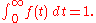Mean time between failure
Encyclopedia
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a system during operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean
(average) time between failure
s of a system. The MTBF is typically part of a model that assumes the failed system is immediately repaired (MTTR
), as a part of a renewal process. This is in contrast to the mean time to failure (MTTF), which measures average time to failure
s with the modeling assumption that the failed system is not repaired (infinite repair rate).
The definition of MTBF depends on the definition of what is considered a system failure
. For complex, repairable
systems, failures are considered to be those out of design conditions which place the system out of service and into a state for repair. Failures which occur that can be left or maintained in an unrepaired condition, and do not place the system out of service, are not considered failures under this definition. In addition, units that are taken down for routine scheduled maintenance or inventory control, are not considered within the definition of failure.
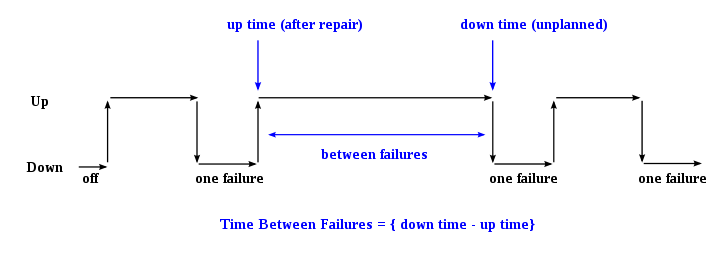
For each observation, downtime is the instantaneous time it went down, which is after (i.e. greater than) the moment it went up, uptime. The difference (downtime minus uptime) is the amount of time it was operating between these two events.
MTBF value prediction is an important element in the development of products.
Reliability engineers / design engineers, often utilize Reliability Software to calculate products' MTBF according to various methods/standards (MIL-HDBK-217F, Telcordia SR332, Siemens Norm, FIDES,UTE 80-810 (RDF2000), etc.). However, these "prediction" methods are not intended to reflect fielded MTBF as is commonly believed. The intent of these tools is to focus design efforts on the weak links in the design.

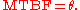
The MTBF is often denoted by the Greek letter θ
, or
The MTBF can be defined in terms of the expected value
of the density function ƒ(t)
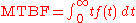
where ƒ is the density function of time until failure – satisfying the standard requirement of density functions –
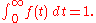
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
(average) time between failure
Failure
Failure refers to the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of success. Product failure ranges from failure to sell the product to fracture of the product, in the worst cases leading to personal injury, the province of forensic...
s of a system. The MTBF is typically part of a model that assumes the failed system is immediately repaired (MTTR
MTTR
MTTR is an abbreviation that has several different expansions, with greatly differing meanings. It is wise to spell out exactly what is meant by the use of this abbreviation, rather than assuming the reader will know which is being assumed. The M can stand for any of minimum, mean or maximum, and...
), as a part of a renewal process. This is in contrast to the mean time to failure (MTTF), which measures average time to failure
Failure
Failure refers to the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of success. Product failure ranges from failure to sell the product to fracture of the product, in the worst cases leading to personal injury, the province of forensic...
s with the modeling assumption that the failed system is not repaired (infinite repair rate).
The definition of MTBF depends on the definition of what is considered a system failure
Failure
Failure refers to the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of success. Product failure ranges from failure to sell the product to fracture of the product, in the worst cases leading to personal injury, the province of forensic...
. For complex, repairable
Repairable
Repairable is a military logistics term for a hardware component of a weapons system that can be designated for repair.Repairable components tend to be more expensive than non-repairable components, known as consumables. This is because for items that are inexpensive to procure, it is often more...
systems, failures are considered to be those out of design conditions which place the system out of service and into a state for repair. Failures which occur that can be left or maintained in an unrepaired condition, and do not place the system out of service, are not considered failures under this definition. In addition, units that are taken down for routine scheduled maintenance or inventory control, are not considered within the definition of failure.
Overview

For each observation, downtime is the instantaneous time it went down, which is after (i.e. greater than) the moment it went up, uptime. The difference (downtime minus uptime) is the amount of time it was operating between these two events.
MTBF value prediction is an important element in the development of products.
Reliability engineers / design engineers, often utilize Reliability Software to calculate products' MTBF according to various methods/standards (MIL-HDBK-217F, Telcordia SR332, Siemens Norm, FIDES,UTE 80-810 (RDF2000), etc.). However, these "prediction" methods are not intended to reflect fielded MTBF as is commonly believed. The intent of these tools is to focus design efforts on the weak links in the design.
Formal definition of MTBF
By referring to the figure above, the MTBF is the sum of the operational periods divided by the number of observed failures. If the "Down time" (with space) refers to the start of "downtime" (without space) and "up time" (with space) refers to the start of "uptime" (without space), the formula will be:
The MTBF is often denoted by the Greek letter θ
Theta
Theta is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth...
, or

The MTBF can be defined in terms of the expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
of the density function ƒ(t)
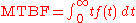
where ƒ is the density function of time until failure – satisfying the standard requirement of density functions –