
Merneith
Encyclopedia
Merneith was a consort
and a regent
of Ancient Egypt
during the first dynasty
. She may have been a ruler of Egypt in her own right. The possibility is based on several official records. Her rule occurred the thirtieth century B.C.
, for an undetermined period of time. Merneith’s name means Beloved by Neith
and her stela contains symbols of that deity
. She was Djet
's senior royal wife and the mother of Den
.
, Djet
and Den
. Merneith may have been the daughter of King Djer
, but there is no conclusive evidence. As the mother of Den
, it is likely that Merneith was the wife of King Djet
. No information about the identity of her mother has been found.
A clay seal
found in the tomb of her son, Den, was engraved with "King's Mother Merneith". It also is known that Den’s father was Djet, making it likely, therefore, that Merneith was Djet’s royal wife.
 Merneith is believed to have become ruler
Merneith is believed to have become ruler
upon the death of her husband, Djet
. The title she held, however, is debated. It is possible that her son Den was too young to rule when Djet died, so she may have ruled as regent until Den was old enough to be the king in his own right.
The strongest evidence that Merneith was a ruler of Egypt is her tomb. This tomb in Abydos
(Tomb Y) is unique among the otherwise exclusively male tombs. Merneith was buried close to Djet
and Den
. Her tomb is of the same scale as the tombs of the kings of that period. Two grave stela were discovered near her tomb. The stela show the name of the Merneith. However, her name is not surrounded by a serekh
which was the prerogative of a king. Merneith's name is not included in the King Lists from the New Kingdom
. A seal containing a list of pharaohs of the first dynasty was found in the tomb of Qa'a
, the third known pharaoh after Den
. However, this list does not mention the reign of Merneith.
A few other pieces of evidence exist elsewhere about Merneith:
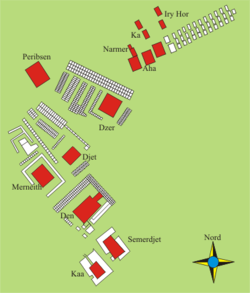 At Abydos
At Abydos
the tomb belonging to Merneith was found in an area associated with other pharaohs of the first dynasty, Umm el-Qa'ab
. Two stela made of stone, identifying the tomb as hers, were found at the site.
In 1900 William Petrie discovered Merneith’s tomb and, because of its nature, believed it belonged to a previously unknown pharaoh. The tomb was excavated and was shown to contain a large underground chamber, lined with mud bricks, which was surrounded by rows of small satellite burials with at least 40 subsidiary graves.
The servants were thought to assist the ruler in the afterlife. The burial of servants with a ruler was a consistent practice in the tombs of the early first dynasty pharaohs. Large numbers of sacrificial assets were buried in her tomb complex as well, which is another honor afforded to pharaohs that provided the ruler with powerful animals for eternal life. This first dynasty burial complex was very important in the Egyptian religious tradition and its importance grew as the culture endured.
Inside her tomb archaeologists discovered a solar boat that would allow her to travel with the sun deity in the afterlife.
Considered one of the most important archaeological sites of ancient Egypt (near the town of al-Balyana), the sacred city of Abydos
was the site of many ancient temples, including Umm el-Qa'ab, the royal necropolis, where early pharaohs were entombed. These tombs began to be seen as extremely significant burials and in later times it became desirable to be buried in the area, leading to the growth of the town's importance as a cult site.
Queen consort
A queen consort is the wife of a reigning king. A queen consort usually shares her husband's rank and holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles. Historically, queens consort do not share the king regnant's political and military powers. Most queens in history were queens consort...
and a regent
Regent
A regent, from the Latin regens "one who reigns", is a person selected to act as head of state because the ruler is a minor, not present, or debilitated. Currently there are only two ruling Regencies in the world, sovereign Liechtenstein and the Malaysian constitutive state of Terengganu...
of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
during the first dynasty
First dynasty of Egypt
The first dynasty of Ancient Egypt is often combined with the Dynasty II under the group title, Early Dynastic Period of Egypt...
. She may have been a ruler of Egypt in her own right. The possibility is based on several official records. Her rule occurred the thirtieth century B.C.
30th century BC
The 30th century BC is a century which lasted from the year 3000 BC to 2901 BC.-Events:* Before 3000 BC: Image of a deity, detail from a cong recovered from Tomb 12, Fanshan, Yuyao, Zhejiang, is made. Neolithic period. Liangzhu culture...
, for an undetermined period of time. Merneith’s name means Beloved by Neith
Neith
In Egyptian mythology, Neith was an early goddess in the Egyptian pantheon. She was the patron deity of Sais, where her cult was centered in the Western Nile Delta of Egypt and attested as early as the First Dynasty...
and her stela contains symbols of that deity
Deity
A deity is a recognized preternatural or supernatural immortal being, who may be thought of as holy, divine, or sacred, held in high regard, and respected by believers....
. She was Djet
Djet
Djet, also known as Wadj, Zet, and Uadji , was the fourth Egyptian pharaoh of the first dynasty...
's senior royal wife and the mother of Den
Den (Pharaoh)
Den, also known as Hor-Den, Dewen and Udimu, is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the 1st dynasty. He is the best archaeologically attested ruler of this period. Den is said to have brought prosperity to his realm and numerous innovations are attributed to his reign...
.
Family
Merneith is linked in a variety of seal impressions and inscribed bowls with DjerDjer
Djer was the second or third pharaoh of the first dynasty of Egypt, which dates from approximately 3100 BC. Some scholars, however, debate whether the first pharaoh, Menes or Narmer, and Hor-Aha might have been different rulers. If they were separate rulers, this would make Djer the third pharaoh...
, Djet
Djet
Djet, also known as Wadj, Zet, and Uadji , was the fourth Egyptian pharaoh of the first dynasty...
and Den
Den
Den may refer to:*Den , a part of a house similar to the living room: a den is about the size of a living room, but smaller than a family room*Den , a Ukrainian newspaper*Den , a Pharaoh of Egypt...
. Merneith may have been the daughter of King Djer
Djer
Djer was the second or third pharaoh of the first dynasty of Egypt, which dates from approximately 3100 BC. Some scholars, however, debate whether the first pharaoh, Menes or Narmer, and Hor-Aha might have been different rulers. If they were separate rulers, this would make Djer the third pharaoh...
, but there is no conclusive evidence. As the mother of Den
Den
Den may refer to:*Den , a part of a house similar to the living room: a den is about the size of a living room, but smaller than a family room*Den , a Ukrainian newspaper*Den , a Pharaoh of Egypt...
, it is likely that Merneith was the wife of King Djet
Djet
Djet, also known as Wadj, Zet, and Uadji , was the fourth Egyptian pharaoh of the first dynasty...
. No information about the identity of her mother has been found.
A clay seal
Cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a cylinder engraved with a 'picture story', used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally wet clay. Cylinder seals were invented around 3500 BC in the Near East, at the contemporary site of Susa in south-western Iran and at the early site...
found in the tomb of her son, Den, was engraved with "King's Mother Merneith". It also is known that Den’s father was Djet, making it likely, therefore, that Merneith was Djet’s royal wife.
Biography

Ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule or line gauge, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing, printing and engineering/building to measure distances and/or to rule straight lines...
upon the death of her husband, Djet
Djet
Djet, also known as Wadj, Zet, and Uadji , was the fourth Egyptian pharaoh of the first dynasty...
. The title she held, however, is debated. It is possible that her son Den was too young to rule when Djet died, so she may have ruled as regent until Den was old enough to be the king in his own right.
The strongest evidence that Merneith was a ruler of Egypt is her tomb. This tomb in Abydos
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos is one of the most ancient cities of Upper Egypt, and also of the eight Upper Nome, of which it was the capital city. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of el-'Araba el Madfuna and al-Balyana...
(Tomb Y) is unique among the otherwise exclusively male tombs. Merneith was buried close to Djet
Djet
Djet, also known as Wadj, Zet, and Uadji , was the fourth Egyptian pharaoh of the first dynasty...
and Den
Den
Den may refer to:*Den , a part of a house similar to the living room: a den is about the size of a living room, but smaller than a family room*Den , a Ukrainian newspaper*Den , a Pharaoh of Egypt...
. Her tomb is of the same scale as the tombs of the kings of that period. Two grave stela were discovered near her tomb. The stela show the name of the Merneith. However, her name is not surrounded by a serekh
Serekh
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a serekh is a rectangular enclosure representing the niched or gated façade of a palace surmounted by the Horus falcon, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name...
which was the prerogative of a king. Merneith's name is not included in the King Lists from the New Kingdom
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom of Egypt, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt....
. A seal containing a list of pharaohs of the first dynasty was found in the tomb of Qa'a
Qa'a
-Legacy:Qa'a had a fairly large tomb in Abydos which measures 98.5 X 75.5 feet or 30 X 23 meters. Manetho gives him a reign of 26 years in his Epitome if this ruler was a certain Biechenes. A long reign is supported by the large size of this ruler's burial site at Abydos...
, the third known pharaoh after Den
Den (Pharaoh)
Den, also known as Hor-Den, Dewen and Udimu, is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the 1st dynasty. He is the best archaeologically attested ruler of this period. Den is said to have brought prosperity to his realm and numerous innovations are attributed to his reign...
. However, this list does not mention the reign of Merneith.
A few other pieces of evidence exist elsewhere about Merneith:
- Merneith’s name appears on a seal found in the tomb of her son, DenDen (Pharaoh)Den, also known as Hor-Den, Dewen and Udimu, is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the 1st dynasty. He is the best archaeologically attested ruler of this period. Den is said to have brought prosperity to his realm and numerous innovations are attributed to his reign...
. The seal includes Merneith on a list of the first dynasty kings. Merneith's name was the only name of a woman included on the list. All of the names on the list are the HorusHorusHorus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
names of the kings. However, Merneith's name is accompanied by the title "King's Mother". - Merneith’s name may have been included on the Palermo StonePalermo stoneThe Palermo Stone is a large fragment of a stele known as the Royal Annals of the Old Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. It contains records of the kings of Egypt from the first dynasty through the fifth dynasty....
. - Items from the great mastabaMastabaA mastaba, or "pr-djt" , is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with outward sloping sides that marked the burial site of many eminent Egyptians of Egypt's ancient period...
(Nr 3503, 16 x 42 m) in SaqqaraSaqqaraSaqqara is a vast, ancient burial ground in Egypt, serving as the necropolis for the Ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara features numerous pyramids, including the world famous Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb due to its rectangular base, as well as a number of...
where her name has been found in inscriptions on stone vessels, jars, as well as the seal impressions. In particular, there is one seal from SaqqaraSaqqaraSaqqara is a vast, ancient burial ground in Egypt, serving as the necropolis for the Ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara features numerous pyramids, including the world famous Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb due to its rectangular base, as well as a number of...
which shows Merneith's name in a serekh. - Merneith Enclosure. This is a group of tombs from the cemetery at Shunet el-Zebib. These tombs are dated to the time of Merneith.
- Merneith's name was found on objects in king DjerDjerDjer was the second or third pharaoh of the first dynasty of Egypt, which dates from approximately 3100 BC. Some scholars, however, debate whether the first pharaoh, Menes or Narmer, and Hor-Aha might have been different rulers. If they were separate rulers, this would make Djer the third pharaoh...
's tomb in Umm el-Qa'ab
Tomb

Abydos, Egypt
Abydos is one of the most ancient cities of Upper Egypt, and also of the eight Upper Nome, of which it was the capital city. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of el-'Araba el Madfuna and al-Balyana...
the tomb belonging to Merneith was found in an area associated with other pharaohs of the first dynasty, Umm el-Qa'ab
Umm el-Qa'ab
Umm el-Qa`āb is the necropolis of the Early Dynastic kings at Abydos, in Egypt. Its modern name means Mother of Pots, as the whole area is littered with the broken pot shards of offerings made in earlier times...
. Two stela made of stone, identifying the tomb as hers, were found at the site.
In 1900 William Petrie discovered Merneith’s tomb and, because of its nature, believed it belonged to a previously unknown pharaoh. The tomb was excavated and was shown to contain a large underground chamber, lined with mud bricks, which was surrounded by rows of small satellite burials with at least 40 subsidiary graves.
The servants were thought to assist the ruler in the afterlife. The burial of servants with a ruler was a consistent practice in the tombs of the early first dynasty pharaohs. Large numbers of sacrificial assets were buried in her tomb complex as well, which is another honor afforded to pharaohs that provided the ruler with powerful animals for eternal life. This first dynasty burial complex was very important in the Egyptian religious tradition and its importance grew as the culture endured.
Inside her tomb archaeologists discovered a solar boat that would allow her to travel with the sun deity in the afterlife.
Considered one of the most important archaeological sites of ancient Egypt (near the town of al-Balyana), the sacred city of Abydos
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos is one of the most ancient cities of Upper Egypt, and also of the eight Upper Nome, of which it was the capital city. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of el-'Araba el Madfuna and al-Balyana...
was the site of many ancient temples, including Umm el-Qa'ab, the royal necropolis, where early pharaohs were entombed. These tombs began to be seen as extremely significant burials and in later times it became desirable to be buried in the area, leading to the growth of the town's importance as a cult site.

