and 14N DNA, either of which would have appeared as DNA of an intermediate density.
The authors continued to sample cells as replication continued. DNA from cells after two replications had been completed was found to consist of equal amounts of DNA with two different densities, one corresponding to the intermediate density of DNA of cells grown for only one division in 14N medium, the other corresponding to DNA from cells grown exclusively in 14N medium. This was inconsistent with dispersive replication, which would have resulted in a single density, lower than the intermediate density of the one-generation cells, but still higher than cells grown only in 14N DNA medium, as the original 15N DNA would have been split evenly among all DNA strands. The result was consistent with the semiconservative replication hypothesis.
Matthew Meselson
Matthew Stanley Meselson is an American geneticist and molecular biologist whose research was important in showing how DNA replicates, recombines and is repaired in cells. In his mature years, he has been an active chemical and biological weapons activist and consultant...
and Franklin Stahl
Franklin Stahl
Dr. Franklin William Stahl is an American molecular biologist. With Matthew Meselson, Stahl conducted the famous Meselson-Stahl experiment showing that DNA is replicated by a semiconservative mechanism, meaning that each strand of the DNA serves as a template for the "replicated" strand.He is...
in 1958 which supported the hypothesis that DNA replication
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
was semiconservative
Semiconservative replication
Semiconservative replication describes the mechanism by which DNA is replicated in all known cells.This mechanism of replication was one of three models originally proposedfor DNA replication:...
. Semiconservative replication means that when the double stranded DNA helix was replicated, each of the two double stranded DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
helices consisted of one strand coming from the original helix and one newly synthesized. It has been called "the most beautiful experiment in biology."
Hypotheses

In the semiconservative hypothesis, proposed by Watson
James D. Watson
James Dewey Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist, and zoologist, best known as one of the co-discoverers of the structure of DNA in 1953 with Francis Crick...
and Crick
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick OM FRS was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist, and most noted for being one of two co-discoverers of the structure of the DNA molecule in 1953, together with James D. Watson...
, the two strands of a DNA molecule separate during replication. Each strand then acts as a template for synthesis of a new strand.
The conservative hypothesis proposed that the entire DNA molecule acted as a template for synthesis of an entirely new one. According to this model, histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
proteins bound to the DNA, distorting it in such a way as to expose both strands' bases for hydrogen bonding.
The dispersive hypothesis is exemplified by a model proposed by Max Delbrück
Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück was a German-American biophysicist and Nobel laureate.-Biography:Delbrück was born in Berlin, German Empire...
, which attempts to solve the problem of unwinding the two strands of the double helix by a mechanism that breaks the DNA backbone every 10 nucleotides or so, untwists the molecule, and attaches the old strand to the end of the newly synthesized one. This would synthesize the DNA in short pieces alternating from one strand to the other.
Each of these three models makes a different prediction about the distribution of the "old" DNA in molecules formed after replication. In the conservative hypothesis, after replication, one molecule is the entirely conserved "old" molecule, and the other is all newly synthesized DNA. The semiconservative hypothesis predicts that each molecule after replication will contain one old and one new strand. The dispersive model predicts that each strand of each new molecule will contain a mixture of old and new DNA.
Experimental procedure and results
NitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
is a major constituent of DNA. 14N is by far the most abundant isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
of nitrogen, but DNA with the heavier (but non-radioactive) 15N isotope is also functional.
E. coli were grown for several generations in a medium with 15N. When DNA is extracted from these cells and centrifuged on a salt density gradient, the DNA separates out at the point at which its density equals that of the salt solution. The DNA of the cells grown in 15N medium had a higher density than cells grown in normal 14N medium. After that, E. coli cells with only 15N in their DNA were transferred to a 14N medium and were allowed to divide; the progress of cell division was monitored by measuring the optical density of the cell suspension.
DNA was extracted periodically and was compared to pure 14N DNA and 15N DNA. After one replication, the DNA was found to have close to the intermediate density. Since conservative replication would result in equal amounts of DNA of the higher and lower densities (but no DNA of an intermediate density), conservative replication was excluded. However, this result was consistent with both semiconservative and dispersive replication. Semiconservative replication would result in double-stranded DNA with one strand of 15N DNA, and one of 14N DNA, while dispersive replication would result in double-stranded DNA with both strands having mixtures of 15N and 14N DNA, either of which would have appeared as DNA of an intermediate density.
The authors continued to sample cells as replication continued. DNA from cells after two replications had been completed was found to consist of equal amounts of DNA with two different densities, one corresponding to the intermediate density of DNA of cells grown for only one division in 14N medium, the other corresponding to DNA from cells grown exclusively in 14N medium. This was inconsistent with dispersive replication, which would have resulted in a single density, lower than the intermediate density of the one-generation cells, but still higher than cells grown only in 14N DNA medium, as the original 15N DNA would have been split evenly among all DNA strands. The result was consistent with the semiconservative replication hypothesis.
External links
- Matthew Meselson iBioMagazine talk: "The Semi-Conservative Replication of DNA"
- DNA From The Beginning A animation which explains the experiment.
- The Meselson–Stahl Experiment Another useful animation.
- Description of the Meselson-Stahl Experiment including original data from Visionlearning

