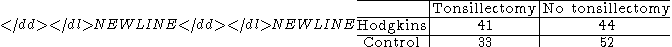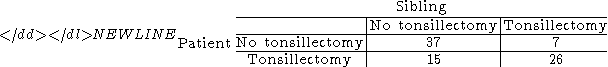McNemar's test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, McNemar's test is a non-parametric method used on nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 contingency table
s with a dichotomous trait, with matched pairs of subjects, to determine whether the row and column marginal frequencies are equal ("marginal homogeneity"). It is named after Quinn McNemar
, who introduced it in 1947.
An application of the test in genetics is the transmission disequilibrium test
for detecting genetic linkage.
The null hypothesis
of marginal homogeneity states that the two marginal probabilities for each outcome are the same, i.e. pa + pb = pa + pc and pc + pd = pb + pd.
Thus the null hypothesis is
Here pa, etc., denote the theoretical probability of occurrences in cells with the corresponding label.
The McNemar test statistic
with Yates's correction for continuity is given by: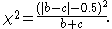
An alternative correction of 1 instead of 0.5 is attributed to Edwards
by Fleiss , resulting in a similar equation: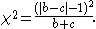
Under the null hypothesis, with a sufficiently large number of discordants (cells b and c),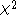 has a chi-squared distribution with 1 degree of freedom
has a chi-squared distribution with 1 degree of freedom
. If either b or c is small (b + c < 25) then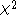 is not well-approximated by the chi-squared distribution. The binomial distribution can be used to obtain the exact distribution for an equivalent to the uncorrected form of McNemar's test statistic. In this formulation, b is compared to a binomial distribution with size parameter equal to b + c and "probability of success" = ½, which is essentially the same as the binomial sign test
is not well-approximated by the chi-squared distribution. The binomial distribution can be used to obtain the exact distribution for an equivalent to the uncorrected form of McNemar's test statistic. In this formulation, b is compared to a binomial distribution with size parameter equal to b + c and "probability of success" = ½, which is essentially the same as the binomial sign test
. For b + c < 25, the binomial calculation should be performed, and indeed, most software packages simply perform the binomial calculation in all cases, since the result then is an exact test
in all cases. When comparing the resulting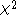 statistic to the right tail of the chi-squared distribution, the p-value that is found is two-sided, whereas to achieve a two-sided p-value in the case of the exact binomial test, the p-value of the extreme tail should be multiplied by 2.
statistic to the right tail of the chi-squared distribution, the p-value that is found is two-sided, whereas to achieve a two-sided p-value in the case of the exact binomial test, the p-value of the extreme tail should be multiplied by 2.
If the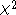 result is significant
result is significant
, this provides sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis, in favour of the alternative hypothesis that pb ≠ pc, which would mean that the marginal proportions are significantly different from each other.
The test requires the same subjects to be included in the before-and-after measurements (matched pairs).
In this example, the null hypothesis of "marginal homogeneity" would mean there was no effect of the treatment. From the above data, the McNemar test statistic with Yates's continuity correction is
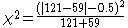
has the value 21.01, which is extremely unlikely from the distribution implied by the null hypothesis. Thus the test provides strong evidence to reject the null hypothesis of no treatment effect.
An extension of McNemar's test exists in situations where independence does not necessarily hold between the pairs; instead, there are clusters of paired data where the pairs in a cluster may not be independent, but independence holds between different clusters. An example is analyzing the effectiveness of a dental procedure; in this case, a pair corresponds to the treatment of an individual tooth in patients who might have multiple teeth treated; the effectiveness of treatment of two teeth in the same patient is not likely to be independent, but the treatment of two teeth in different patients is more likely to be independent.
It is to the second table that McNemar's test can be applied. Notice that the sum of the numbers in the second table is 85—the number of pairs of siblings—whereas the sum of the numbers in the first table is twice as big, 170—the number of individuals. The second table gives more information than the first. The numbers in the first table can be found by using the numbers in the second table, but not vice versa. The numbers in the first table give only the marginal totals of the numbers in the second table.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, McNemar's test is a non-parametric method used on nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 contingency table
Contingency table
In statistics, a contingency table is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the frequency distribution of the variables...
s with a dichotomous trait, with matched pairs of subjects, to determine whether the row and column marginal frequencies are equal ("marginal homogeneity"). It is named after Quinn McNemar
Quinn McNemar
Quinn McNemar was a US psychologist and statistician. He is known for his work on IQ tests, for his book Psychological Statistics and for McNemar's test, the statistical test he introduced in 1947....
, who introduced it in 1947.
An application of the test in genetics is the transmission disequilibrium test
Transmission disequilibrium test
The transmission disequilibrium test was proposed by Spielman, McGinnis and Ewens as a family-based association test for the presence of genetic linkage between a genetic marker and a trait...
for detecting genetic linkage.
Definition
The test is applied to a 2 × 2 contingency table, which tabulates the outcomes of two tests on a sample of n subjects, as follows.| Test 2 positive | Test 2 negative | Row total | |
| Test 1 positive | a | b | a + b |
| Test 1 negative | c | d | c + d |
| Column total | a + c | b + d | n |
The null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
of marginal homogeneity states that the two marginal probabilities for each outcome are the same, i.e. pa + pb = pa + pc and pc + pd = pb + pd.
Thus the null hypothesis is
- pb = pc.
Here pa, etc., denote the theoretical probability of occurrences in cells with the corresponding label.
The McNemar test statistic
Test statistic
In statistical hypothesis testing, a hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, which is a function of the sample; it is considered as a numerical summary of a set of data that...
with Yates's correction for continuity is given by:
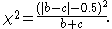
An alternative correction of 1 instead of 0.5 is attributed to Edwards
by Fleiss , resulting in a similar equation:
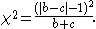
Under the null hypothesis, with a sufficiently large number of discordants (cells b and c),
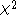 has a chi-squared distribution with 1 degree of freedom
has a chi-squared distribution with 1 degree of freedomDegrees of freedom (statistics)
In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary.Estimates of statistical parameters can be based upon different amounts of information or data. The number of independent pieces of information that go into the...
. If either b or c is small (b + c < 25) then
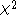 is not well-approximated by the chi-squared distribution. The binomial distribution can be used to obtain the exact distribution for an equivalent to the uncorrected form of McNemar's test statistic. In this formulation, b is compared to a binomial distribution with size parameter equal to b + c and "probability of success" = ½, which is essentially the same as the binomial sign test
is not well-approximated by the chi-squared distribution. The binomial distribution can be used to obtain the exact distribution for an equivalent to the uncorrected form of McNemar's test statistic. In this formulation, b is compared to a binomial distribution with size parameter equal to b + c and "probability of success" = ½, which is essentially the same as the binomial sign testSign test
In statistics, the sign test can be used to test the hypothesis that there is "no difference in medians" between the continuous distributions of two random variables X and Y, in the situation when we can draw paired samples from X and Y...
. For b + c < 25, the binomial calculation should be performed, and indeed, most software packages simply perform the binomial calculation in all cases, since the result then is an exact test
Exact test
In statistics, an exact test is a test where all assumptions upon which the derivation of the distribution of the test statistic is based are met, as opposed to an approximate test, in which the approximation may be made as close as desired by making the sample size big enough...
in all cases. When comparing the resulting
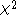 statistic to the right tail of the chi-squared distribution, the p-value that is found is two-sided, whereas to achieve a two-sided p-value in the case of the exact binomial test, the p-value of the extreme tail should be multiplied by 2.
statistic to the right tail of the chi-squared distribution, the p-value that is found is two-sided, whereas to achieve a two-sided p-value in the case of the exact binomial test, the p-value of the extreme tail should be multiplied by 2.If the
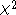 result is significant
result is significantStatistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
, this provides sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis, in favour of the alternative hypothesis that pb ≠ pc, which would mean that the marginal proportions are significantly different from each other.
Example
In the following example, a researcher attempts to determine if a drug has an effect on a particular disease. Counts of individuals are given in the table, with the diagnosis (disease: present or absent) before treatment given in the rows, and the diagnosis after treatment in the columns.The test requires the same subjects to be included in the before-and-after measurements (matched pairs).
| After: present | After: absent | Row total | |
| Before: present | 101 | 121 | 222 |
| Before: absent | 59 | 33 | 92 |
| Column total | 160 | 154 | 314 |
In this example, the null hypothesis of "marginal homogeneity" would mean there was no effect of the treatment. From the above data, the McNemar test statistic with Yates's continuity correction is
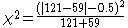
has the value 21.01, which is extremely unlikely from the distribution implied by the null hypothesis. Thus the test provides strong evidence to reject the null hypothesis of no treatment effect.
Discussion
An interesting observation when interpreting McNemar's test is that the elements of the main diagonal do not contribute to the decision about whether (in the above example) pre- or post-treatment condition is more favourable.An extension of McNemar's test exists in situations where independence does not necessarily hold between the pairs; instead, there are clusters of paired data where the pairs in a cluster may not be independent, but independence holds between different clusters. An example is analyzing the effectiveness of a dental procedure; in this case, a pair corresponds to the treatment of an individual tooth in patients who might have multiple teeth treated; the effectiveness of treatment of two teeth in the same patient is not likely to be independent, but the treatment of two teeth in different patients is more likely to be independent.
Information in the pairings
John Rice wrote:
85 Hodgkin'sHodgkin's lymphomaHodgkin's lymphoma, previously known as Hodgkin's disease, is a type of lymphoma, which is a cancer originating from white blood cells called lymphocytes...
patients [...] had a sibling of the same sex
who was free of the disease and whose age was within 5 years of
the patient's. These investigators presented the following table:
They calculated a chi-squared statistic of 1.53, which is not significantStatistical significanceIn statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
.[...] [they] had made an error in their analysis by ignoring the pairings.[...] [their] samples were not independent, because the siblings were paired [...] we set up a table that exhibits the pairings:
It is to the second table that McNemar's test can be applied. Notice that the sum of the numbers in the second table is 85—the number of pairs of siblings—whereas the sum of the numbers in the first table is twice as big, 170—the number of individuals. The second table gives more information than the first. The numbers in the first table can be found by using the numbers in the second table, but not vice versa. The numbers in the first table give only the marginal totals of the numbers in the second table.
Related tests
- The Cochran's Q test is a generalization that allows for more than two row and/or column categories.
- The Liddell's exact test is an exact alternative to McNemar's test.
- The Stuart–Maxwell test is different generalization of the McNemar test, used for testing marginal homogeneity in a square table with more than two rows/columns.
- The Bhapkar's test (1966) is a more powerful alternative to the Stuart–Maxwell test.