McCumber relation
Encyclopedia
The McCumber relation refers to the effective cross-sections of absorption and emission of light in the physics of solid-state laser
s
.
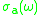 be the effective absorption cross-section
be the effective absorption cross-section 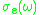 be effective emission cross-sections at frequency
be effective emission cross-sections at frequency  , and let
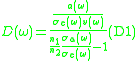
, and let 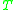 be the effective temperature of the medium. The McCumbner relation is
be the effective temperature of the medium. The McCumbner relation is
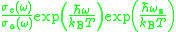
where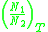
is thermal steady-state ratio of populations; frequency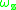 is called "zero-line" frequency ;
is called "zero-line" frequency ;
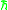 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
and
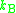 is the Boltzmann constant. Note that the right-hand side of Equation (1) does not depend on
is the Boltzmann constant. Note that the right-hand side of Equation (1) does not depend on 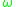 .
.
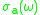
and the emission cross-section
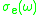
at frequency can be related to the lasers gain in such a way, that the gain at this frequency can be determined as follows:
can be related to the lasers gain in such a way, that the gain at this frequency can be determined as follows: 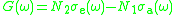
D.E.McCumber had postulated these properties and found that the emisison and absorption cross-sections are not independent
for the emission and absorption
which preserves the Max Planck formula for the
black body radiation leads to equality of cross-section of absorption and emission. In the solid-state lasers the splitting of each of laser levels leads to the broadening which greatly exceeds the natural spectral linewidth. In the case of an ideal two-level atom, the product of the linewidth and the lifetime is of order of unity, which obeys the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. In solid-state laser materials, the linewidth is several orders of magnitude larger so the spectra of emission and absorption are determined by distribution of excitation among sublevels rather than by the shape of the spectral line of each individual transition between sublevels. This distribution is determined by the effective temperature within each of laser levels. The McCumber hypothesis is that the distribution of excitation among sublevels is thermal. The effective temperature determines the spectra of emission and absorption ( The effective temperature is called a temperature by scientists even if the excited medium as whole is pretty far from the thermal state )
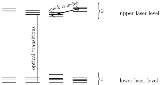
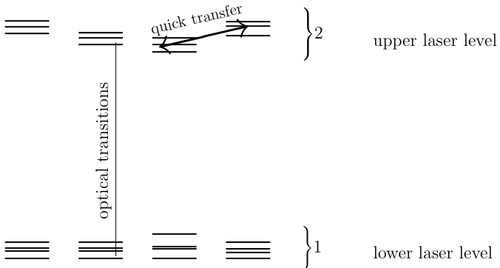 Consider the set of active centers (fig.1.). Assume fast transition between sublevels within each level, and slow transition between levels.
Consider the set of active centers (fig.1.). Assume fast transition between sublevels within each level, and slow transition between levels.
According to the McCumber hypothesis, the cross-sections and
and  do not depend on the populations
do not depend on the populations 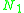 and
and 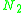 .
.
Therefore, we can deduce the relation, assuming the thermal state.
Let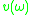 be group velocity of light in the medium, the product
be group velocity of light in the medium, the product 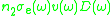 is spectral rate of
is spectral rate of
stimulated emission
, and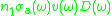 is that of absorption;
is that of absorption; 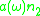 is spectral rate of spontaneous emission
is spectral rate of spontaneous emission
. (Note that in this approximation, there is no such thing as a spontaneous absorption)
The balance of photons gives: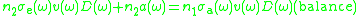
Which can be rewritten as
The thermal distribution of density of photons follows from
blackbody radiation
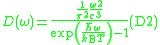
Both (4) and (5) hold for all frequencies .
.
For the case of idealized two-level active centers,
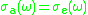 , and
, and 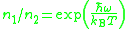 ,
,
which leads to the relation between the spectral rate of spontaneous emission
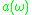 and the emission cross-section
and the emission cross-section 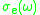
.
(We keep the term probability of emission for the quantity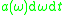 ,
,
which is probability of emission of a photon within small spectral interval
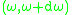
during a short time interval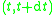 , assuming that at time
, assuming that at time  the atom is excited.)
the atom is excited.)
The relation (D2) is a fundamental property of spontaneous and stimulated emission, and perhaps the only way to prohibit a spontaneous break of the thermal equilibrium in the thermal state of excitations and photons.
For each site number , for each sublevel number
, for each sublevel number 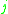 , the partial spectral emission
, the partial spectral emission
probability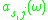 can be expressed from consideration of idealized two-level atoms
can be expressed from consideration of idealized two-level atoms
Solid-state laser
A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid such as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers .-Solid-state...
s
.
Definition
Let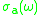 be the effective absorption cross-section
be the effective absorption cross-section 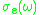 be effective emission cross-sections at frequency
be effective emission cross-sections at frequency  , and let
, and let 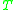 be the effective temperature of the medium. The McCumbner relation is
be the effective temperature of the medium. The McCumbner relation is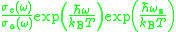
where
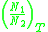
is thermal steady-state ratio of populations; frequency
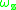 is called "zero-line" frequency ;
is called "zero-line" frequency ; is the Planck constant
is the Planck constantPlanck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
and
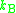 is the Boltzmann constant. Note that the right-hand side of Equation (1) does not depend on
is the Boltzmann constant. Note that the right-hand side of Equation (1) does not depend on  .
.Gain
It is typical that the lasing properties of a medium are determined by the temperature and the population at the excited laser level, and are not sensitive to the method of excitation used to achieve it. In this case, the absorption cross-section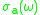
and the emission cross-section
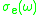
at frequency
 can be related to the lasers gain in such a way, that the gain at this frequency can be determined as follows:
can be related to the lasers gain in such a way, that the gain at this frequency can be determined as follows: 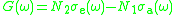
D.E.McCumber had postulated these properties and found that the emisison and absorption cross-sections are not independent
- they are related with Equation (1)
Idealized atoms
In the case of an idealized two-level atom the detailed balanceDetailed balance
The principle of detailed balance is formulated for kinetic systems which are decomposed into elementary processes : At equilibrium, each elementary process should be equilibrated by its reverse process....
for the emission and absorption
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
which preserves the Max Planck formula for the
black body radiation leads to equality of cross-section of absorption and emission. In the solid-state lasers the splitting of each of laser levels leads to the broadening which greatly exceeds the natural spectral linewidth. In the case of an ideal two-level atom, the product of the linewidth and the lifetime is of order of unity, which obeys the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. In solid-state laser materials, the linewidth is several orders of magnitude larger so the spectra of emission and absorption are determined by distribution of excitation among sublevels rather than by the shape of the spectral line of each individual transition between sublevels. This distribution is determined by the effective temperature within each of laser levels. The McCumber hypothesis is that the distribution of excitation among sublevels is thermal. The effective temperature determines the spectra of emission and absorption ( The effective temperature is called a temperature by scientists even if the excited medium as whole is pretty far from the thermal state )
Deduction of the McCumber relation

According to the McCumber hypothesis, the cross-sections
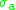 and
and 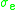 do not depend on the populations
do not depend on the populations 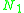 and
and 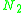 .
.Therefore, we can deduce the relation, assuming the thermal state.
Let
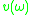 be group velocity of light in the medium, the product
be group velocity of light in the medium, the product 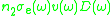 is spectral rate of
is spectral rate ofstimulated emission
Stimulated emission
In optics, stimulated emission is the process by which an atomic electron interacting with an electromagnetic wave of a certain frequency may drop to a lower energy level, transferring its energy to that field. A photon created in this manner has the same phase, frequency, polarization, and...
, and
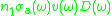 is that of absorption;
is that of absorption; 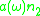 is spectral rate of spontaneous emission
is spectral rate of spontaneous emissionSpontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process by which a light source such as an atom, molecule, nanocrystal or nucleus in an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower energy, e.g., the ground state and emits a photon...
. (Note that in this approximation, there is no such thing as a spontaneous absorption)
The balance of photons gives:
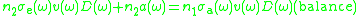
Which can be rewritten as

The thermal distribution of density of photons follows from
blackbody radiation
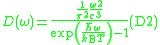
Both (4) and (5) hold for all frequencies
 .
.For the case of idealized two-level active centers,
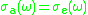 , and
, and 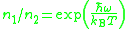 ,
,which leads to the relation between the spectral rate of spontaneous emission
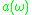 and the emission cross-section
and the emission cross-section 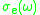
.
(We keep the term probability of emission for the quantity
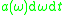 ,
,which is probability of emission of a photon within small spectral interval
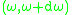
during a short time interval
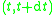 , assuming that at time
, assuming that at time  the atom is excited.)
the atom is excited.)The relation (D2) is a fundamental property of spontaneous and stimulated emission, and perhaps the only way to prohibit a spontaneous break of the thermal equilibrium in the thermal state of excitations and photons.
For each site number
 , for each sublevel number
, for each sublevel number 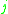 , the partial spectral emission
, the partial spectral emissionprobability
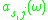 can be expressed from consideration of idealized two-level atoms
can be expressed from consideration of idealized two-level atoms
-
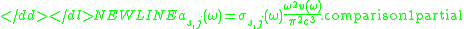
Neglecting the cooperative coherent effects, the emission is additive:
for any concentration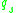 of sites and for any partial population
of sites and for any partial population 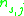
of sublevels, the same proportionality between and
and 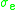
holds for the effective cross-sections:
Then, the comparison of (D1) and (D2) gives the relation
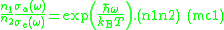
This relation is equivalent of the McCumber relation (mc), if we define the
zero-line frequency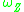 as solution of equation
as solution of equation
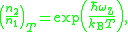
the subscript indicates that the ratio of populations in evaluated in the
indicates that the ratio of populations in evaluated in the
thermal state. The zero-line frequency can be expressed as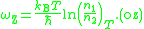
Then (n1n2) becomes equivalent of the McCumber
relation (mc).
No specific property of sublevels of active medium is required to keep the McCumber relation. It follows from the
assumption about quick transfer of energy among excited laser levels and among lower laser levels.
The McCumber relation (mc) has the same range of validity as the concept of the emission cross-section
itself.
Confirmation of the McCumber relation
The McCumber relation is confirmed for various media .
In particular relation (1) makes it possible to approximate two functions of frequency, emission and absorption cross sections, with single fit
.
Violation of the McCumber relation and perpetual motion
In 2006 the strong violation of McCumber relation was "observed" for Yb:Gd2SiO5 and reported in 3 independent journals. Typical behaivor of the cross-sections reported is shown in FIg.2 with thick curves. The emission cross-section is practically zero at wavelength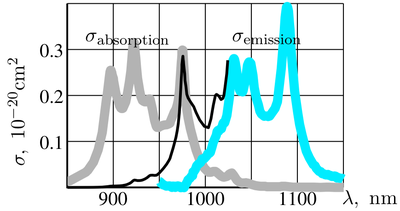
975 nm; this property makes Yb:Gd2SiO5 an excellent material for efficient solid-state laserSolid-state laserA solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid such as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers .-Solid-state...
s.
However, the property reported (thick curves) is not compatible with the Second Law of thermodynamicsSecond law of thermodynamicsThe second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and...
. With such a material, the Perpetual motionPerpetual motionPerpetual motion describes hypothetical machines that operate or produce useful work indefinitely and, more generally, hypothetical machines that produce more work or energy than they consume, whether they might operate indefinitely or not....
device would be possible. It would be sufficient to fill a box with reflecting walls with Yb:Gd2SiO5 and allow it to exchange radiation with a blackbody through a spectrally-selective window which is transparent in vicinity of 975 nm and reflective at other wavelengths. Due to the lack of emissivity at 975 nm the medium should warm, breaking the thermal equilibrium.
On the base of the Second Law of thermodynamicsSecond law of thermodynamicsThe second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and...
, the experimental results
were refuted in 2007. WIth the McCumner theory, the correction was suggested for the effective emission cross section (black thin cirve) . Then this correction was confirmed experimentally.

