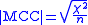Matthews Correlation Coefficient
Encyclopedia
The Matthews correlation coefficient is used in machine learning
as a measure of the quality of binary (two-class) classifications. It takes into account true and false positives and negatives and is generally regarded as a balanced measure which can be used even if the classes are of very different sizes. The MCC is in essence a correlation coefficient between the observed and predicted binary classifications; it returns a value between −1 and +1. A coefficient of +1 represents a perfect prediction, 0 an average random prediction and −1 an inverse prediction. The statistic is also known as the phi coefficient
. MCC is related to the chi-square statistic for a 2×2 contingency table
where n is the total number of observations.
While there is no perfect way of describing the confusion matrix
of true and false positives and negatives by a single number, the Matthews correlation coefficient is generally regarded as being one of the best such measures. Other measures, such as the proportion of correct predictions (also termed accuracy), are not useful when the two classes are of very different sizes. For example, assigning every object to the larger set achieves a high proportion of correct predictions, but is not generally a useful classification.
The MCC can be calculated directly from the confusion matrix
using the formula:
Machine learning
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, is a scientific discipline concerned with the design and development of algorithms that allow computers to evolve behaviors based on empirical data, such as from sensor data or databases...
as a measure of the quality of binary (two-class) classifications. It takes into account true and false positives and negatives and is generally regarded as a balanced measure which can be used even if the classes are of very different sizes. The MCC is in essence a correlation coefficient between the observed and predicted binary classifications; it returns a value between −1 and +1. A coefficient of +1 represents a perfect prediction, 0 an average random prediction and −1 an inverse prediction. The statistic is also known as the phi coefficient
Phi coefficient
In statistics, the phi coefficient is a measure of association for two binary variables introduced by Karl Pearson. This measure is similar to the Pearson correlation coefficient in its interpretation...
. MCC is related to the chi-square statistic for a 2×2 contingency table
Contingency table
In statistics, a contingency table is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the frequency distribution of the variables...
where n is the total number of observations.
While there is no perfect way of describing the confusion matrix
Confusion matrix
In the field of artificial intelligence, a confusion matrix is a specific table layout that allows visualization of the performance of an algorithm, typically a supervised learning one . Each column of the matrix represents the instances in a predicted class, while each row represents the...
of true and false positives and negatives by a single number, the Matthews correlation coefficient is generally regarded as being one of the best such measures. Other measures, such as the proportion of correct predictions (also termed accuracy), are not useful when the two classes are of very different sizes. For example, assigning every object to the larger set achieves a high proportion of correct predictions, but is not generally a useful classification.
The MCC can be calculated directly from the confusion matrix
Confusion matrix
In the field of artificial intelligence, a confusion matrix is a specific table layout that allows visualization of the performance of an algorithm, typically a supervised learning one . Each column of the matrix represents the instances in a predicted class, while each row represents the...
using the formula:
-
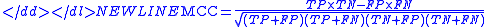
In this equation, TP is the number of true positives, TN the number of true negatives, FP the number of false positives and FN the number of false negatives. If any of the four sums in the denominator is zero, the denominator can be arbitrarily set to one; this results in a Matthews correlation coefficient of zero, which can be shown to be the correct limiting value.
See Also
- Phi coefficientPhi coefficientIn statistics, the phi coefficient is a measure of association for two binary variables introduced by Karl Pearson. This measure is similar to the Pearson correlation coefficient in its interpretation...
- F1 scoreF1 ScoreIn statistics, the F1 score is a measure of a test's accuracy. It considers both the precision p and the recall r of the test to compute the score: p is the number of correct results divided by the number of all returned results and r is the number of correct results divided by the number of...
- Cramér's V, a similar measure of association between nominal variables.
- Phi coefficient