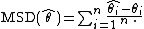Mean signed difference
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the mean signed difference (MSD), also known as mean signed error (MSE), is a sample statistic
that summarises how well an estimator
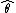 matches the quantity
matches the quantity 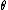 that it is supposed to estimate. It is one of a number of statistics that can be used to assess an estimation procedure, and it would often be used in conjunction with a sample version of the mean square error.
that it is supposed to estimate. It is one of a number of statistics that can be used to assess an estimation procedure, and it would often be used in conjunction with a sample version of the mean square error.
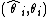 , where
, where 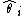 is an estimate of the parameter
is an estimate of the parameter  in a case where it is known that
in a case where it is known that 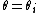 . In many applications, all the quantities
. In many applications, all the quantities 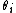 will share a common value. When applied to forecasting
will share a common value. When applied to forecasting
in a time series analysis context, a forecasting procedure might be evaluated using the mean signed difference, with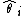 being the predicted value of a series at a given lead time
being the predicted value of a series at a given lead time
and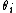 being the value of the series eventually observed for that time-point. The mean signed difference is defined to be
being the value of the series eventually observed for that time-point. The mean signed difference is defined to be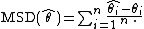
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the mean signed difference (MSD), also known as mean signed error (MSE), is a sample statistic
Statistic
A statistic is a single measure of some attribute of a sample . It is calculated by applying a function to the values of the items comprising the sample which are known together as a set of data.More formally, statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function...
that summarises how well an estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
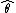 matches the quantity
matches the quantity 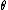 that it is supposed to estimate. It is one of a number of statistics that can be used to assess an estimation procedure, and it would often be used in conjunction with a sample version of the mean square error.
that it is supposed to estimate. It is one of a number of statistics that can be used to assess an estimation procedure, and it would often be used in conjunction with a sample version of the mean square error.Definition
The mean signed difference is derived from a set of n pairs,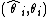 , where
, where 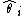 is an estimate of the parameter
is an estimate of the parameter  in a case where it is known that
in a case where it is known that 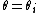 . In many applications, all the quantities
. In many applications, all the quantities 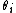 will share a common value. When applied to forecasting
will share a common value. When applied to forecastingForecasting
Forecasting is the process of making statements about events whose actual outcomes have not yet been observed. A commonplace example might be estimation for some variable of interest at some specified future date. Prediction is a similar, but more general term...
in a time series analysis context, a forecasting procedure might be evaluated using the mean signed difference, with
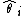 being the predicted value of a series at a given lead time
being the predicted value of a series at a given lead timeLead time
A lead time is the latency between the initiation and execution of a process. For example, the lead time between the placement of an order and delivery of a new car from a manufacturer may be anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months...
and
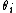 being the value of the series eventually observed for that time-point. The mean signed difference is defined to be
being the value of the series eventually observed for that time-point. The mean signed difference is defined to be